Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 16 May 2025
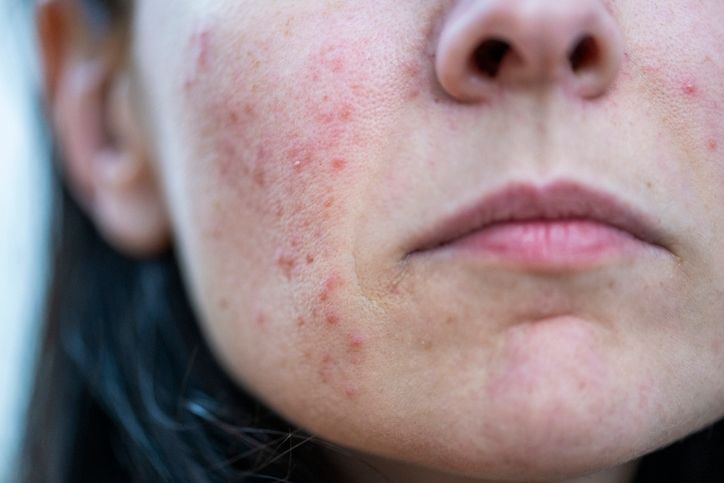
You can treat melasma without harming your skin barrier. Some ingredients are strong enough to fade dark spots but still gentle on your skin. Tranexamic acid, azelaic acid, and niacinamide are great starting points—they help with brown patches, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and other signs of melasma without making your skin dry or sensitive. Melasma is a common skin condition. It often shows up as light brown or dark brown patches, especially on the cheeks, upper lip, and forehead. It’s more common in pregnant women, people with thyroid problems, or those taking birth control pills. Sun exposure, heat, and visible light can also make it worse, especially in darker skin types. That’s why good sun protection is so important. Some people try chemical peels or laser therapy, but you don’t always need those to see results. If you're looking for something gentler, there are topical treatments that can help fade patches and even out your skin without causing damage. Keep reading to learn about 10 ingredients that do the job while keeping your skin calm and healthy.

Treating Melasma with Tranexamic Acid
How tranexamic acid helps with melasma and dark spots
Tranexamic acid is one of the most reliable ingredients for fading melasma hyperpigmentation without irritating your skin. Originally used in oral medications to reduce bleeding, it’s now a trusted topical treatment in skincare for fading brownish pigmentation linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, and visible light.
It works by stopping pigment cells from overproducing melanin, which causes the dark patches seen in epidermal melasma and dermal pigment build-up. Instead of peeling or stripping the surface skin like some harsher options, it targets deeper triggers while leaving the skin barrier intact. That makes it especially useful for melasma patients with darker skin types, where stronger treatments can cause post inflammatory hyperpigmentation or even worsen melasma lesions.
Using tranexamic acid safely in your routine
A 2–3% concentration is usually enough to see visible improvements. You can start with one application a day, then move up to twice daily if your skin handles it well. Tranexamic acid works best when used regularly alongside daily sun protection, especially in sun exposed areas like the upper lip and cheeks. Use a broad spectrum sunscreen that can also block visible light to help prevent melasma relapses.
This ingredient also works well in combination therapy, especially with other topical medications like niacinamide or azelaic acid, making it a good fit for a balanced treatment regimen.

Treating Melasma with Azelaic Acid

Importance of azelaic acid in reducing dark spots and melasma hyperpigmentation
Azelaic acid helps fade dark brown patches caused by melasma without irritating your skin. It slows melanin production, which makes it useful for treating epidermal melasma and post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Unlike stronger treatments such as chemical peels or laser therapy, azelaic acid is usually well tolerated. This is especially helpful for people with darker skin types, who may be more prone to melasma relapses or irritation from harsh topical treatments.
It also reduces inflammation, which is often linked to melasma flare-ups. For those with sensitive skin or other skin disorders, this can make a big difference in how well their skin handles a treatment regimen. Azelaic acid also helps clear out pores with mild antibacterial action, supporting clearer skin overall.
Benefits of azelaic acid for texture and skin clarity
Azelaic acid gently exfoliates the surface skin, helping improve uneven texture caused by melasma lesions. As an antioxidant, it protects your skin from daily exposure to UV light and visible light, which are known to make brownish pigmentation worse over time. This makes it useful for both fading existing patches and preventing new ones from forming—especially in sun exposed areas.
It’s often used in combination therapy alongside other topical medications like niacinamide or vitamin C, supporting both brightening and skin barrier care. Start with a 10% concentration, apply twice daily, and allow a few months to see visible improvements. Most formulas come as a cream or gel, making it easy to work into any treatment routine.
Read More
Book Now to Experience
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Using Vitamin C to Treat Melasma and Dark Spots

