Book Now to Experience
B6 Bust Lift Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Author: Leila Tan|Updated: 23 July 2024
Does going through breast augmentation with implants will affect my ability to breastfeed? Can I breastfeed while having breast implants? Well certainly YES! You can breastfeed after having breast implant surgery. However it does depend on the size, location, and the kind of surgery you went through. Although there are a few outliers, the majority of women with breast implants are able to breastfeed. The original condition of your breasts prior to surgery and potentially the sort of incision utilised will determine whether you are able to breastfeed or not.

1
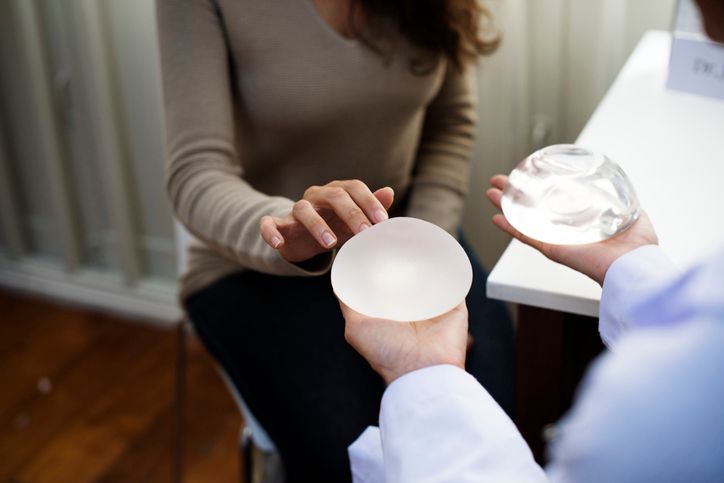
What is breast implant
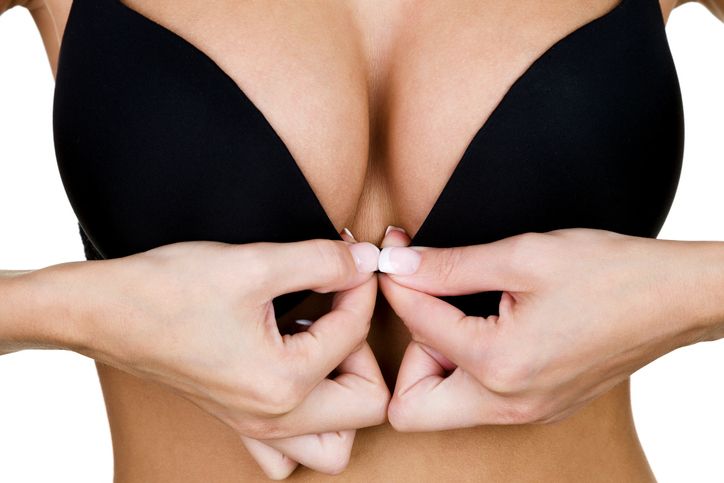

Breast implants are prosthetic objects that are surgically placed inside your breasts. Breast implants consist of silicone casings that are either filled with silicone gel or saline (sterile salt water). Usually, breast augmentation or reconstruction treatments employ these implants. With over 300,000 breast augmentation procedures carried out annually in the United States, breast implant surgery is currently the most prevalent cosmetic procedure.

2
Saline and Silicone Breast Implants
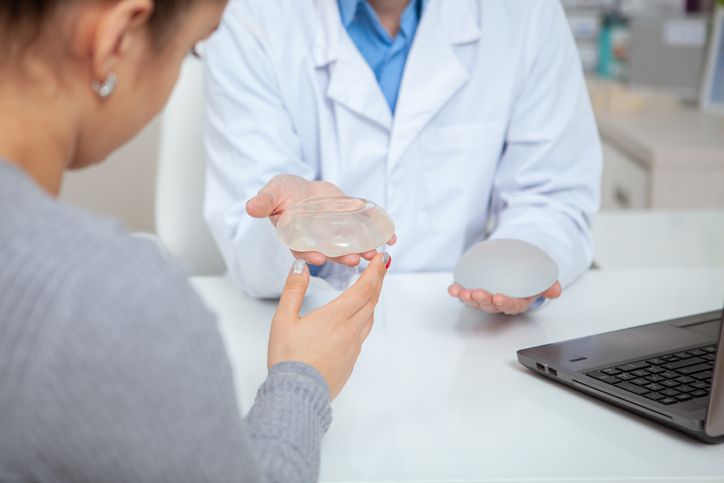

Breast implants come in two basic varieties: silicone gel and saline.
Saline-filled implants contain silicone shells filled with sterile salt water (saline). Some are filled as the implant is being inserted, while some are already filled.
These implants' silicone casings are filled with a polyethylene gel (silicone). Many women contend that silicone gel implants feel more natural than saline implants do, yet they are more risky if they leak.
Both silicone and saline have a range of sizes and smooth or textured outer shell options. Everyone has their own preferences, and each has benefits and drawbacks.

