Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 8 May 2025
Eating more food might sound like the opposite of how to lose weight, but it can actually help — if you’re choosing the right kinds. Volume eating is about filling up on low calorie foods that take up space in your stomach without pushing your calorie count too high. Foods with high water content and fiber, like vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins, help you feel full faster and stay full longer. That’s because they physically fill your stomach, which signals your brain to stop eating. Instead of cutting meals or skipping snacks, you can eat bigger portions of foods like cooked cauliflower, green beans, or apple slices — all packed with nutrients but with very few calories. These types of meals are more satisfying and easier to stick to than strict, low-volume diets that leave you hungry. You’ll still be getting fiber, protein, vitamins like vitamin C, and other important nutrients, without the extra sugar, fat, or carbs that often lead to weight gain. Curious how this strategy works and which foods make the biggest difference? Keep reading — we’ll break it down step by step.

Low Calorie Foods for Volume Eating and Satiety

How Food Volume Helps You Feel Full
Your stomach uses stretch to help regulate how much you eat. When it expands, it sends signals to your brain that you’re getting full. This is one reason volume eating works well for weight control. By choosing low calorie foods with high water and fiber content, you fill your stomach with fewer calories.
For example, compare one cup of raisins to one cup of grapes. They contain a similar number of calories, but grapes have more water and take up more space. That volume helps your stomach feel full faster.
The Role of Water and Fiber
Many vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins have high water content and are naturally low in calories. Raw carrots, cooked cauliflower, green beans, spinach, tomatoes, and leafy green vegetables are good examples. These are rich in fiber, which slows digestion and helps you feel fuller longer.
Soups made with vegetables and broth, salads with leafy greens and raw or cooked vegetables, and high protein dishes using low fat cottage cheese or yogurt can fill your stomach without a high calorie count.
Visual Fullness
Seeing more food on your plate also plays a role. A full plate of vegetable dishes looks more satisfying than a small portion of high-fat or high-sugar foods. Your brain responds to this visual volume and may help reduce the urge to snack or overeat later.
Together, this physical and visual satisfaction supports a calorie deficit without leaving you feeling deprived. Eating larger servings of low calorie, nutrient-rich foods helps manage hunger while keeping your overall calorie intake low.
Understanding Energy Density
Energy density refers to the number of calories in a specific amount of food. Foods with high energy density, like nuts and seeds, pack a lot of calories into a small portion, while foods with low energy density, such as fruits and vegetables, offer fewer calories in a larger portion. Understanding energy density can help you make informed choices about what you eat, supporting your weight loss goals. A systematic review of studies on energy density found that diets with low energy density can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in overall health. Consulting a registered dietitian can help you develop a personalized meal plan that incorporates low-energy-dense foods, ensuring you stay on track with your health and weight loss goals.

Best Low-Calorie Foods for Maximum Volume
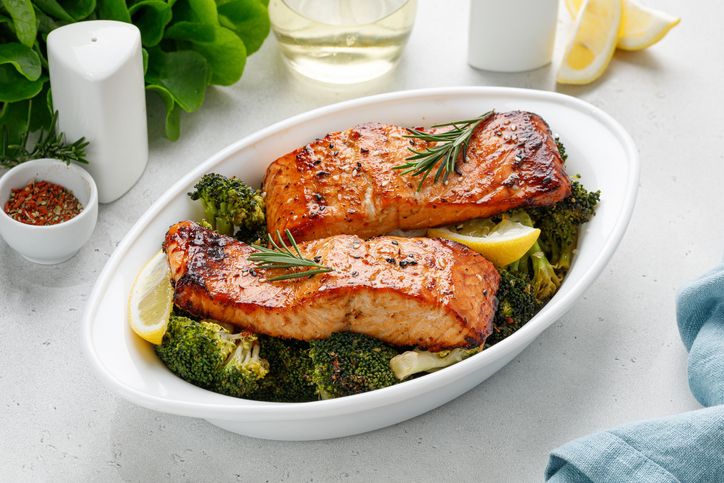

1. Fruits and Vegetables That Fill Without the Calories
Fruits and vegetables with high water content are ideal for volume eating. You can eat a full cup of foods like watermelon, strawberries, cucumber, tomato, apple slices, and leafy green vegetables without consuming many calories. These foods are rich in vitamin C and other nutrients that support overall health and eye health, while keeping the calorie count low. Many of these foods also provide a significant percentage of the daily value of essential vitamins and minerals.
