Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 7 May 2025
Hair miniaturization happens when a hormone called DHT starts shrinking your hair follicles. These follicles produce thinner hairs over time, which leads to visible hair thinning and a drop in overall hair density. This process can affect both men and women and is often linked to male pattern baldness and female pattern hair loss. As hair follicle miniaturization continues, healthy hairs are gradually replaced by shorter, finer strands that struggle to grow back properly. If this keeps up, those once strong terminal hairs may stop growing altogether. That’s when pattern hair loss becomes harder to ignore—whether it’s a widening part, a receding hairline, or more hair left behind in the shower drain. While the changes might feel sudden, the shift in your hair growth cycle usually starts slowly. And if you catch it early, there are ways to slow hair loss, protect the follicles, and promote hair growth—naturally or with clinical treatments. Keep reading to learn how this process works and what you can actually do to support healthy hair growth, prevent extensive hair loss, and even reverse some damage before it gets worse.

The Hair Growth Cycle and Hair Miniaturization Process
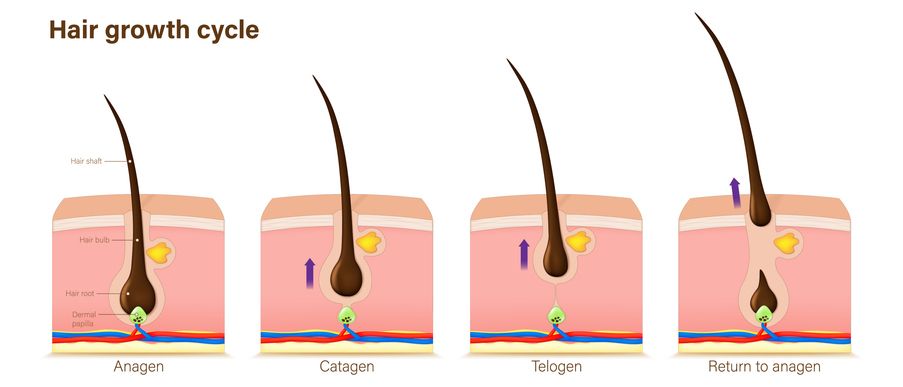
The Hair Growth Cycle: What It Does
Hair grows in repeating cycles. Each follicle moves through three main phases:
• Anagen – this is the growth phase, where the follicle produces a strand that can keep growing for years
• Catagen – a short transition period that lasts a few weeks. Growth stops, but the hair stays in place
• Telogen – the resting phase. The strand stays put for a while, then falls out, making space for new growth
Hair enters different phases of the hair growth cycle, particularly in relation to telogen effluvium, where stressors cause hair to prematurely enter the telogen phase. This early transition leads to significant hair thinning and miniaturization, indicating a detrimental impact on hair health and growth.
In a healthy hair cycle, each follicle can produce strong terminal hairs that grow long and thick. But once hair miniaturization starts, this pattern begins to change.
How Hair Miniaturization Disrupts the Cycle
Hair miniaturization occurs when the normal growth cycle gets shorter. The anagen phase becomes too brief to grow full hairs, and the follicle starts producing thinner hairs that fall out more easily.
This process is often driven by dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a form of the male sex hormone testosterone. DHT binds to receptors in sensitive hair follicles, especially in areas affected by male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss. Over time, these follicles shrink, and the hair shaft size becomes smaller. The shrinking of the dermal papilla affects the hair bulb, leading to hair miniaturization and diminished follicle function.
The result is finer, weaker hair that barely grows. These are called vellus hairs, and they often replace what used to be full, thick strands. If the process continues, miniaturized follicles may stop producing hair altogether.
Where It Leads
Without early support or intervention, the scalp affected by this process starts showing clear signs of pattern hair loss. You might see a receding hairline, hair thinning at the crown, or even extensive hair loss. This change in the hair follicle growth cycle can be gradual, but it's usually progressive unless treated.