3
Risk of breast implants
Having breast implants can come along with some health problems. But this risks is not common for all the women and remember these side effects can be overcome with the help of professional help. Few of the risks are such as:
* Breast soreness and changes in nipple and breast feeling are two implant problems. * Scar tissue that alters the breast implant's form (capsular contracture) * Further procedures, with or without device removal (also see Implant Removal Options) * Breast cancer, certain uncommon cancers that can arise in the scar tissue (capsule) surrounding breast implants. * Breast implant rupture and deflation * Breast pain * Changes in the breast and nipple's sensation

4
Breastfeeding with implants
According to John Hopkins medicine, breast implants are inserted during breast augmentation surgery between your chest wall and your breast, avoiding any interference with the breast ducts or mammary glands that secrete milk. When breasts are reduced, some glandular tissue is removed, but often there is still enough breast tissue to allow for postoperative milk production.

Your ability to produce enough breast milk may be impacted after the breast implant surgery. But do not worry as there is no change in milk production.
You may see changes in your breast size and form during pregnancy and after breastfeeding which is normal and remember that your implants won't be impacted by breastfeeding, although your breasts' general size and shape can change.
You shouldn't have any issues breastfeeding whether the incisions are made through your armpit or under the fold of your breast. If the incision is made near the areola it may cause the milk ducts to be severed.

Book Now to Experience
B6 Bust Lift Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

5
How do breast implants impact breastfeeding?

When breastfeeding, the nerves near your nipples are crucial. The hormones prolactin and oxytocin are released more readily when a baby is sucking on the breast. Breast milk production is triggered by prolactin, whereas letdown is triggered by oxytocin. Sensation is lessened when these nerves are injured.
The manner and purpose of your operation are the most crucial factors in influencing breastfeeding success. Some of them are:
Location where the incisions made
Some of your milk ducts and nerves may have been severed if they cross your areolas or nipples. If so, breastfeeding might not be successful. Yet, it's likely that your incisions were placed close to the armpits or beneath the breasts. You should be able to produce milk because your surgeon most likely preserved important nerves in that situation.
Feeling around nipple
That's a good indication that your nerves are functioning as they should, though complete nipple sensation might not have yet returned if your operation was recent (within the previous year or two) (but you still may be able to breastfeed just fine).
Location of the implants
It's preferable for breastfeeding if they're under your chest muscle. The production of milk can occasionally be hampered by implants that are directly beneath the glandular tissue of your breasts (and on top of the chest muscle).
Can you breastfeed while having implants?
There is no accurate way to measure silicone levels in breast milk. Yet, a research that evaluated silicon levels found no difference in levels between moms with and without silicone implants in their breast milk. Silicone implant contains the element silicon.


6
Does implant affect milk supply?

Even if they are able to breastfeed, some women with breast implants may not be able to produce a sufficient amount of milk. Occasionally it's as a result of surgical injury to the nerves or milk ducts. At times, the pressure from breast implants can mimic the sense of engorgement (milk-filled breasts), which could tell the body to stop producing milk. Greater symptoms of engorgement or decreased nerve sensitivity may be linked to larger breast implants, which may affect nursing.
No matter the size of the implant, a woman has a 75% chance of successfully breastfeeding with implants overall, according to a study of more than 1,000 breastfeeding mothers with implants.