Importance of vitamin C in brightening skin and reducing pigmentation
Vitamin C helps treat melasma by slowing down melanin production and protecting the skin from daily exposure to sun and pollution. It blocks the enzyme tyrosinase, which triggers pigment cell activity in melasma patients. By reducing this activity, vitamin C helps fade dark spots and prevent new ones from forming, especially in sun exposed areas like the upper lip or cheeks.
It also fights oxidative stress from ultraviolet radiation and visible light. These are two major factors that can make brownish pigmentation worse, particularly in people with darker skin. Vitamin C supports surface skin repair, which makes it useful for fading patches left behind by other skin conditions or post inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Best way to apply vitamin C for melasma treatment
Use a vitamin C serum with a concentration between 10% and 20%, preferably in the form of L-ascorbic acid. Apply it in the morning after cleansing and before moisturizer. This gives your skin daily antioxidant protection and supports any topical therapy you’re already using for melasma.
If you’re just starting out, go for a lower concentration and do a patch test first. Vitamin C is sensitive to heat and light, so store it in a cool, dark place. If it starts turning brownish, it has oxidized and should be replaced. When used consistently, vitamin C helps improve overall tone while supporting your daily sun protection efforts.

Treating Melasma with Kojic Acid
Importance of kojic acid in blocking melanin and fading dark patches
Kojic acid is a naturally derived ingredient that helps fade melasma by stopping excess melanin from forming. It blocks the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a major role in developing melasma hyperpigmentation. This makes kojic acid a useful option for reducing dark spots, liver spots, and brownish pigmentation caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or oral contraceptives.
It works well for people with darker skin types, where other treatments might cause irritation or lead to post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Kojic acid is often used to support topical treatments for dermal melasma or melasma lesions that don’t respond well to strong chemical peels or laser treatment.
Using kojic acid safely in your skincare routine
Start with a product containing 1% kojic acid and apply it every other night. Once your skin adjusts, you can slowly increase usage to once daily. It usually takes 8 to 12 weeks of consistent use to see visible changes in pigmentation. Products that combine kojic acid with other brightening ingredients like vitamin C or niacinamide may improve results over time.
Always use sunscreen combining protection against ultraviolet radiation and visible light during the day. Kojic acid makes your skin more sensitive to sun exposure, so skipping sun protection may slow progress or trigger melasma relapses.
Book Now to Experience
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Treating Melasma with Niacinamide

Importance of niacinamide in brightening skin and supporting the barrier
Niacinamide helps reduce melasma hyperpigmentation while strengthening the skin barrier. It controls how much melanin gets transferred to skin cells, which helps fade dark spots and prevents patches from getting worse. This makes it especially useful for melasma patients dealing with upper lip pigmentation, sun spots, or uneven tone caused by sun exposure or hormonal changes.
It also supports the skin’s natural barrier by boosting ceramide production. This is important for people with sensitive or irritated skin, especially those using other active ingredients like salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or retinoids. Niacinamide is gentle and works well even on darker skin types, which may react badly to stronger treatments like intense pulsed light or hydroquinone.
Using niacinamide to improve skin tone and texture
Use niacinamide at concentrations between 2% and 5%. Start on the lower end if you’re new to it, then increase as your skin builds tolerance. It blends easily with other topical medications like tranexamic acid, vitamin C, and peptides, which makes it a good part of any treatment regimen.
Apply it twice daily after cleansing, before moisturizer. Some products include niacinamide along with hyaluronic acid or peptides to help hydrate and support overall skin health. With regular use, you’ll notice a more even tone and stronger skin barrier without irritation.