Slow hair follicle miniaturization is possible with the right steps. In the next section, you’ll see what actually helps support healthy hairs, slow hair loss, and promote hair growth.

Identifying Early Warning Signs of Hair Thinning
Changes You Might Notice First
Hair thinning often starts quietly. You might see more hair than usual in your brush or after washing your hair. The shower drain might collect more strands than it used to, indicating shower drain hair loss, which can be a visible sign of hair thinning and miniaturization. These early signs can mean hair miniaturization has begun.
Another sign is a part line that looks wider than before. This can happen when hair follicles begin producing thinner hairs, making the scalp more visible. If you pull your hair back into a ponytail, it might feel smaller or lighter than it once did.
1. Texture and Thickness
Miniaturized follicles don’t grow the same type of hair. Instead of producing thick, terminal hairs, they start growing fine, short strands that are more brittle and break easily. During a pull test, you might notice that these strands break or come out, indicating issues related to hair loss or thinning. These thinner hairs change how your hair feels and looks.
You might also find that your hair doesn’t hold styles as well, or it appears flat even after styling. These changes can show up anywhere on the scalp but are often more noticeable near the temples or crown—areas commonly affected by male pattern hair loss or female pattern baldness.
2. Scalp Visibility and Volume
Pay attention to how easily you can see your scalp in bright light or after styling. If your hair once covered the scalp well but now seems see-through, that’s a strong sign of follicle miniaturization. This kind of thinning usually doesn’t happen overnight. It builds over time through shifts in the hair follicle growth cycle.
Spotting these changes early gives you a better chance to slow hair loss and promote hair growth. The next section covers the hormone behind these changes—and why it plays such a big role in male and female pattern hair loss.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

The Role of DHT in Hair Follicle Shrinkage
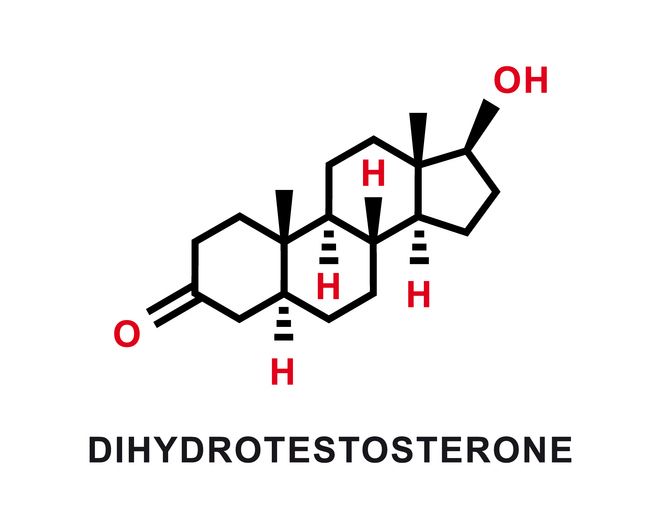
What Is DHT and Why It Matters
Dihydrotestosterone, or DHT, is a hormone made from testosterone. It’s stronger than testosterone and plays a key role in how your body develops. But in people with pattern hair loss, DHT also has a damaging effect on hair follicles.
When DHT attaches to receptors in your follicles, it triggers a process that slowly reduces their size. This change doesn’t happen all at once. Over several hair growth cycles, the affected follicles start producing thinner hairs until some stop growing hair entirely.
This process is called hair follicle miniaturization and is influenced by factors DHT, a hormonal factor contributing to hair loss, particularly in androgenetic alopecia. DHT is derived from testosterone and is a significant male sex hormone associated with the miniaturization of hair follicles, leading to thinner and shorter hair strands. It’s one of the main causes behind male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, and thinning seen in areas like the temples or crown.
How DHT Affects the Hair Growth Cycle
The damage from DHT builds in stages:
• Early: DHT binds mildly to follicle receptors. The follicle starts to narrow slightly.
• Progressive: Follicles become more sensitive. You’ll start to see visible hair thinning.
