Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 13 May 2025
Hair loss can be one of the more frustrating changes that come with hyperthyroidism. If you’ve been noticing more hair in the shower drain or your part looks a little wider than usual, you’re not imagining it. An overactive thyroid can throw off the delicate balance that keeps your hair growing strong and steady. This small gland controls your hormone levels, and when it speeds up, so does your entire system — including your hair cycle. More hairs shift into the resting phase too early and fall out before they’re ready. At the same time, new hair grows back slower, and what does grow may feel finer or weaker. For many people with thyroid disorders like Graves disease or autoimmune thyroid conditions, this kind of hair thinning doesn’t show up all at once. It creeps in slowly, sometimes alongside other symptoms like dry skin, weight changes, or brittle strands that break too easily. Hyperthyroidism hair loss isn’t just about losing volume. It’s about your body working against the normal rhythm of hair growth. Hormonal shifts, immune activity, and changes in how your body processes nutrients all play a role. Ahead, we’ll break down six ways an overactive thyroid can lead to hair thinning and shedding, so you can better understand what’s happening beneath the surface.

Accelerated Hair Shedding from Disrupted Growth Cycle

An overactive thyroid affects more than just your energy levels. It speeds up the human hair cycle too, pushing more strands into the resting phase before they’re ready. This is one of the main ways hyperthyroidism hair loss begins.
Shift into the telogen phase
The normal hair cycle moves through three stages: growth (anagen), transition (catagen), and rest (telogen). When thyroid hormone levels rise too high, the shift into the telogen phase happens too early. This sudden change causes more hairs to stop growing at the same time.
Impact on hair density and texture
This process, called telogen effluvium, leads to noticeable hair shedding. You might see more hair fall when brushing or washing, and your scalp may start to feel less full. Hair can also grow back finer or become more brittle, especially if the thyroid condition isn’t treated.
This kind of shedding is common with thyroid disorders and is closely linked to changes in hormone production. Without proper thyroid function, the timing of your hair growth gets thrown off — and the effects often show up strand by strand.

Hormonal Imbalance Weakens Hair Follicles

In hyperthyroidism, excess thyroid hormones overstimulate the body, and your hair follicles take a direct hit. These hormones speed up your metabolism, which puts constant pressure on your follicles and throws off the balance that keeps them healthy.
Hormone disruption affects hair strength
When thyroid hormone levels rise too high, the entire body shifts into overdrive — including the systems responsible for hair growth. The follicles don’t get enough time or resources to grow strong, healthy hair. Instead, they weaken, and more hairs enter the resting phase early. This leads to increased hair shedding and reduced hair density over time.
Strain on protein and nutrient use
The hormonal imbalance also affects how your body processes protein and absorbs nutrients. Hair needs both to grow and stay anchored to the scalp. But with thyroid dysfunction, your body becomes less efficient at using these building blocks. The stress on your system creates a ripple effect that disrupts hair production from the root.
Inflammation around follicles
Another issue linked to hormone imbalance is inflammation. When your thyroid stays overactive, the area around each hair follicle can become inflamed. This hidden irritation makes it harder for the follicles to function, leading to thinner strands that break more easily.
These changes don’t happen overnight, but over time, the stress from hormonal shifts adds up and your hair starts to reflect it.
Read More
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Nutritional Deficiencies from Fast Metabolism

Hyperthyroidism speeds up your metabolism, which causes your body to burn through nutrients quicker than usual. Even if your diet is balanced, your hair follicles may not get what they need to stay strong and support healthy hair growth.
Nutrients lost through poor absorption
An overactive thyroid increases digestive speed, which means food moves too quickly through your system. This fast transit time affects how well your body absorbs essential nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and protein. These are all critical for the hair follicle and its ability to support regular hair production.
Breakdown of nutrients happens too fast
Thyroid hormone levels that are too high make your cells work harder and faster. As a result, nutrients break down at a faster rate than normal. Key elements like vitamins B and D, zinc, and protein are depleted quickly. Your follicles become undernourished, and hair growth slows down. What grows back may be thinner or more prone to breakage.
High demand leaves follicles undernourished
Your body naturally focuses its resources on essential organs. During hyperthyroidism, that means the scalp and hair follicles get less support. Even with healthy meals, the increased nutrient demand may outpace what you can take in. Over time, this leads to weaker hair and visible thinning, especially when combined with other thyroid symptoms like dry skin or brittle hair.

