Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Author: Natalie Ng|23 April 2025
If you're noticing more hair falling out than usual—especially if you're losing over 50 to 100 strands a day—you’re not alone. It’s normal to shed some hair daily, but when the amount increases, it could point to something else going on. There are many reasons for hair loss, and most of them are treatable. These include stress, changes in hormones, nutrient deficiencies (like low iron or protein), certain medications, thyroid disease, or even how you care for your hair. Genetics also play a big role in thinning hair, especially in cases of male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss. The earlier you figure out what's causing your hair to fall, the easier it is to slow or treat it. From adjusting your diet to medical treatments that support hair growth, there are ways to manage it. Keep reading to learn about the common causes of hair loss, what they mean for your scalp and hair follicles, and how to catch them early before they lead to further hair loss or bald spots.

1
Stress and Anxiety: The Mind-Body Connection to Hair Loss
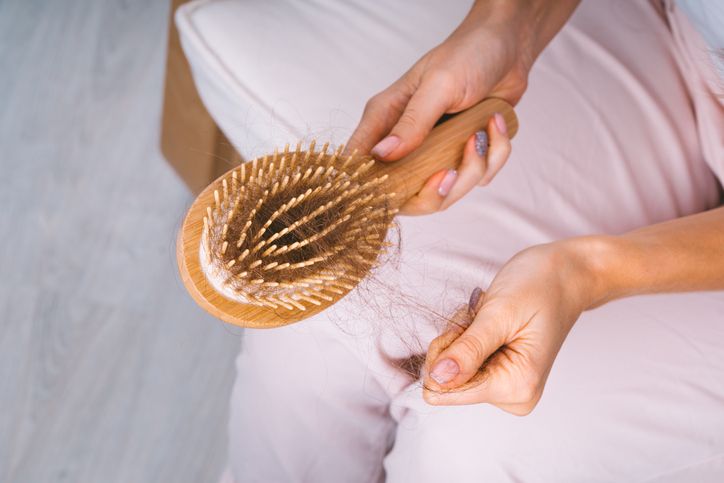

How Stress Affects Hair Growth
Why Early Action Helps


2
Nutritional Deficiencies and Dietary Impacts

How Nutrient Deficiencies Cause Hair Loss
Supporting Hair Growth Through Nutrition
Read More

3
Hormonal Changes and Imbalances

How Hormones Impact Hair Growth
Androgenic Alopecia and Hormonal Hair Loss


4
Thyroid Problems

How Thyroid Disease Affects Hair Follicles
Identifying and Treating Thyroid-Linked Hair Loss

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

5
Pregnancy and Postpartum Effects

What Happens to Hair During and After Pregnancy
Supporting Hair Recovery Postpartum


6
Birth Control Side Effects
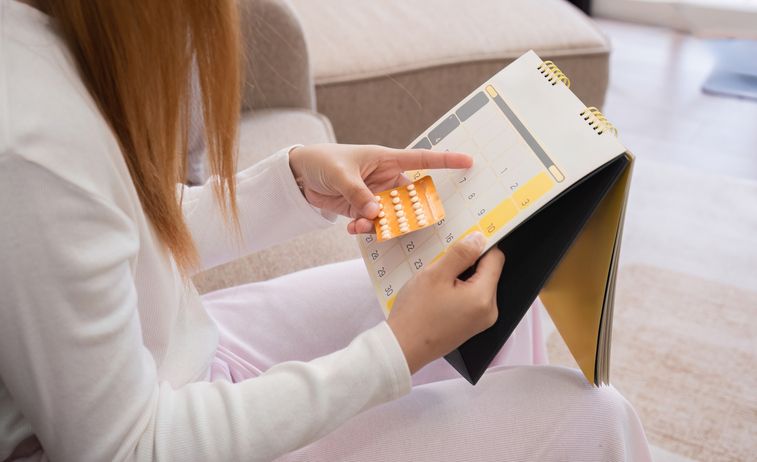

How Birth Control Affects Hair
Read More

7
Medications and Medical Treatments
Common Medications That Cause Hair Loss
Hair Loss Treatments and Side Effects
What to Do If You Notice Hair Loss


8
Harsh Hair Care Practices and Chemical Damage

Everyday Habits That Can Harm Your Hair
How to Prevent Further Hair Loss from Styling Damage

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

9
Genetics and Age-Related Hair Loss

How Genetic Hair Loss Works
Can You Treat Genetic Hair Loss?


10
Supporting Hair Regrowth with Targeted Scalp Treatment

What Is F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment?
How the Treatment Works
Advantages of the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
Who Can Benefit?
FAQ
Can Wearing Hats Frequently Cause Hair Loss?
Wearing hats doesn't directly cause hair loss, but poor hat hygiene can contribute to scalp issues. Your hair won't fall out simply from wearing a hat, as hair follicles are located deep within your skin. However, if you're wearing dirty hats or ones that are too tight, you might experience traction alopecia or bacterial growth. Keep your hats clean and choose ones that fit comfortably to protect your scalp health.
How Many Hairs Falling Out per Day Is Considered Normal?
While you might obsess over every strand you find in your brush, losing 50-100 hairs per day is completely normal and part of your natural hair growth cycle. Your scalp contains about 100,000 hair follicles, and each follows a continuous cycle of growth, rest, and shedding. If you're noticing substantially more hair loss than this baseline, it's worth consulting with a healthcare provider to identify potential underlying causes.
Does Swimming in Chlorinated Pools Contribute to Hair Loss?
Swimming in chlorinated pools can contribute to hair damage and temporary shedding, but it doesn't cause permanent hair loss. Chlorine strips your hair's natural oils and protein, making it dry, brittle, and prone to breakage. You can protect your hair by wearing a swim cap, wetting it with fresh water before swimming, using a clarifying shampoo afterward, and applying a leave-in conditioner to restore moisture.
Can Certain Sleeping Positions Affect Hair Loss Patterns?
While sleeping positions don't directly cause hair loss, certain positions can contribute to mechanical damage and breakage. If you consistently sleep on one side, you might experience increased friction between your hair and pillowcase, leading to localized thinning. To minimize these effects, you can switch to a silk or satin pillowcase, vary your sleeping positions, and consider wearing a soft sleep cap to protect your strands during the night.
Does Frequent Scalp Massage Help Prevent or Reduce Hair Loss?
Like a gentle rain nourishing parched soil, regular scalp massage can help combat hair loss by improving blood circulation to your follicles. You'll find that massaging your scalp for 5-10 minutes daily stimulates the hair roots and can enhance nutrient delivery. While it won't cure pattern baldness, scalp massage reduces stress hormones and tension, which may contribute to hair loss, and it encourages the production of natural oils that strengthen your hair.

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.