• Advanced: The follicle shrinks further. Hairs become finer and shorter.
• Final: The follicle is miniaturized. It may stop producing hair altogether.
These changes impact your scalp over time. The hair shaft size becomes smaller, the follicle weakens, and the natural growth cycle shortens. Follicles that once produced healthy hairs now produce thinner, more fragile hairs due to miniaturization. Instead of growing terminal hairs, your follicles may produce soft, fine vellus hairs that are more prone to falling out.
Genetics and DHT Sensitivity
Not everyone reacts to DHT the same way. Your genetics determine how sensitive your follicles are to the hormone. If you have a family history of pattern baldness, your risk is higher. In these cases, areas like the crown and temples are often the first to show thinning or a receding hairline.
The DHT-driven process is part of a hormone-driven biological process that affects both men and women. Once miniaturization begins, early action is the best way to slow hair loss and protect your existing hair density.

How To Stop Hair Miniaturization?
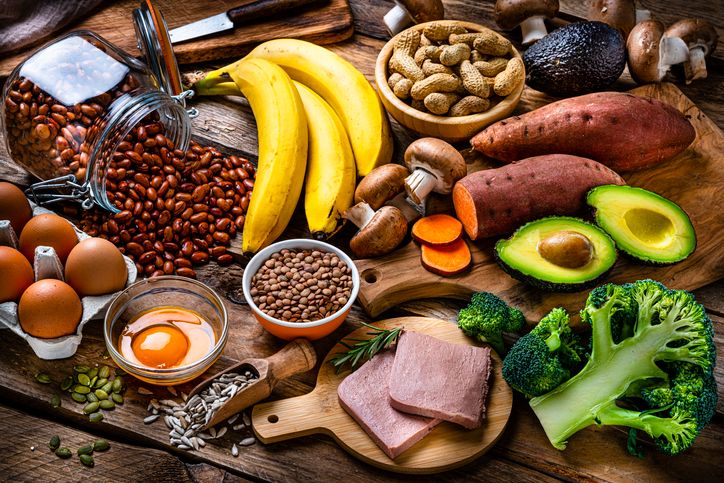

1. Combat Hair Miniaturization With Essential Nutrients
Hair follicles need the right nutrients to stay healthy and function properly. Without them, the hair growth cycle can become disrupted, and miniaturization may speed up. Certain vitamins and minerals help support healthy hairs, slow hair follicle miniaturization, and create the conditions needed for thicker, stronger strands.
Key Nutrients That Support Hair Follicle Health
Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Biotin helps your body make keratin, which is the main protein in your hair shaft. It also supports the strength and structure of each strand. People low in biotin may notice brittle hair, slower growth, or increased breakage. You can find biotin in foods like eggs, nuts, and sweet potatoes, or take it as a natural hair growth supplement.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a role in the hair's growth cycle. It helps stimulate new follicle formation and supports overall scalp health. Low levels of vitamin D are linked to conditions like alopecia areata and chronic telogen effluvium, which can cause more hair to fall out and lead to visible thinning.
Iron and Zinc
Iron carries oxygen to the hair roots. If your iron levels are low, follicles can’t get the nutrients they need. Zinc supports tissue repair and helps regulate oil glands around the follicles. Without enough zinc, hair follicles may become weak or enter the resting phase too early.
Together, iron and zinc help maintain hair follicle function and promote healthy hair growth.
How to Get These Nutrients
You can get these nutrients through a diet that includes:
• Lean proteins (chicken, fish, eggs)
• Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
• Whole grains and legumes
• Nuts and seeds
If you’re not getting enough through food, supplements can help—but it’s best to check with a doctor or get a blood test before starting anything new.
2. Lifestyle Changes to Protect Hair Follicle Health
How Lifestyle Affects Hair Follicles
The health of your hair follicles isn’t only about what products you use—it’s also shaped by your everyday habits. Factors like nutrition, stress, sleep, and physical activity all affect the hair growth cycle. Making small changes in these areas can help slow hair miniaturization and support healthy hair growth over time.