Autoimmune Reaction Damages Hair Follicles

In many cases, hyperthyroidism is caused by an autoimmune thyroid disease like Graves disease. This means your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue — including your hair follicles — thinking they don’t belong.
Immune attacks trigger hair loss
When the immune system targets the hair follicle, it creates inflammation that disrupts the natural human hair growth cycle. Instead of growing normally, the follicle becomes damaged and weak. Hair strands grow in thinner or fall out before completing a full growth phase.
Lasting damage to the follicle
If the immune response continues without control, scarring can form around the follicles. This makes it harder for them to grow new hair, and in some cases, may stop new hair growth entirely. This damage can lead to diffuse thinning across the scalp or visible patches of hair loss.
Signs linked to autoimmune thyroid conditions
Autoimmune thyroid reactions can also cause changes beyond the scalp. Many people notice thinning at the temples or crown, along with symptoms like dry skin, brittle hair, or weight changes. These signs point to a deeper thyroid problem that’s affecting hair health from the inside.
Autoimmune-related hair thinning is closely linked to thyroid dysfunction, and without addressing the immune response and hormone levels, hair loss caused by thyroid disease may continue to get worse.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Scalp Blood Flow Changes from Thyroid Dysfunction
Thyroid dysfunction affects more than just hormones — it also changes how blood moves through your body, including your scalp. These changes can limit how well your hair follicles get the nutrients and oxygen they need to support healthy hair growth.
Faster blood flow reduces nutrient absorption
Hyperthyroidism increases your heart rate and overall circulation. While this sounds helpful, blood may start flowing too quickly through the scalp’s tiny vessels. Hair follicles need steady, balanced circulation to absorb nutrients. When blood rushes through too fast, there’s not enough time for that exchange to happen.
Blood gets redirected away from follicles
With an overactive thyroid, your body shifts resources to vital organs like the heart and brain. This can reduce blood flow to the scalp, leaving the hair follicle undernourished. Over time, the lack of oxygen and nutrients leads to hair that grows back thinner or falls out more easily.
Signs of disrupted circulation
You might notice your scalp feels warmer than usual or more sensitive in certain areas. These can be signs that blood flow patterns have changed. The result is often gradual thinning and brittle hair, especially when combined with other thyroid symptoms like fatigue or dry skin.
These circulation issues don’t usually cause sudden bald patches, but they can slowly affect overall hair density — making the hair feel weaker and look less full over time.

Stress-Driven Hair Loss Caused by Thyroid Dysfunction

Living with hyperthyroidism puts your body in a constant state of high alert. This prolonged stress — both physical and emotional — can lead to noticeable hair shedding and reduced hair density.
Thyroid-related stress overloads your system
An overactive thyroid increases production of stress hormones like cortisol. This constant pressure activates your body’s fight-or-flight response and makes it harder for non-essential functions, like hair growth, to continue. The hair follicle becomes one of the first areas to slow down or shut off during this state.
Telogen effluvium linked to thyroid stress
Excess stress from thyroid dysfunction often pushes hair follicles into the telogen phase too early. Known as telogen effluvium, this type of hair shedding usually shows up a few months after the stress begins. You may notice more hair falling out all at once, especially during brushing or washing.
Emotional strain makes symptoms worse
Hyperthyroidism can also bring on anxiety, irritability, and sleep problems — all of which add to emotional stress. This mental strain can deepen the physical impact, creating a cycle where both your thyroid and your stress levels contribute to ongoing hair loss.
When stress and thyroid issues overlap, they make it harder for the body to focus on repair and recovery. Hair growth slows down, follicles become less active, and visible thinning becomes more noticeable. Addressing both the thyroid condition and your stress levels is key to breaking the cycle.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

