Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 8 May 2025
To lose fat and gain muscle, you’ll need more than just cutting calories. The goal is to change your body composition by dropping body fat while building muscle. That means eating enough protein, lifting regularly, and giving your body time to recover. Simple habits like eating around workouts, sleeping well, and managing stress help keep muscle mass while losing fat. A few supplements like whey protein or creatine can also support your progress. If you want to gain muscle without gaining fat, or lose weight without losing strength, keep going. These strategies will show you how to make it work.

1. Maintain a Moderate Caloric Deficit
Why fewer calories can still support muscle growth
To lose body fat, you need to eat fewer calories than you burn. This is known as a calorie deficit. But to maintain muscle mass or gain muscle during weight loss, the deficit can’t be too extreme. Very low calorie diets increase the risk of muscle loss, including skeletal muscle mass, especially if protein intake is low or training is too light.
Focus on gradual fat loss
Losing fat and gaining muscle at the same time—body recomposition—is possible, especially if you're newer to resistance training or returning after a break. It works best when your calorie intake is slightly below maintenance, not drastically lower. A moderate deficit supports fat loss without slowing muscle protein synthesis.
Support your body with enough nutrients
Even in a calorie deficit, your body can build or preserve lean muscle mass if your diet includes enough protein and you follow a resistance training plan. This balance helps protect fat free mass while reducing body weight. It also lowers the risk of skeletal muscle mass loss, which can happen with low calorie diets or cardio-only programs.

2. Prioritize High-Quality Protein Intake

Why protein timing supports muscle growth
Protein intake plays a central role in building muscle and supporting fat loss. To gain muscle without gaining fat, or to lose fat and gain muscle, you need enough protein spaced across the day. Aiming for 20 to 30 grams every 3 to 4 hours helps keep muscle protein synthesis active and supports lean body mass while you're in a calorie deficit.
After resistance training or strength training, your body is more responsive to nutrients. This makes post-workout meals a good time to get fast-digesting protein with some carbohydrates to support muscle recovery. Having protein before bed can also help preserve muscle mass overnight, especially if you're eating fewer calories during the day.
Best sources for muscle protein synthesis
Lean meats like chicken breast, turkey, and lean beef are high in protein and low in fat, which helps support muscle growth while controlling body fat. Fish like salmon and tuna offer both protein and healthy fats, while eggs and dairy provide complete proteins that are easy to digest.
If you're following a plant-based diet, foods like quinoa, soy, lentils, and legumes can help maintain muscle mass, especially when combined for a full amino acid profile. Dairy options like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and whey protein are especially helpful after workouts thanks to their fast absorption rate.
Supporting body composition goals
Spreading your protein intake throughout the day helps protect muscle tissue, especially during fat loss phases. It’s a key part of preserving healthy muscle while reducing overall body weight. This strategy supports positive body composition changes and can help prevent skeletal muscle mass loss as you eat fewer calories to lower body fat percentage.
Date should not be before minimal date

3. Implement Progressive Overload Training
Why gradual increases build muscle
To increase muscle mass, you need to challenge your muscles regularly. This happens through progressive overload, which means slowly increasing the weight, reps, or sets in your workouts. Without this, your body adapts and stops building muscle.
Tracking your workouts helps you stay on target. Note how much weight you lift, how many reps you complete, and how your body feels. This lets you make small changes over time, which keeps the muscles working harder and prevents plateaus.
Best exercises for progressive overload
Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. These exercises work several muscle groups at once and create a strong stimulus for growth. They also help you gain strength faster and support overall improvements in body composition.
Start with a weight that challenges you but still allows good form. Once you can complete all your sets and reps with control, increase the load slightly or add a rep or two. This gradual push helps promote muscle growth and reduce fat mass, especially when paired with a high protein diet.