Treating Melasma with Alpha Arbutin

Importance of alpha arbutin as a safe melanin inhibitor
Alpha arbutin fades melasma without the irritation linked to stronger ingredients like hydroquinone. It blocks tyrosinase, the enzyme that controls melanin production, making it useful for treating epidermal melasma, sun spots, and dark patches caused by oral contraceptives, thyroid disorders, or visible light.
It works well on darker skin types and sun exposed areas without damaging the surface skin. This makes it a safer option for people prone to post inflammatory hyperpigmentation or those looking for a long-term maintenance therapy. Alpha arbutin is also less likely to trigger side effects like hydroquinone induced exogenous ochronosis, which can darken patches further if used incorrectly.
Using alpha arbutin effectively in your treatment routine
Use products with 2% to 3% alpha arbutin. Apply once or twice daily depending on your skin’s response. It pairs well with other topical treatments such as tranexamic acid, vitamin C, or niacinamide, and helps even out dark brown or light brown patches over time.
Results usually appear after 8 to 12 weeks of regular use. Since alpha arbutin is stable in most skincare formulas, it’s easy to add into your daily routine without worrying about breakdown or irritation. Always follow with broad spectrum sunscreen to prevent melasma relapses and protect the progress you’ve made.
Book Now to Experience
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Treating Melasma with Licorice Root Extract

Importance of licorice root extract in blocking pigmentation and calming the skin
Licorice root extract helps fade melasma by targeting the root cause of pigmentation without irritating the skin. Its active compound, glabridin, blocks tyrosinase, which slows down melanin production. This makes it helpful for treating brownish pigmentation, age spots, and melasma caused by UV light, hormonal changes, or birth control pills.
It also reduces inflammation, which is important for melasma patients with sensitive or reactive skin. Inflammation often triggers melanin production, leading to more noticeable dark patches. Licorice root extract helps calm this process, especially in darker skin types that are more prone to developing melasma from sun exposure or visible light.
Benefits of licorice root extract for skin tone and antioxidant defense
Licorice root offers antioxidant protection that helps prevent melasma relapses caused by daily exposure to environmental stress. It supports more even pigment distribution across the surface skin, helping reduce patchy tone across the forehead, cheeks, and upper lip.
Use products with 0.5% to 2% licorice root extract twice daily. It combines well with other brightening ingredients and fits into both combination therapy and maintenance therapy routines. It’s gentle enough for long-term use, especially in people managing melasma lesions or dark brown pigmentation.

Treating Melasma with Peptides

Importance of peptides in reducing pigmentation and supporting skin structure
Peptides help treat melasma by sending signals to your skin cells that reduce excess melanin production and improve overall skin repair. These short chains of amino acids target pigmentation at the root while also boosting collagen, which supports healthier, more even-toned skin. For melasma patients with surface skin damage or uneven texture, peptides provide a gentle way to improve both tone and structure without irritation.
They are especially helpful in darker skin types, where stronger treatments like laser therapy or aggressive chemical peels may cause post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Peptides work slowly and steadily, making them suitable for people with sensitive skin or those using a long-term treatment regimen.
Types of peptides and their benefits for melasma
Different peptides target different concerns linked to melasma and other forms of brownish facial pigmentation:
• Oligopeptides help reduce melanin activity
• Hexapeptides brighten overall tone
• Tetrapeptides improve skin texture and firmness
Look for serums that combine multiple peptide types. A concentration around 2% is a good starting point. Apply once or twice daily, and allow at least 8 to 12 weeks of consistent use to see visible improvements. Peptides work best when combined with other topical treatments like niacinamide or vitamin C, especially for stubborn melasma lesions or areas affected by visible light.
Book Now to Experience
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Treating Melasma with Glutathione

Importance of glutathione in fading dark patches and protecting skin
Glutathione helps fade melasma by slowing down melanin production while protecting the skin from oxidative stress. As a strong antioxidant, it neutralizes free radicals triggered by UV light, visible light, and environmental damage—all of which can worsen dark spots and lead to melasma relapses.
It also supports skin repair, making it useful for fading patches linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, or oral contraceptives. For people with darker skin types or those prone to melasma hyperpigmentation, glutathione offers a gentler way to support skin brightening without harming the barrier.
Using glutathione in both topical and oral treatments
Glutathione is available in topical creams and oral treatments. Using both forms together may provide better results, especially for stubborn dermal melasma or brownish pigmentation that doesn’t respond to topical therapy alone. Always check with a healthcare provider before starting oral supplements.
Topical products usually contain 1–2% glutathione. Apply them at night to clean skin, before moisturizers or heavier creams. During the day, always use broad spectrum sunscreen, especially in sun exposed areas like the upper lip or cheeks, to help protect your skin and maintain results.