Diet and Nutrient Intake
Your hair needs nutrients every day. A diet lacking in key vitamins and minerals can weaken follicles and trigger hair thinning. To help your follicles stay strong, include:
• Protein-rich foods like eggs, chicken, and fish—hair is made of keratin, a type of protein
• Biotin-rich options such as nuts, seeds, and sweet potatoes to support keratin production
• Iron-rich foods like leafy greens and lentils to help deliver oxygen to follicles
• Zinc sources like pumpkin seeds and whole grains to keep your hair’s oil balance in check
If your diet doesn’t supply enough, a natural hair growth supplement might be useful, especially in cases of hair loss caused by nutritional gaps.
Sleep and Stress Management
Lack of sleep and high stress can throw off hormone levels, raising cortisol. Too much cortisol affects hair follicles by shortening the growth phase and pushing more hairs into the resting phase. Over time, this may lead to faster hair miniaturization.
To reduce the impact:
• Aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night
• Set a regular sleep schedule
• Use relaxation methods that work for you—light stretching, listening to music, or taking quiet breaks during the day
Lowering daily stress can also help regulate hormones linked to androgenetic alopecia and slow hair follicle shrinkage.
Exercise for Hair Growth
Physical activity supports blood flow, which helps carry oxygen and nutrients to your scalp. It also reduces stress and keeps hormone levels more stable. That’s important for slowing pattern hair loss caused by the DHT hormone.
Aim for:
• 30 minutes of cardio (like brisk walking or cycling) most days
• Strength training two to three times a week to balance hormones
• Gentle movement practices like yoga or tai chi to ease stress and support circulation
These habits create a better environment for hair follicle growth and can help reduce the effects of scalp inflammation and hormonal imbalances.
3. Medical Treatments and Professional Interventions
When to Consider Medical Options
If hair miniaturization continues despite lifestyle changes, clinical treatments may help. These options target the root causes of pattern hair loss, like the DHT hormone, and can support the hair follicle growth cycle. Some treatments aim to block the effects of DHT, while others stimulate miniaturized follicles to grow thicker, healthier hairs.
Prescription Hair Loss Medications
Doctors often recommend prescription treatments to slow hair loss and promote hair growth. These are usually most effective during the early or moderate stages of miniaturization.
• Finasteride blocks the enzyme that turns testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By lowering DHT levels, it helps protect hair follicles from shrinking. It’s typically used for male pattern hair loss.
• Dutasteride works in a similar way but blocks both types of the enzyme. Though not FDA-approved for hair loss, it may be prescribed off-label in some cases.
• Oral minoxidil was originally developed for blood pressure, but low doses can help improve blood flow to the scalp and extend the growth phase in both men and women.
These treatments don’t restore lost follicles, but they may slow the process and allow remaining follicles to produce healthier hairs.
Hair Transplant Surgery Options
For people with more advanced miniaturization or large areas of hair loss, surgical hair restoration, such as hair transplants, may be the next step. Hair transplant surgery moves active follicular units from denser areas to thinning zones.
Two common methods are:
• Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of scalp is removed from the donor area. Follicles are separated and implanted into thinning spots.
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are harvested using a small tool and transplanted one by one. This method doesn’t leave a linear scar and is preferred by those who wear shorter hairstyles.
Both procedures can help rebuild natural hair density, especially in areas with permanent follicle shrinkage from male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss. While hair transplants can be beneficial for individuals with extensive hair thinning, they are not a cure for androgenic alopecia and can be quite costly.
In-Office Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that stimulates hair follicles using focused light. As part of a broader range of clinical options designed to address hair miniaturization, laser treatments like LLLT can increase blood flow, support cellular repair, and improve scalp health.
