Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Author: Natalie Ng|21 April 2025
Your hair follows a natural rhythm. It grows, rests, and sheds in repeating cycles that keep your scalp healthy and full. But sometimes, this rhythm gets thrown off. When that happens, your hair may fall out earlier than expected — and often, faster than it can grow back. There are seven common reasons why this can happen. Things like hormone shifts, thyroid problems, ongoing stress, poor nutrition, certain medications, scalp issues, or even how you style your hair can all play a role. These factors can interrupt different phases of the hair cycle — like the anagen phase (active hair growth), the catagen phase (transition phase), or the telogen phase (resting phase) — and lead to earlier hair shedding, thinning, or even stalled new hair growth. Understanding how the hair growth cycle works, and what might cause it to go off track, is a good first step to improving your hair health. In the sections that follow, we’ll walk through each of these reasons and how they affect your hair follicles, hair strands, and overall hair growth. Keep reading to find out what could be affecting your hair follicle stem cells, disrupting your hair growth, and what you can do to support healthy hair growth again.

1
Hormonal Imbalances and Thyroid Dysfunction
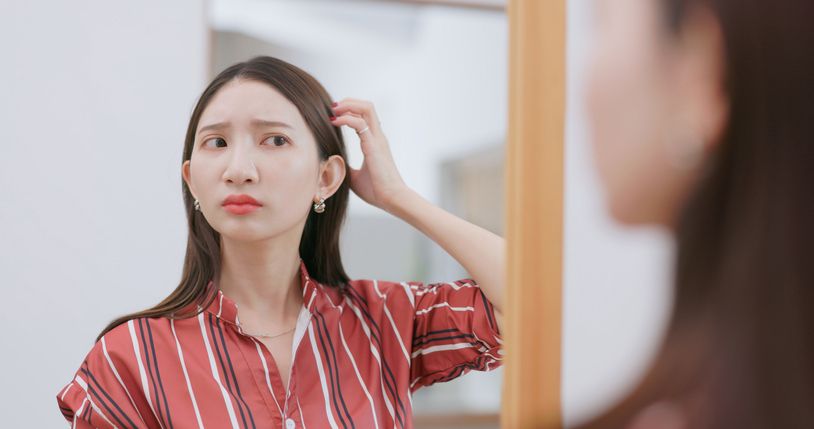

Impact Of Hormonal Changes On Hair Follicles
Thyroid Function and Hair Growth


2
Chronic Stress and Elevated Cortisol Levels
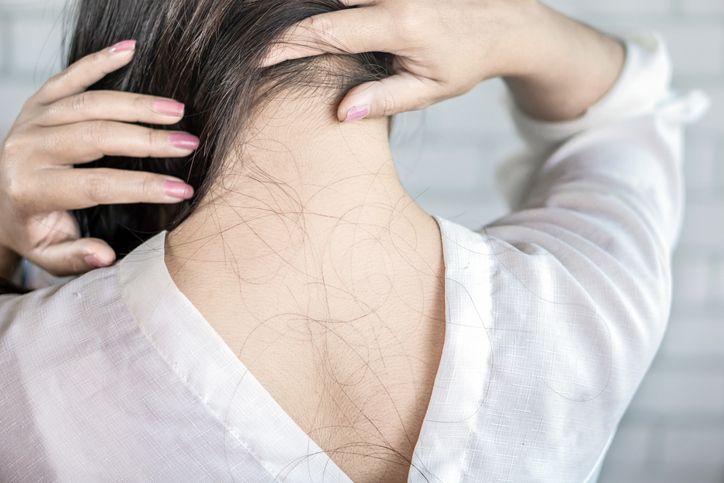

How Cortisol Disrupts Hair Growth
Read More

3
Nutritional Deficiencies and Poor Diet
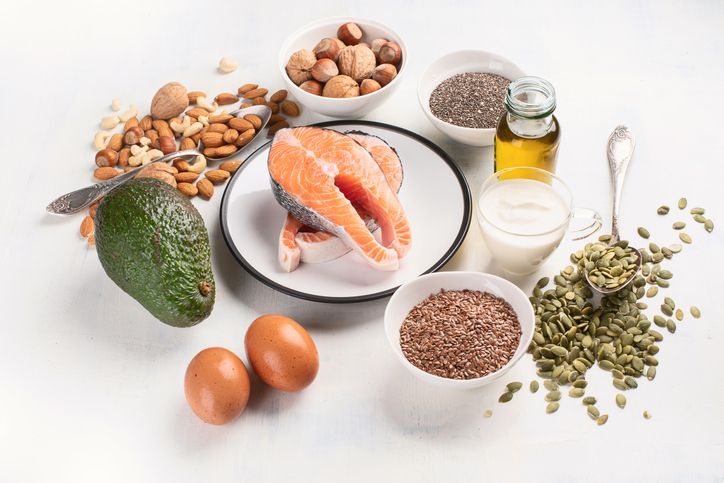

How Missing Nutrients Affect Hair Growth
The Impact of Protein and Iron Deficiency