7
Tips for breastfeeding
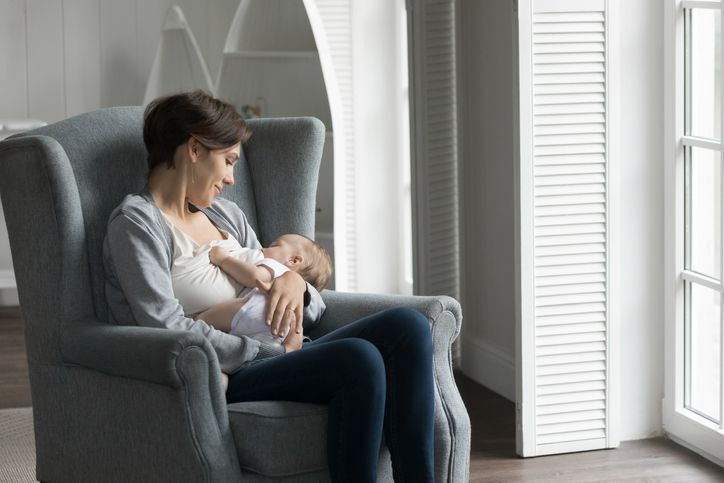

Routinely empty your breasts
The process of emptying your breasts is crucial for milk production. To enhance milk production, try using a breast pump or manually expressing milk after feedings.
According to a study, pumping both breasts at once enhanced milk output. Moreover, it made breast milk more caloric and fatty.
If your baby won't latch, you can alternatively hand-express or pump breast milk into a bottle to feed them.
Frequently breastfeed
8 to 10 feedings a day might assist develop and sustain milk production in your infant. Your body produces milk in response to your baby sucking on your breast. Your body will produce more milk the more frequently you breastfeed.
Each time you feed your baby, even if you can only produce a small bit of milk, you are still giving him or her nutrition and antibodies.
Moreover, breastfeeding from both breasts can improve your milk production. consuming natural supplements that are believed to increase milk production, such as fenugreek and blessed thistle, and possibly speaking with your doctor about obtaining a prescription for domperidone, the medication that increases milk production, to keep on hand in case you do experience a shortage.
Ensure that your infant latches properly
Your baby can benefit most from feedings with a good latch.
Making sure your baby takes enough of your breast into their mouth is essential for a successful latch. To start, make sure that their mouth is open widely when they latch on. Your baby's gums and tongue should cover your areola by an inch or two when your nipple is positioned far enough into their mouth.
Make sure your infant is properly positioned before directing them towards your breast. Your infant may latch on more readily if you hold your breast in a "C" shape with your thumb and forefinger right behind the areola.
Check to see if your baby is latching properly if not speak with a lactation consultant or a nursing clinic. Usually, your hospital or doctor's office can get you one. They can watch you feed and offer advice on your child's latch and positioning.
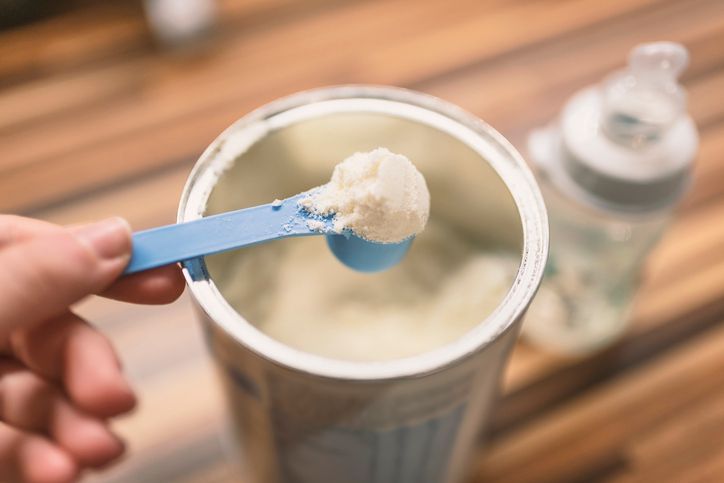
Using a formula
Breast implants may prevent you from producing a sufficient amount of milk, in which case you can supplement your baby's diet with formula or pasteurised breast milk from a human donor. According to research, mothers with breast implants are less likely than mothers without implants to nurse their children exclusively, although they can still participate in the bonding process.

Another indication of an adequate or insufficient milk production is your baby's weight. Before starting to acquire weight, most newborns lose 7 to 10 percent of their body weight in the first two to four days of life.
If you are worried about your milk production or your baby's weight increase, let the paediatrician know. See your baby's paediatrician or a lactation consultant about supplementing your breastfeeding with formula if you're only producing modest amounts of milk.

8
Conclusion

Going through breast augmentation or breast reduction may come along certain risks. But the risks of breast implants can be preventable with right care and procedure. So don't be hesitant to seek your plastic surgeons if you ever need any help.
According to a consultant for the prenatal lactation programme at The Johns Hopkins Hospital, incisions made during breast surgery that cut the nerves that are triggered by nursing in the breast and nipple may also reduce milk production.
Before your operation, speak with a breastfeeding consultant and your reconstructive surgeon. While your breast tissue may change after giving birth, waiting to have breast augmentation, reduction, or lift surgery may help reduce the need for additional adjustments or modifications. Also go for regular screenings to avoid any complications that may arise such as silicone breast implants silent rupture.
FAQ
Does having implants make breastfeeding more challenging?
The nerves and ducts in the breast may be impacted by breast augmentation, lift, and reduction surgeries, which could influence lactation. Compared to implants above the muscle, breast implants below the muscle often have a less impact on milk output. If you have breast implant illness it is recommended to consult a doctor for further treatments as it can be a hindrance for breastfeeding.
Does breastfeeding cause implant rupture?
There is no evidence to support the notion that implant rupturing or other harm will result from pumping. Nonetheless, you must use caution when positioning the flange, particularly if the periareolar incision approach was employed. The flange may irritate scar tissue that has accumulated around the interior of the areola.
Do my implants have the potential to leak and contaminate my breast milk?
No, there is virtually little chance of leakage with either saline or silicone implants. Additionally, since breast milk is produced and delivered through its own network of mammary glands and milk ducts, there is no path for contamination if the implant were to leak.
How can I tell if my child is getting enough milk at the breast?
Most newborns right after delivery have a very successful breastfeeding session at the breast, followed by several hours of sleep. It's typical for a breastfed infant to eat regularly as they start to wake up once more. Your infant should need to eat at least every two to three hours after the first 24 hours.
Does my ability to breastfeed depend on the size or form of my breasts?
A substantial risk factor for decreased milk production is because of insufficient glandular tissue. Your milk production can be insufficient for your kid if you undergone breast augmentation because of undeveloped (hypoplastic) breasts. Breasts that lack normal fullness and are hypoplastic are quite narrow and may appear bulging at the tip. Before augmentation, hypoplastic breasts can appear widely spread, uneven, or tubular because they either do not expand during pregnancy or only grow very little. You run a higher chance of having limited milk supply if this was how your breasts looked naturally before getting augmentation.

Book Now to Experience
B6 Bust Lift Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.