What to expect:
• Sessions usually last 15 to 30 minutes
• Most people go two to three times per week for several months
• Results vary, but best outcomes often come when paired with other treatments like minoxidil or prescription medications
LLLT may help slow hair follicle miniaturization and promote hair growth, especially in early stages of androgenetic alopecia.
In the next section, we’ll look at natural remedies and supplements that some people turn to as alternatives or add-ons to these clinical options.
4. Natural Remedies and Supplements for Hair Growth
What to Know Before Trying Natural Options
Many people explore natural remedies or supplements as part of their hair care plan. While some ingredients are promising, the scientific evidence behind them is often limited. These options may help promote hair growth or slow hair miniaturization, especially when used alongside other treatments, but they shouldn't replace clinically proven methods.
Common Natural Ingredients and Their Claimed Benefits
Saw Palmetto
Saw palmetto is often marketed as a natural DHT blocker. Some small studies suggest it may help slow male pattern hair loss by reducing DHT levels in the scalp. However, research is limited, and results vary.
Biotin
Biotin helps produce keratin, which supports hair shaft strength. Many people take biotin supplements to improve hair texture and reduce breakage. While biotin deficiency can lead to hair thinning, most people get enough through food unless there's an underlying condition.
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Pumpkin seed oil has been linked to improved hair density in a few early studies. It may help block the effects of DHT on hair follicles, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in slowing hair follicle miniaturization.
Fish Oil
Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, which may reduce scalp inflammation and support a healthy hair growth cycle. While not a direct treatment for pattern baldness, it may help support scalp health and follicle function.
Essential Oils
Some essential oils like rosemary or peppermint are believed to improve circulation in the scalp. These are typically used in diluted form and massaged into the scalp. Evidence is limited, but they may offer mild benefits when used regularly.
Proceeding with Caution
Natural supplements may work for mild cases or as part of a broader strategy, but results are not guaranteed. Always check with your doctor before starting any new supplements, especially if you take prescription medications or have a health condition. Some ingredients may interact with other treatments or cause side effects.
5. Scalp Care Practices to Prevent Further Thinning
Why Scalp Care Matters
Your scalp is where every hair strand begins. If it’s not in good condition, your hair follicles can struggle to produce healthy hairs. Scalp buildup, irritation, or inflammation can block growth and speed up hair miniaturization. Keeping your scalp clean and balanced is a simple but powerful way to support hair health.
Cleanse Regularly, But Gently
Washing your scalp removes oil, dead skin, and product residue that can clog follicles and affect the hair cycle. Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo to avoid stripping natural oils or disturbing your scalp’s pH.
How to cleanse effectively:
• Wash 2–3 times per week or as needed, depending on oil levels
• Rinse thoroughly to avoid product buildup
• Focus on your scalp, not just your hair strands
Avoid over-washing, which can dry out your scalp and trigger irritation.
Massage to Stimulate Follicles
Massaging your scalp boosts blood flow and helps deliver nutrients to the follicles. This may support healthier follicle activity and slow hair loss.
Tips for effective massage:
• Use your fingertips (not nails) in small circles
• Apply light pressure for 3 to 5 minutes
• Gently pull upward on sections of hair to stimulate follicles
• Do this during or after shampooing, or with a few drops of scalp oil
Gentle massage may also help loosen buildup and ease scalp tension, both of which can improve conditions for hair growth.
Protect the Scalp from External Stress
Sun, pollution, and harsh chemicals can harm the scalp and weaken hair follicles. Protect your scalp the same way you protect your skin.
Simple protection tips:
• Wear a hat in direct sun
• Apply scalp-safe sunscreen if you’re exposed often
• Avoid chemical-heavy products and bleaching agents
• Let your scalp breathe—skip tight styles that pull on the roots
A healthy scalp environment helps preserve hair density and slow hair follicle shrinkage over time.
6. Hair Care Techniques That Minimize Damage
Why Daily Hair Habits Matter
Even if your follicles are healthy, poor hair care practices can cause breakage, split ends, and make hair thinning look worse. Hair that's already thinner due to miniaturization is more fragile. Gentle, consistent care helps you protect existing strands and prevent extra shedding.