Treating Melasma with Beta Carotene

Importance of beta carotene in protecting skin from UV damage
Beta carotene supports melasma treatment by helping the skin defend itself against sun exposure, one of the most common triggers for melasma hyperpigmentation. As a natural antioxidant found in orange and yellow fruits and vegetables, beta carotene helps reduce the skin’s reaction to ultraviolet radiation and visible light. This is especially useful for melasma patients who spend time outdoors or live in sunny climates.
Unlike topical treatments that target melasma lesions directly, beta carotene works from within. It supports the body’s ability to manage oxidative stress and prevent pigment cells from overproducing melanin, which leads to dark brown or light brown patches on the skin.
Best way to add beta carotene to your routine
You can increase beta carotene through your diet by eating foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, cantaloupe, and butternut squash. Aim for about 8–10 mg per day, which equals roughly two medium carrots or one large sweet potato. If you prefer supplements, start with 5 mg daily and adjust based on how your skin responds.
For better absorption, pair beta carotene-rich foods with a small amount of healthy fat, such as olive oil or avocado. This helps the body convert beta carotene into vitamin A, which supports overall skin repair and reduces the risk of pigment buildup in sun exposed areas.

Treating Melasma with PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
How PicoCure supports melasma treatment and improves skin clarity
If you’ve been managing melasma hyperpigmentation with topical treatments but want something that works deeper, PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment may help enhance your results. This non-invasive laser treatment uses both picosecond and nanosecond laser technology to break down excess melanin found in melasma lesions. It works by reaching pigment cells at different skin depths, making it effective for both surface-level and deeper dermal melasma.
PicoCure combines four laser wavelengths (1064nm, 650nm, 585nm, and 532nm) to target melanin precisely. The laser energy travels fast—entering and exiting the skin in a split second—so it avoids heat buildup that can irritate or damage surrounding tissue. This makes it a safer choice for people with darker skin types who may not respond well to traditional laser treatment options.
Advantages of PicoCure for melasma patients
PicoCure is not just about fading dark spots—it also improves the skin from within. The treatment stimulates collagen growth, which helps refine skin texture and reduce the appearance of pores and fine lines. It can also brighten dull areas, lessen acne scars, and increase skin elasticity, all while addressing common triggers of melasma, such as sun exposure and hormonal changes.
The speed and accuracy of the laser mean fewer side effects, no downtime, and a comfortable treatment experience. Most people return to their normal routine right after their session. With regular sessions, PicoCure can support your overall treatment regimen by reducing existing pigmentation and helping to prevent new patches from forming.
Ready to boost your treatment of melasma with PicoCure? Book your consultation today and take the next step toward clearer, even-toned skin.
New Beauty's PicoCure Pigmentation Removal TreatmentBook Now to Experience
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
Is melasma the same as liver spots or sun spots?
No, melasma is a specific type of pigmentation caused mainly by hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. Liver spots (also known as age spots or sun spots) are caused by prolonged ultraviolet radiation over time and are usually more common in older individuals. While they may look similar, melasma typically appears in symmetrical patches on sun exposed areas like the cheeks and upper lip, and often affects younger adults, especially pregnant women or those on birth control pills.
Can visible light cause melasma even if I wear sunscreen?
Yes, visible light can still affect melasma hyperpigmentation even when using standard sunscreen. Most sunscreens protect against UV light but don’t block visible light, which has also been shown to worsen pigmentation in melasma patients. Look for sunscreen combining protection with iron oxide or tinted formulas to help block visible light along with ultraviolet radiation.
How is dermal melasma different from epidermal melasma?
Epidermal melasma is pigmentation located in the upper layers of the skin, and it's usually more responsive to topical therapy and laser treatment. Dermal melasma involves deeper pigment that settles below the surface skin, making it harder to treat. It may require longer treatment regimens or combination therapy using topical medications and laser technologies like PicoCure to see improvements over time.
Can oral treatments help with melasma?
Yes, some oral treatments, such as oral tranexamic acid, have been shown in clinical and epidemiological review studies to reduce melasma lesions in certain patients. Oral medications may be prescribed in specific cases where topical treatments and procedures haven’t delivered enough improvement. They are typically used under medical supervision and in combination with other forms of melasma treatment.
Is melasma linked to thyroid disease?
Yes, research suggests a possible connection between thyroid disorders and melasma. Thyroid disease may contribute to hormonal imbalances that trigger brownish pigmentation, especially in women. In some cases, treating the underlying thyroid condition can help improve the skin condition or prevent melasma relapses. If you have persistent melasma and also symptoms of thyroid imbalance, it’s worth discussing with your healthcare provider.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.