When to Get a Thyroid Blood Test for Hair Loss
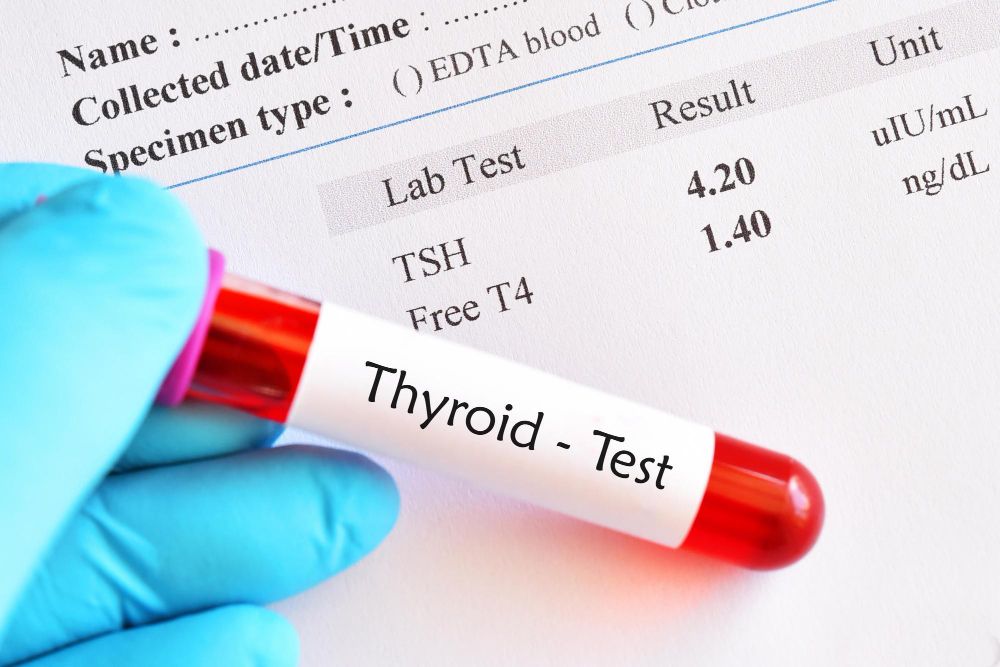
If you're noticing ongoing hair thinning, sudden hair shedding, or changes in hair texture that don’t improve with usual care, it could be time to check your thyroid. Thyroid dysfunction — whether from an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid — can directly affect the human hair cycle. Getting a thyroid blood test helps identify if hormone levels are the cause behind your hair loss.
Signs that suggest thyroid-related hair loss
Certain symptoms tend to appear alongside thyroid related hair loss. If you're experiencing one or more of the following, a blood test can provide useful answers:
• Unexpected weight loss or weight gain
• Fatigue or sleep disturbances
• Irregular periods
• Dry skin or brittle hair
• Hair shedding across the scalp, not in patches
• An enlarged thyroid or visible swelling at the neck
These may point to thyroid disorders such as Graves disease or other autoimmune thyroid conditions, which often go undetected until symptoms like hair loss become visible.
What a thyroid blood test checks
A typical thyroid profile includes:
• Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) – assesses pituitary gland function
• T3 and T4 levels – measure active thyroid hormones
• Thyroid antibody tests – check for autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto's or Graves
This helps your healthcare provider see if you have abnormal thyroid hormone levels that may be affecting hair follicle function and slowing new hair growth.
Early testing leads to better outcomes
The sooner thyroid issues are diagnosed, the better your chances of reducing further hair loss. Early treatment helps stabilize hormone production, support healthy hair regrowth, and prevent long-term follicle damage.

How to Support Hair Health During Hyperthyroidism

Managing hyperthyroidism is the first step, but supporting your hair during this time can make a real difference in how it grows, sheds, and recovers. While thyroid dysfunction often disrupts the human hair growth cycle, there are ways to reduce its impact and help promote hair growth.
Focus on nutrient-rich foods
A well-balanced diet supports both your thyroid and your hair. Prioritise foods rich in iron, protein, zinc, and vitamins B12 and D — all of which are often depleted by an overactive thyroid. Leafy greens, eggs, lean meats, fish, seeds, and legumes are great options to help restore what your body may be burning through too quickly.
Monitor your thyroid hormone levels
Regular blood tests help you and your healthcare provider track thyroid hormone levels and adjust your treatment as needed. Keeping thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) within a healthy range can ease stress on your hair follicles and slow excess shedding. If you're on thyroid medication, check in frequently to make sure your dosage still fits your current needs.
Be gentle with your hair
Avoid using harsh products or hot tools like hair straighteners while your hair is weak. Excessive heat and chemical styling can increase breakage, especially if you're already dealing with brittle hair from thyroid issues. Choose mild shampoos, limit tight hairstyles, and allow your hair to air dry when possible.
Targeted supplements
In some cases, supplements can help fill in nutritional gaps caused by hyperthyroidism. Iron, vitamin D, or biotin may support new hair growth if blood tests show you're deficient. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting anything new, especially if you’re already on thyroid medication.
Supporting your hair during hyperthyroidism means working with your body — not against it. A mix of nutrient support, gentle care, and thyroid management gives your follicles the best chance to recover and grow stronger over time.