Use Gentle Products
Start with a mild, sulfate-free shampoo. Harsh shampoos can dry out your scalp and damage the hair shaft. Always follow with a moisturizing conditioner to maintain softness and prevent tangles.
Tips for washing:
• Avoid hot water—it can strip natural oils
• Rinse thoroughly to remove product buildup
• Focus shampoo at the scalp, and conditioner at the mid-lengths and ends
Handle Wet Hair Carefully
Hair is most fragile when wet. Stretching or tugging on it during brushing can cause strands to break.
• Use a wide-toothed comb
• Start detangling from the ends, working up to the roots
• Pat hair dry with a towel instead of rubbing it
These small adjustments help prevent breakage and protect miniaturized hairs from falling out too early in the cycle.
Limit Heat and Tight Styling
High heat can weaken the hair shaft, and tight hairstyles can cause traction alopecia—another form of hair loss.
Best practices:
• Keep hot tools below 375°F (190°C)
• Always use a heat protectant before styling
• Avoid tight ponytails, braids, or clips that pull on the scalp
• Switch to soft hair ties and gentle accessories
Protect While You Sleep
Friction from rough pillowcases can wear down your hair overnight. Switching your sleep setup helps prevent damage.
• Use a silk or satin pillowcase
• Tie your hair loosely or wrap it in a soft scarf
• Avoid sleeping with wet hair
These changes help reduce breakage and support stronger, longer-lasting strands—especially important if you’re working to slow hair follicle miniaturization.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Long-Term Strategies for Hair Loss Prevention

Why a Long-Term Plan Matters
Hair thinning caused by miniaturization often happens gradually, and keeping it under control requires consistent effort over time. While daily care helps, long-term strategies are what keep follicles healthier, longer. These steps focus on preventing future damage, protecting existing hair, and supporting the natural hair cycle.
Keep Hormones Balanced
Hormonal changes—especially involving testosterone and its byproduct DHT—can lead to pattern baldness and hair follicle miniaturization. Stable hormone levels help reduce the rate at which DHT affects sensitive follicles.
To help manage this naturally:
• Get regular, uninterrupted sleep
• Exercise consistently to reduce excess stress hormones
• Avoid extreme diets or rapid weight loss, which can disrupt hormone levels
• If needed, consult your doctor for a blood test to check hormone imbalances
Stable hormone levels support healthy hair growth and slow hair loss over time.
Use Proven Supplements Consistently
Some supplements can support follicle function if used long term. While results vary, maintaining proper levels of specific nutrients helps create a better environment for strong, healthy hairs.
Consider:
• Biotin for keratin production
• Vitamin D to support the hair growth cycle
• Omega-3 fatty acids (from fish oil) to reduce scalp inflammation
Consistency matters more than short-term use. Supplements often take several months before any changes in hair growth or texture appear.
Monitor Hair and Scalp Health Regularly
Early signs of hair thinning are easier to treat than advanced hair loss. Keeping track of your hair’s condition can help you act faster.
Good habits include:
• Checking your part line and hair density every few months
• Watching for increased hair in your brush or shower
• Taking occasional photos under the same lighting to track subtle changes
• Doing a gentle pull test if you notice more shedding than usual
If you suspect miniaturization is progressing, book a scalp biopsy or clinical evaluation. A doctor or trichologist can help confirm what’s going on below the surface. While there are practical tests like the pull test and grading systems such as the Norwood scale, it's important to note that there is no truly scientific test to definitively diagnose hair miniaturization.

F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment: Support for Miniaturized Hair Follicles
Hair miniaturization is one of the most common causes of progressive hair thinning. As hair follicles shrink due to the effects of the DHT hormone, they begin to produce weaker, shorter strands. If left untreated, these miniaturized follicles can eventually stop growing hair altogether. The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment offers a non-invasive option to help support these struggling follicles and improve scalp conditions that contribute to healthy hair growth.