4. Master Compound Exercise Movements
Why compound lifts matter for muscle growth
Compound exercises target multiple muscle groups in one movement. This helps build more muscle tissue, improve strength, and support better body composition overall. These exercises also burn more calories compared to isolation moves, which can support fat loss while maintaining muscle mass.
Focusing on compound lifts allows you to train efficiently, especially if you're working with limited time or only your own body weight. They also trigger a stronger hormonal response, which supports muscle growth and recovery.
Key compound exercises to include
These are the best compound movements to build muscle mass and improve strength:
Squat
• Primary muscles: Quadriceps, glutes
• Secondary muscles: Core, calves
Deadlift
• Primary muscles: Lower back, glutes
• Secondary muscles: Hamstrings, traps
Bench Press
• Primary muscles: Chest, shoulders
• Secondary muscles: Triceps, core
How to get the most from your lifts
• Use proper form to avoid injury and get full muscle activation
• Control the weight through the entire movement
• Focus on quality reps rather than lifting too heavy too soon
• Allow full recovery between sessions targeting the same muscle groups
These lifts help improve strength and increase lean mass while reducing body fat, making them essential for successful body recomposition.

5. Optimize Sleep and Recovery
Why rest supports muscle growth
Muscle growth doesn’t happen during training—it happens during rest. Sleep and recovery are what allow your body to rebuild muscle tissue, especially after resistance training. Without enough rest, your risk of muscle loss goes up, and your ability to gain muscle slows down.
Getting 7 to 9 hours of sleep every night supports healthy hormone function, including growth hormone and testosterone. These hormones help maintain lean muscle mass and support fat loss during a calorie deficit.
How to improve recovery between workouts
Give muscles time to recover
• Rest specific muscle groups for at least 48 hours before training them again
• Alternate training days between different muscle groups to avoid overtraining
• Use light movement like walking or stretching to improve blood flow
Support recovery with daily habits
• Stay hydrated throughout the day
• Eat enough protein to promote muscle repair
• Avoid lifting heavy on back-to-back days targeting the same muscles
Why quality sleep matters
Sleep is when your body repairs muscle tissue and resets energy systems. Poor sleep can increase cortisol levels, which makes it harder to lose body fat and easier to lose muscle. To protect muscle growth, aim for deep, uninterrupted sleep each night.
Small changes like limiting screen time before bed, avoiding caffeine late in the day, and keeping a regular sleep schedule can all improve your recovery and support better results in both fat loss and gaining muscle mass.
Date should not be before minimal date

6. Incorporate Strategic Resistance Training
Why resistance training shapes your body composition
Resistance training is one of the most effective ways to lose fat and gain muscle at the same time. It helps preserve lean muscle mass while you're in a calorie deficit and promotes muscle protein synthesis needed for growth. This form of training also improves body composition by increasing fat free mass and reducing body fat percentage.
To support healthy weight loss without losing muscle, your workouts should challenge your muscles regularly and target all major muscle groups.
How to structure your workouts
A well-rounded resistance training routine includes both compound and isolation movements. Compound exercises work multiple muscle groups, while isolation exercises help fine-tune specific muscle areas for balance and proportion.
Include these in your weekly plan
• Compound lifts like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows
• Isolation movements like bicep curls, leg extensions, or lateral raises
• Resistance tools such as dumbbells, resistance bands, machines, or your own body weight
Training volume and rest
To promote muscle growth and avoid overtraining:
• Train each muscle group 2 times per week
• Aim for 3 to 4 sets of 8 to 12 reps for hypertrophy (muscle building)
• Rest 48 to 72 hours before training the same muscle group again
Keeping your workouts structured helps improve strength, increase muscle mass, and support long-term fat loss without sacrificing muscle tissue.

7. Balance Hormones Through Diet and Lifestyle
Why hormones affect body composition
Your hormone levels directly affect muscle growth, fat storage, energy levels, and recovery. If you're trying to lose fat and gain muscle, keeping hormones like cortisol, testosterone, and insulin in balance can make the process more efficient. Diet, sleep, and training habits all play a part.
Support testosterone production
Testosterone helps promote muscle growth and preserve lean muscle mass. Low levels can lead to muscle loss and increased fat mass, especially with low calorie diets.
To support healthy levels:
• Include healthy fats from foods like eggs, fatty fish, nuts, and olive oil
• Get enough zinc and vitamin D from beef, oysters, or sunlight exposure
• Train with resistance exercises, especially compound lifts
• Sleep at least 7–9 hours to support natural hormone rhythms
Keep cortisol under control
Cortisol is a stress hormone. If it's always high, it can lead to muscle loss and fat gain around the belly. Poor sleep and overtraining raise cortisol.
To help regulate cortisol:
• Stick to a consistent sleep schedule
• Avoid training hard every day without breaks
• Limit caffeine in the afternoon
Improve insulin response with meal timing
Insulin helps your body use nutrients after meals, especially after workouts. When insulin works well, more nutrients go to muscle instead of being stored as fat.
Try this strategy:
• Eat most of your carbs before and after training
• Focus on protein and healthy fats during other meals
• Avoid large amounts of sugar or refined carbs when not training
These simple habits help support a hormonal environment that favors muscle growth and fat loss without needing extreme diet changes.