Cooked cauliflower, cabbage, brussels sprouts, carrots, spinach, and green beans are excellent choices. They’re packed with fiber and water, so they fill your stomach and help reduce hunger between meals.
2. High-Fiber Foods That Satisfy
Fiber plays a key role in volume eating. It slows digestion, helps regulate blood sugar, and makes you feel fuller for longer. Choose whole grains like oatmeal, brown rice, and other grains that are a good source of nutrition. Beans, lentils, and popcorn (air-popped, without added sugar or fat) are also filling options that come with very few calories per serving.
Including fiber-rich foods regularly supports weight loss and helps control appetite throughout the day.
3. Low-Fat, High-Protein Options
Protein supports muscle health and keeps hunger in check. Lean proteins like egg whites, low fat cottage cheese, white fish, chicken breast, and Greek yogurt are smart options. They’re lower in fat, which means you can eat a larger portion for the same number of calories compared to higher-fat meats or full-fat dairy.
You can pair protein with vegetables to build high protein dishes that are both satisfying and low calorie.
4. Crunchy Snacks That Don’t Add Up
If you like to snack, go for foods that add volume without loading up on fat or sugar. Celery, raw carrots, apple slices, and frozen grapes are simple snacks that help satisfy cravings. You can also try rice cakes or a small serving of yogurt with fruit and seeds for a filling option that supports your healthy diet. For an extra flavorful, low-calorie snack, consider adding a drizzle of honey to nonfat Greek yogurt.
5. Additional High-Volume, Low-Calorie Foods
Expanding your choices can make volume eating more enjoyable and sustainable. Here are additional foods that are low in calories but high in volume, helping you feel full without consuming too many calories:
• Zucchini: With its high water content, zucchini can be spiralized into noodles or added to stir-fries, providing bulk with minimal calories.
• Mushrooms: These can add a meaty texture to dishes without the calorie load, making them a great addition to various meals.
• Chia Seeds: When soaked, they expand and can be used to make puddings or added to smoothies, providing fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
• Air-Popped Popcorn: A whole grain snack that’s low in calories and high in volume, helping to satisfy hunger between meals.
• Cucumber: Extremely low in calories and high in water, cucumbers are refreshing and hydrating, perfect for salads or as a snack.
• Spinach: This leafy green is low in calories and rich in nutrients, making it a great base for salads or addition to cooked dishes. Many of these foods are also rich in essential minerals.
• Tomatoes: Juicy and low in calories, tomatoes can be added to salads, sandwiches, or eaten on their own.
• Egg Whites: High in protein and low in calories, egg whites can be used in omelets or baking to increase protein intake without added fat.
• Greek Yogurt: Opt for the non-fat variety to get a good source of protein and calcium with fewer calories.
• Cabbage: Whether raw in salads or cooked in soups, cabbage is a versatile vegetable that’s low in calories and high in fiber.
Incorporating these foods into your meals can help you maintain a calorie deficit while still feeling satisfied.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

How Volume Eating Low Calorie Foods Supports Sustainable Weight Loss
1. Volume Eating Supports a Caloric Deficit Without Hunger
Volume eating helps reduce calories without leaving you feeling empty. Foods with high water content like watermelon, cucumbers, spinach, and cooked cauliflower fill your stomach, which activates stretch receptors that signal fullness. This happens without adding many calories to your meals. For example, one cup of raw spinach has very few calories but takes up space in your stomach and adds bulk to your plate.