How the F8 Treatment Works
The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment uses low-level laser energy combined with a specialized hair growth serum. During the session, the therapist applies laser energy across the scalp to stimulate blood flow and activate the hair papilla and nearby capillaries. This helps improve nutrient delivery to hair follicles that have become dormant or weak due to the hair follicle miniaturization process.
Once the laser step is complete, the therapist applies a nutrient-rich hair growth serum to the scalp. This serum absorbs more effectively due to the laser’s effect on the skin barrier. It works to cleanse the scalp, reduce excess sebum, unclog follicles, and hydrate the scalp environment. Together, these steps help create better conditions for hair growth and support the scalp affected by pattern hair loss or thinning.
Advantages of F8 for Hair and Scalp Health
• Non-invasive: There’s no surgery, no needles, and no downtime. The treatment is gentle and suitable for both male and female pattern hair loss.
• Targets hair miniaturization: By improving microcirculation and stimulating the follicle directly, F8 helps slow the miniaturization process and support terminal hairs.
• Scalp care included: The serum helps remove buildup, reduce inflammation, and calm oil production—all of which are linked to issues like hair thinning and chronic telogen effluvium.
• Safe and suitable for many users: Most people experience no irritation, and the treatment is suitable even for those with sensitive scalps.
If you’re noticing signs of hair loss like a receding hairline, thinner hairs, or reduced density, F8 may help strengthen your follicles and promote more hair growth.
Book F8 today and take the first step toward healthier scalp and hair follicle support.
New Beauty's F8 Hair Regrowth TreatmentBook Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
Can Hair Miniaturization Be Reversed if Caused by Wearing Tight Hairstyles?
Nearly 30% of people who regularly wear tight hairstyles experience traction alopecia, but you can reverse hair miniaturization if you catch it early. It's also important to check for any underlying medical condition that might be contributing to hair loss, as diagnosing and treating such conditions can be crucial. You’ll need to immediately stop wearing tight hairstyles, as continued tension damages your hair follicles permanently. To promote recovery, you can use minoxidil treatments, take hair-supporting supplements like biotin, and switch to loose, protective styling methods that don’t strain your follicles.
Does Swimming in Chlorinated Pools Accelerate Hair Miniaturization?
Chlorinated pools don't directly cause hair miniaturization, but they can damage your hair's structure and make existing hair problems worse. When you swim regularly in chlorinated water, the chemical strips your hair's natural oils and proteins, leading to brittleness, breakage, and increased susceptibility to damage. To protect your hair, you should wear a swim cap, wet your hair with fresh water before swimming, and use specialized swimmers' shampoo afterward.
Can Certain Medications Trigger Sudden Hair Miniaturization?
Yes, certain medications can trigger sudden hair miniaturization, particularly those that affect your hormone levels or immune system. Common culprits include blood pressure medications, antidepressants, retinoids, chemotherapy drugs, and hormone treatments. You'll often notice this effect within 2-4 months of starting medication, as the drugs can interfere with your hair's natural growth cycle, causing follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker strands.
Is Hair Miniaturization Hereditary From the Mother's or Father's Side?
Hair miniaturization can be inherited from both your mother's and father's side, contrary to the common myth that it's solely from your maternal line. The genetic factors responsible for hair loss, particularly androgenetic alopecia, are polygenic, meaning multiple genes from both parents contribute to the condition. You'll find that variations in the androgen receptor gene, which can come from either parent, play a vital role in this process.
Does Frequent Hair Coloring Contribute to Premature Hair Miniaturization?
While hair coloring alone doesn't directly cause hair miniaturization, frequent chemical treatments can contribute to hair damage and breakage, which may make existing miniaturization more noticeable. The harsh chemicals in hair dyes, particularly bleach and permanent colors, can weaken your hair shaft and irritate your scalp, potentially disrupting healthy hair growth cycles and exacerbating underlying conditions that lead to miniaturization.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.