4
Medications and Medical Treatments
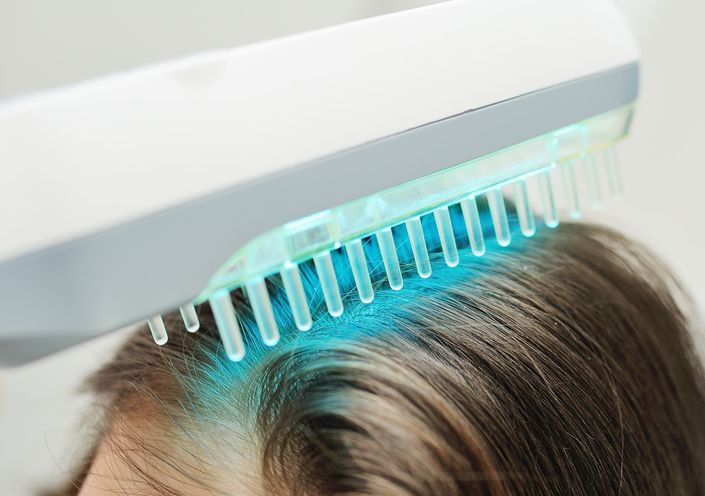

How Treatments Affect Hair Cycle Phases
Treatment Type
Primary Impact
Secondary Impact
Duration
Chemotherapy
Complete shedding
Hair follicle damage
Temporary
Hormone therapy
Pattern baldness
Androgenic alopecia
Long-term
Blood thinners
Extended catagen phase
Increased shedding
Variable
Antidepressants
Disrupted hair cycle
Noticeable thinning
Reversible

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

5
Genes and Family History

Genetic Influence the Hair Growth Cycle


6
Scalp Conditions and Infections

How Scalp Issues Disrupt the Hair Growth Cycle
Read More

7
Aggressive Hair Care Practices and Styling

Styling Habits That Disrupt Hair Growth


8
How F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment Supports the Hair Growth Cycle

How the Treatment Works
Benefits of the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
FAQ
Can Hair Growth Supplements Interact With Other Medications I'm Taking?
Hair growth supplements can interact with medications you're taking, potentially causing adverse effects or reducing the effectiveness of either substance. You should always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplements, as ingredients like biotin can interfere with lab test results, and certain vitamins may interact with blood thinners, thyroid medications, or antibiotics. It's crucial to review your complete medication list with a professional.
How Long Does It Take for Hair to Grow Back After Treatment?
After treatment, your hair's regrowth timeline depends on several factors. You'll typically notice new growth within 3-6 months, though full regrowth can take 12-18 months. The timeframe varies based on the cause of hair loss, treatment type, and your overall health. Your genetics, nutrition, and hair care routine will influence recovery speed, and you'll see the best results when following your healthcare provider's recommendations consistently.
Does Wearing Hats Frequently Contribute to Increased Hair Loss?
Wearing hats doesn't directly cause hair loss, despite popular misconceptions. Your hair follicles receive nutrients through your blood vessels, not from the air, so covering your head won't affect hair growth. However, if you're wearing tight hats that pull on your hair or dirty caps that can cause scalp infections, you might experience traction alopecia or other scalp conditions that could lead to temporary hair loss.
Can Swimming in Chlorinated Pools Damage Hair and Cause Shedding?
Yes, swimming in chlorinated pools can damage your hair and cause shedding. When you're exposed to chlorine regularly, it strips your hair's natural oils, weakens the protein structure, and makes strands brittle and prone to breakage. Your hair can become dry, discolored, and more susceptible to tangling. To protect your hair, wear a swim cap, wet your hair with non-chlorinated water before swimming, and use a clarifying shampoo afterward.
What Role Does Air Pollution Play in Premature Hair Loss?
Air pollution can affect your hair health in several ways: 1) Airborne toxins and particulate matter settle on your scalp, potentially blocking hair follicles and impeding growth, 2) Free radicals from pollution can damage your hair's protein structure and weaken strands, 3) Environmental pollutants may trigger oxidative stress, leading to premature hair aging and loss. You can protect your hair by regularly cleansing and using antioxidant-rich hair products.

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.