By replacing calorie-dense foods with large servings of low calorie vegetables and fruits, you can lower your daily intake while still eating plenty. This reduces hunger, helps you feel more satisfied after meals, and makes it easier to maintain a calorie deficit — the foundation of weight loss.
2. Slows Eating and Improves Fullness Signals
Foods like raw carrots, apple slices, whole grains, and green beans require more chewing. This naturally slows your eating pace, which gives your brain time to register when you're full. Eating too quickly can lead to consuming more calories than needed before your body catches up.
Volume eating encourages meals that take longer to eat — large salads with leafy greens, vegetable dishes, and whole grain bowls filled with oats or brown rice — all slow digestion and extend the meal experience. This supports better portion control and improves your awareness of hunger and satiety.
3. Helps with Digestion and Craving Control
High fiber foods — such as oatmeal, beans, chia seeds, lentils, brussels sprouts, and flaxseeds — support your digestive system by promoting regular bowel movements and feeding healthy gut bacteria. Fiber also helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which lowers the chance of sharp energy crashes and sugar cravings.
When your meals contain a mix of fiber, protein, and low glycemic carbohydrates from sources like leafy greens, whole grains, and cooked vegetables, your body maintains steady energy. This prevents the kind of spikes and dips that often lead to cravings for sugar, fat, or processed snacks.
4. Reduces the Mental Pressure of Dieting
Diets that involve tiny portions can feel frustrating. With volume eating, your meals still look generous and satisfying, which helps reduce the sense of restriction. A large salad loaded with raw vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains might have the same calorie count as a small fast food item, but it offers more volume, more texture, and more flavor variety.
Seeing a full plate — visually and mentally — creates a sense of satisfaction. This reduces the stress associated with dieting and makes it easier to stay consistent without feeling like you're constantly missing out.
5. Encourages Steady, Long-Term Progress
Crash diets often lead to rapid weight loss, but they rarely last. Hunger, fatigue, and boredom set in, and weight gain usually follows. Volume eating supports slow, consistent weight loss through meals that are filling, balanced, and enjoyable.
You’re not cutting out food groups or skipping meals. You’re focusing on what to add — like high-volume foods that are rich in fiber, low in sugar, and packed with nutrients. This method creates habits you can stick to, which is key for long-term weight control and better overall health.

Practical Tips for Building Volume-Based Meals

1. Fill Half Your Plate with Non-Starchy Vegetables
Start every meal by filling half your plate with vegetables that are low in calories but high in water and fiber. Examples include:
• Leafy greens like spinach, cabbage, and romaine lettuce
• Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, brussels sprouts, and cauliflower
• Water-rich choices like zucchini, cucumber, and tomatoes
These foods help fill your stomach quickly without raising your calorie count. They also add nutrients like vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants that support your health while helping you feel full.
2. Add Lean Protein to One Quarter of Your Plate
Lean proteins keep you full for longer and help support muscle mass during weight loss. Choose options like:
• Chicken breast or turkey (skinless)
• Egg whites or tofu
• White fish like cod or tilapia
• Low fat cottage cheese or Greek yogurt
• Legumes like lentils and black beans
Protein slows digestion and works together with fiber to keep hunger in check. Try mixing beans into vegetable dishes or topping your salad with grilled chicken or tofu for a balanced, filling meal.
3. Include Complex Carbohydrates for Energy
Use the remaining quarter of your plate for complex carbohydrates. These carbs provide steady energy and are less likely to cause blood sugar spikes. Go for:
• Quinoa, brown rice, or barley
• Sweet potatoes or pumpkin
• Whole grain pasta or oats
These options are higher in fiber than refined carbs and help round out the meal. They’re also more filling, especially when paired with vegetables and protein.