8. Structure Meal Timing and Frequency
Why regular meals support muscle growth and fat loss
Eating at regular intervals helps your body maintain muscle protein synthesis throughout the day. This is especially important when you're eating fewer calories to reduce body fat. Spacing meals every 3 to 4 hours keeps your energy steady and supports recovery after resistance training.
You don’t need to eat every two hours, but long gaps between meals can make it harder to hit your protein intake targets or recover properly from workouts. Aim for 4 to 6 meals or snacks a day, each with enough protein and a balance of carbs and healthy fats to support both energy and muscle repair.
Focus on key meals around your workouts
The most important meals are the ones before and after you train. Having protein and carbs 1 to 2 hours before lifting can improve performance, while a meal soon after training helps your body recover and rebuild muscle tissue. If you're training late in the day, a protein-rich snack before bed can also support overnight recovery and muscle growth.
Simple structure in your meal timing makes it easier to lose body fat, gain lean mass, and avoid energy crashes or cravings while you're working toward better overall body composition.
Date should not be before minimal date

9. Leverage Supplements for Enhanced Results
Why supplements can support progress
Supplements aren't a replacement for whole foods, but they can help fill gaps and support your goals when used the right way. If you're trying to lose fat and gain muscle, certain supplements can make it easier to meet your protein intake, improve recovery, or support strength during resistance training.
You don’t need a long list of products. Just a few well-researched options can be enough.
Useful supplements to consider
• Whey protein helps you hit daily protein targets and is especially useful after training or when you’re short on time for meals
• Creatine monohydrate supports strength, performance, and lean mass gains with consistent daily use
• BCAAs may help during fasted training, though they’re less important if your total protein intake is already high
• Beta-alanine can help reduce fatigue during high intensity workouts, especially for those doing a mix of cardio and resistance training
Best times to take supplements
Use whey protein after your workout or between meals to support muscle recovery. Take creatine at any time daily—timing doesn’t matter as much as consistency. If you're using BCAAs or beta-alanine, they work best when taken around your workouts.
Used correctly, these supplements can support muscle growth, reduce fat mass, and help you recover faster—without replacing the basics of good nutrition and proper training.

10. Use Cardio Wisely to Support Fat Loss
Why cardio should support, not replace, resistance training
Cardiovascular exercise can help with fat loss by increasing your daily calorie burn. But too much cardio, especially without enough food or recovery, can lead to muscle loss. If your goal is to lose fat and gain muscle, cardio should support your routine—not take it over.
Resistance training should stay at the center of your program to preserve lean muscle mass. Cardio helps with calorie deficit and heart health, but it won’t promote muscle growth on its own.
Choosing the right type and amount
Low intensity steady state (LISS) and moderate intensity cardio are great for burning calories without interfering with muscle recovery. High intensity interval training (HIIT) is time-efficient and can help with fat loss, but it’s more demanding on recovery and should be used in moderation.
For best results, include:
• 2 to 3 cardio sessions per week
• LISS like walking or cycling for longer durations
• HIIT sessions only if your recovery, sleep, and training are all on track
Cardio is most effective when it’s planned around your resistance training, not competing with it. Used correctly, it helps lower body fat percentage while preserving healthy muscle and supporting overall body composition goals.