F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment for Thyroid-Related Hair Loss
For those experiencing hair thinning or excessive shedding from hyperthyroidism, targeted scalp care can make a difference — especially when the hair follicles are under stress from shifting thyroid hormone levels. One treatment that supports hair and scalp recovery during this time is the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment.
This non-invasive therapy uses low-energy laser technology combined with a nutrient-rich hair growth serum to support hair follicle health, stimulate blood circulation, and create a scalp environment that promotes hair growth. For people dealing with thyroid disorders, where hair follicles often weaken or enter the telogen phase too early, this treatment offers direct support without causing further irritation or stress to the scalp.
How F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment Works
The treatment begins with a detailed scalp analysis by a hair expert to check the health of your scalp and follicles. Once your hair loss pattern is confirmed, a gentle, low-energy laser is applied evenly across the scalp. This step activates weakened follicles and strengthens surrounding blood vessels, which improves nutrient delivery — a key issue for people with thyroid dysfunction or poor circulation linked to hyperthyroidism.
Next, a specially formulated hair growth serum is applied. Thanks to the laser's stimulation, the serum absorbs more effectively, helping to unclog follicles, hydrate the scalp, and reduce sebum buildup. This step creates a cleaner, balanced environment where new hair can grow more easily and existing strands are less likely to shed.
Why F8 Works Well for Hyperthyroidism Hair Loss
• Strengthens weakened follicles caused by elevated thyroid hormone levels
• Improves blood flow and microcirculation, which may be disrupted in thyroid conditions
• Helps control scalp oil and inflammation, common in stressed or nutrient-deficient scalps
• Safe for sensitive skin with no downtime or harsh chemicals
• Boosts absorption of nutrients directly into the scalp — helpful when nutrient delivery is compromised by thyroid dysfunction
The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment supports both men and women dealing with hair loss caused by thyroid conditions like Graves disease, thyroid nodules, or hormonal imbalances linked to the pituitary gland. It’s a safe and effective option that pairs well with medical treatment for hyperthyroidism to support better scalp and hair health over time.
Book the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment today and support your scalp with a treatment that encourages stronger, fuller hair — even during thyroid-related hair loss.
New Beauty's F8 Hair Regrowth TreatmentBook Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
What is the link between autoimmune thyroid diseases and alopecia areata?
Autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Graves disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, are closely linked to alopecia areata — another autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss. When your immune system is overactive, it may mistakenly attack both the thyroid gland and hair follicles. This dual effect can increase the risk of more severe or irregular hair loss patterns, especially in people already predisposed to autoimmune issues.
Can thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer affect hair growth?
Yes. While thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer don’t always affect hormone levels directly, they can interfere with thyroid function if they impact hormone production. In some cases, treatment for thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer — such as surgery or radioactive iodine — may lead to temporary changes in thyroid hormone levels, which can disrupt hair growth and cause shedding. Monitoring your thyroid profile during and after treatment helps reduce hair-related side effects.
How does an underactive thyroid compare to an overactive thyroid in terms of hair loss?
Both underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can lead to hair thinning, but for different reasons. An underactive thyroid slows down your metabolism and reduces hormone production, which may cause hair to grow slower and fall out more gradually. In contrast, an overactive thyroid accelerates the hair cycle, often causing sudden shedding. Both types of thyroid disorder causing hair loss require proper hormone level management to restore hair health.
Are certain hair products or tools worse for thyroid-related hair loss?
Yes. If you have thyroid related hair loss, using harsh products or high-heat tools like hair straighteners can make things worse. Hair affected by thyroid disorders tends to be more fragile and prone to breakage. Choosing sulfate-free shampoos, avoiding frequent heat styling, and limiting chemical treatments can help protect your existing hair while promoting new hair growth.
Does weight loss from hyperthyroidism affect hair quality?
Unintentional weight loss caused by hyperthyroidism can affect hair health. Rapid weight loss often comes with reduced nutrient intake or absorption, which affects hair production. Combined with increased metabolic demand and thyroid dysfunction, this creates the perfect conditions for thinning hair and brittle strands. Restoring stable thyroid hormone levels and meeting your nutritional needs can help improve hair quality over time.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.