4. Add Extra Volume by Mixing Vegetables into Main Dishes
You can stretch the volume of your meals by blending vegetables directly into the dish. Some easy ideas:
• Add riced cauliflower to cooked rice to double the portion without doubling calories
• Spiralize zucchini or carrots and mix them into pasta
• Stir chopped spinach or cabbage into soups, stews, and scrambled eggs
• Layer sliced tomato, cucumber, and greens into sandwiches or wraps for crunch and bulk
This technique lets you eat a bigger serving size while keeping the calorie count low.
5. Use High-Fiber Add-Ons to Boost Satiety
Fiber-rich foods expand in the stomach and help keep you full between meals. Include:
• Chia seeds or ground flaxseeds sprinkled over yogurt, oatmeal, or salads
• Oats added to smoothies or baked into healthy snacks
• Beans and lentils stirred into soups, grain bowls, or mixed salads
These small additions help support digestion, slow down the release of energy from your food, and reduce the chance of feeling hungry shortly after eating.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Volume Eating
1. Overeating Calorie-Dense Foods Just Because They’re “Healthy”
Foods like nuts, seeds, avocados, cheese, and olive oil are rich in nutrients and healthy fats, but they also contain a high number of calories in small portions. Just one tablespoon of oil or a small handful of nuts can add 100–200 calories to a meal. These foods are part of a healthy diet, but portion size matters. If your goal is weight loss, it’s best to treat them as toppings or condiments, not as the base of your meals.
2. Forgetting to Prioritize Protein
Some people load up on vegetables and fruits but forget to include enough protein. Without enough protein, you may feel full for a short time but get hungry again quickly. This can lead to snacking or overeating later. Protein also helps preserve lean muscle during weight loss. Include a source of lean protein in every meal — chicken breast, egg whites, Greek yogurt, low fat cottage cheese, tofu, or legumes all work well.
3. Ignoring Liquid Calories and Condiments
A salad can go from 300 to over 600 calories if you drizzle on too much dressing or add high-fat extras like cheese, bacon, or creamy sauces. Drinks can be another hidden source of calories — milk tea, fruit juices, sugary coffee drinks, or even large servings of plant-based milk can quickly add up.
Always check dressings, sauces, and beverages. Use lemon juice, vinegar, mustard, salsa, or a small amount of olive oil if needed. Choose low calorie drink options like water, sparkling water, or unsweetened tea to avoid adding unnecessary sugar and carbs.
4. Eating Too Quickly
Eating fast doesn’t give your body enough time to detect fullness. Stretch receptors in your stomach and hormones that regulate hunger take around 20 minutes to activate. If you finish your meal in 5–10 minutes, you might still feel hungry even if you’ve had enough food.
Slow down your pace. Chew your food well. Put your fork down between bites. Take time to enjoy your meals, especially when they are rich in texture — like raw vegetables, whole grains, or high fiber dishes. Savoring the taste of healthy foods can enhance the eating experience and support mindful eating.
5. Skipping Meals to “Save Calories”
Skipping meals might seem like a shortcut to weight loss, but it often backfires. Long gaps without food can increase hunger later, leading to overeating or choosing high calorie snacks like chips or sweetened drinks. Instead, eat balanced meals throughout the day. This keeps your blood sugar stable and makes it easier to stick to your eating plan.
Volume eating works best when you spread your intake across regular meals — each built with fiber, protein, and low calorie foods that help you feel fuller, longer.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Boost Your Results with S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
Volume eating with low calorie foods helps reduce overall calorie intake while keeping you full, but sometimes stubborn fat areas don’t respond as easily to diet alone. That’s where S6 Body Sculpting Treatment can help. It’s a non-invasive treatment that works alongside your healthy diet to speed up visible fat loss — especially in areas like the belly, thighs, back, and arms.