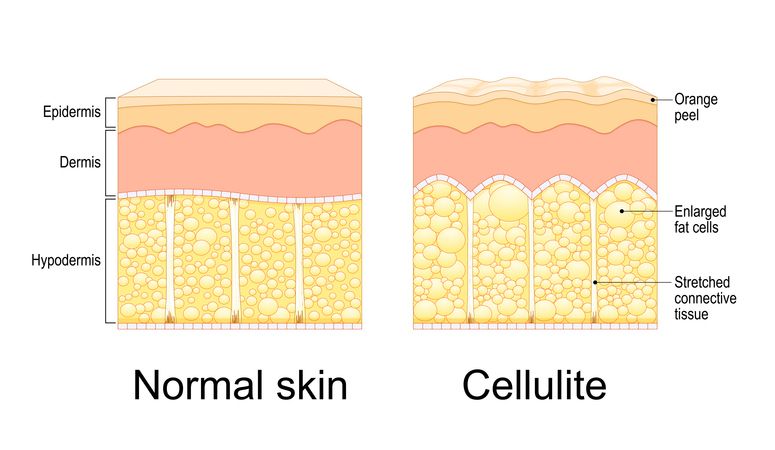
Support Fat Loss with S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
How this non-invasive treatment fits your body goals
If you're already focused on resistance training and a high protein diet to gain muscle, adding body contouring can help highlight your results. The S6 Body Sculpting Treatment supports fat loss in areas that are often slow to respond to training and diet alone—helping you shape your body more efficiently without affecting muscle mass.
This treatment works by using a low-energy bio-laser that targets subcutaneous fat. It breaks down fat cells by encouraging them to release fatty acids, which are then drained naturally through your lymphatic system. At the same time, vacuum suction technology stimulates blood flow, increases metabolism, and helps tighten the skin. This is especially helpful when you're losing fat and want to avoid sagging in areas like the belly, arms, or thighs.
Treatment benefits that support body recomposition
S6 Body Sculpting is non-surgical and non-invasive. There’s no downtime, no injections, and no medication required. That means you can return to daily activities right after the session without interrupting your training routine.
It’s ideal for reducing fat mass while keeping your lean body mass intact. That’s a major advantage when you're aiming to lose fat and gain muscle at the same time.
Key benefits:
• Targets stubborn fat in areas like the waist, thighs, arms, back, and belly
• Stimulates collagen to help tighten skin during fat reduction
• Boosts metabolism to support faster fat breakdown
• Helps define your body outline by reducing fat cells without affecting healthy muscle
This treatment works best as part of a complete plan that includes resistance exercise, a high protein diet, and proper recovery. It supports your body composition changes by reducing unwanted fat and improving how lean muscle shows through.
Book your S6 Body Sculpting session today to support your fat loss goals and make the most of your efforts in the gym.
S6 Body Sculpting TreatmentDate should not be before minimal date
FAQ
1. Can I lose fat and gain muscle at the same time without lifting weights?
Yes, but it’s harder. While bodyweight workouts and resistance bands can help maintain or build some muscle mass, lifting weights or other forms of resistance training are more effective for muscle growth and strength. If you're aiming to change your body composition by reducing body fat and increasing lean mass, resistance training gives the best results.
2. How much protein should I eat daily to support muscle growth during fat loss?
To support muscle protein synthesis and avoid losing muscle, aim for around 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of your body weight each day. High protein intake helps preserve lean muscle mass when you’re in a calorie deficit, especially during fat loss phases.
3. Does doing cardio every day slow down muscle growth?
Daily cardio can interfere with gaining muscle mass if it's high intensity or done for long durations, especially without enough recovery or food. To lose fat and gain muscle, combine moderate cardio with strength training, and be sure your calorie intake and sleep support muscle recovery.
4. Why am I gaining weight even though I’m losing fat and working out?
If you're gaining muscle while losing fat, your overall body weight might stay the same or even increase slightly. This is common during body recomposition. Focus on how your body looks, your strength levels, and changes in body fat percentage rather than only looking at the scale.
5. Is there a difference between losing body fat and losing weight?
Yes. Losing weight can include water, fat, and even muscle mass. Losing body fat specifically means reducing fat mass while trying to preserve or increase muscle mass. For healthy weight loss and long-term results, focus on body composition assessment instead of just your body weight.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.