How S6 Body Sculpting Works
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment uses low-energy bio-laser technology to break down fat cells underneath the skin. The laser helps release fatty acids from these cells, which are then flushed out naturally through your lymphatic system. A built-in vacuum suction massage boosts circulation and supports faster drainage of these released fats, while also increasing metabolic activity.
At the same time, the laser energy helps stimulate collagen production, which tightens the skin — making it especially useful for people worried about sagging after fat loss. Each session targets specific areas where fat tends to stay, even when you’ve lowered your calorie count and improved your nutrition with high volume, nutrient-rich meals.
Why It Complements a Volume Eating Strategy
Eating meals packed with leafy green vegetables, high protein dishes, whole grains, and low calorie fruits helps you lose weight gradually. But if you're aiming for faster visible changes in problem areas, S6 Treatment can enhance these effects. Instead of relying solely on exercise or cutting calories further, the treatment provides a non-surgical option to reshape your figure while you continue to focus on healthy habits.
It’s suitable for those who want help contouring their body while avoiding downtime, injections, or surgery. Since there's no damage to the skin, you can return to normal activities right after your session. Results can be seen over a course of 10 to 12 treatments, spaced a month apart — giving your body time to adjust while you maintain progress with balanced meals full of low calorie vegetables, fruit, fiber, and protein.
Advantages of the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
• Targets stubborn fat in seven major areas: belly, waist, thighs, arms, back, calves, and buttocks
• Supports fat loss in areas where diet and exercise may fall short
• Enhances metabolism using vacuum suction massage
• Promotes skin firmness by stimulating collagen
• Safe, non-invasive, and suitable for different body types
• No recovery time needed — continue daily activities immediately
Combining S6 Body Sculpting Treatment with meals that focus on vegetables, fiber, and healthy fats gives you a well-rounded approach to weight loss. You’re not only eating smarter, you’re helping your body shape itself more efficiently.
Ready to take your results to the next level? Book your S6 Body Sculpting session today and accelerate your weight loss journey.Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
1. What are some low calorie foods that are high in protein?
Low calorie, high protein foods include egg whites, low fat cottage cheese, plain Greek yogurt, white fish (like cod or tilapia), tofu, and skinless chicken breast. These foods help build and maintain muscle while supporting weight loss by increasing satiety without adding too many calories. Including high protein dishes regularly can reduce hunger and help manage your calorie count more effectively.
2. Can I eat low calorie foods all day and still gain weight?
Yes — while low calorie foods help control weight, eating beyond your total daily calorie needs, even from healthy options, can lead to weight gain over time. Portion sizes, frequency of meals, and hidden sources of sugar or fat (such as in dressings or sauces) also matter. Weight control depends on maintaining a calorie deficit, not just the type of food consumed.
3. Are raw vegetables better than cooked ones for weight loss?
Both raw and cooked vegetables are excellent for weight loss, but they offer different benefits. Raw vegetables like carrots, celery, and spinach are great as snacks and tend to take longer to chew, which may increase satiety. Cooked vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and green beans are easier to digest and can be eaten in larger quantities. Cooking also enhances the absorption of some nutrients like beta-carotene in carrots. Including both raw and cooked vegetables adds variety and balance to your diet.
4. How can I add more low calorie vegetables into my meals without changing the taste?
You can blend cooked cauliflower into mashed potatoes or mix riced cauliflower into rice to boost volume without changing flavor. Add leafy greens like spinach or cabbage into soups, stews, or pasta sauces. Grated zucchini can go into omelets or meatballs, and tomato slices or cucumber add crunch and freshness to sandwiches. These swaps increase fiber, lower overall calories, and keep the texture and taste of your favorite dishes.
5. Is volume eating suitable for people with diabetes?
Yes, volume eating can be helpful for people managing blood sugar levels, especially when meals are built around low glycemic, high fiber foods like leafy greens, non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean protein. These foods help slow glucose absorption and prevent blood sugar spikes. Always work with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to create a plan that fits your individual health needs.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.