Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 22 May 2025
You can spot early signs of baldness by watching for changes in your hair and scalp. Keep an eye on an M-shaped receding hairline, more hair left behind in the shower or on your brush, thinning at the crown, or a part line that’s slowly getting wider. You may also feel your hair getting finer, growing slower, or notice your scalp feels sensitive. These early shifts are worth paying attention to, as they can point to male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, or conditions like alopecia areata and other hair and scalp disorders. Hair loss is linked to different causes, like hereditary hair loss, hormonal changes, thyroid diseases, scalp infections, or underlying health issues. Some people notice patchy hair loss, others see general thinning across the scalp, and for some, it’s a sudden loss that seems to come out of nowhere. By spotting these signs early, you give yourself a chance to slow further hair loss and protect the hair you still have. Keep reading to learn more about the signs of hair fall baldness and ways to care for your scalp and hair health.

Hair Loss Sign 1: Receding Hairline and Temple Thinning
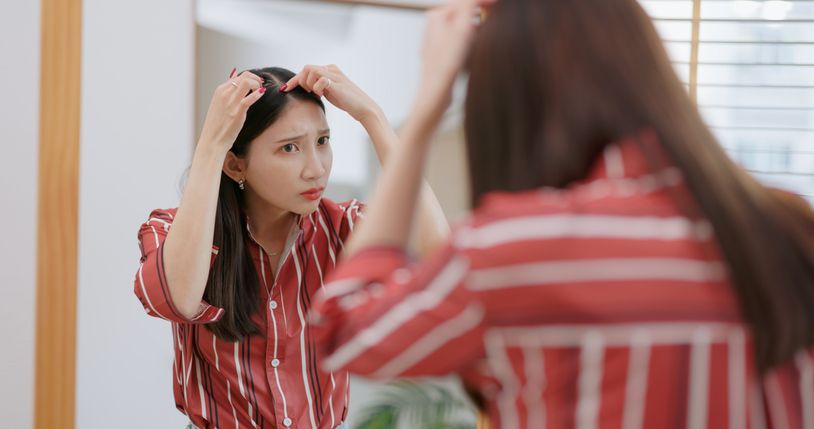

Early signs of hairline changes
A receding hairline is one of the first visible signs of hair loss. It often starts with the hair at the temples pulling back, forming an M-shaped pattern across the forehead. The center of the hairline may stay stable at first, but the hair at the sides gradually moves back, leaving more of the scalp exposed. This change tends to happen over months or years and is most common in male pattern baldness, though it can also appear in female pattern hair loss.
Thinning at the temples
Hair at the temples often becomes finer before it disappears completely. You might notice it feels soft, almost like baby hair, or that it struggles to hold its shape. As hair follicles shrink, they produce thinner and weaker strands. Over time, this thinning creates visible gaps along the hairline, especially when you pull your hair back or style it.
What these signs mean
A receding hairline is a sign that the hair follicles are producing fewer and thinner strands, which can eventually lead to permanent hair loss in those areas. The earlier this pattern is spotted, the better chance there is to slow the process or prevent further loss.

Hair Loss Sign 2: Excessive Hair in Your Brush or Shower Drain
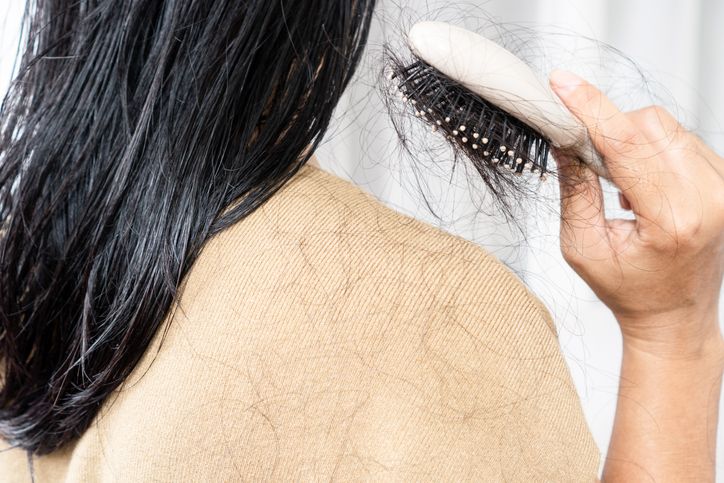
Normal hair shedding vs hair fall baldness
Losing around 50 to 100 hairs a day is normal and part of the hair’s natural cycle. This daily shedding is usually spread out, so you may see a few strands in your brush, on your pillow, or in the shower.
But when you start to see large clumps of hair, or when your brush fills up much faster than it used to, it could be an early sign of hair fall baldness, telogen effluvium, or androgenetic alopecia. Finding hair in places where you usually don’t—like on your clothes, in the car, or after gently running your fingers through your hair—can also be a red flag.
How to spot excessive hair loss
A quick way to check is to run your hands through your hair and see how many strands come loose. If it’s more than 10-15 hairs each time, or if you consistently notice large amounts of hair collecting in your drain after a shower, this points to an increase in hair shedding.
Large amounts of hair fall may also signal an underlying issue, such as hormonal imbalances, thyroid diseases, autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata, or the effects of certain medications.
Read More
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Hair Loss Sign 3: Visible Scalp at the Crown
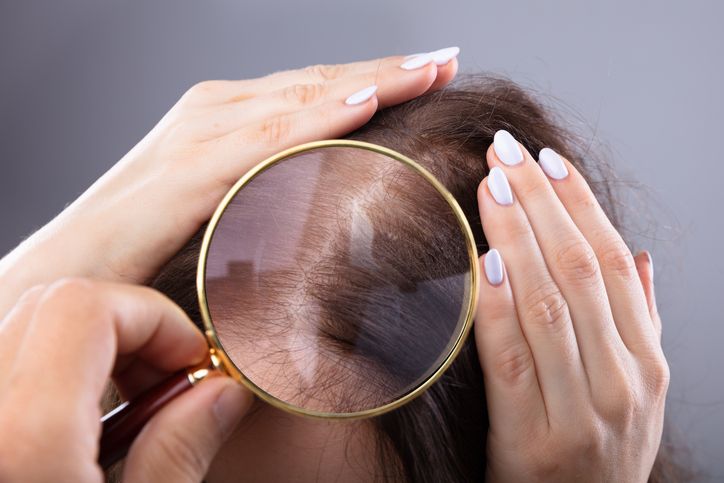

Early signs of crown thinning
A thinning crown often looks like a small, circular patch where more scalp becomes visible over time. It’s one of the most common signs of male pattern baldness and can also appear in female pattern hair loss. You might notice this change first when looking in bright light or when parting your hair, as the hair starts to thin out and the skin underneath shows through more clearly.
Crown thinning vs a normal part
It’s important to tell the difference between normal parting and true thinning. A normal hair part will stay consistent, with even hair density on both sides. Crown thinning, on the other hand, shows up as a widening circle or oval at the top of the head. This patch may become shinier over time as the scalp reflects more light due to the loss of hair.
Spotting early signs of thinning
You may not notice this change until the patch becomes larger, so it’s helpful to be aware of how your hair looks under bright lighting. If the area at your crown looks noticeably lighter or more reflective than the rest of your hair, this can be a sign of thinning linked to pattern hair loss, androgenic alopecia, or other hair and scalp disorders.

Hair Loss Sign 4: Changes in Hair Texture and Volume
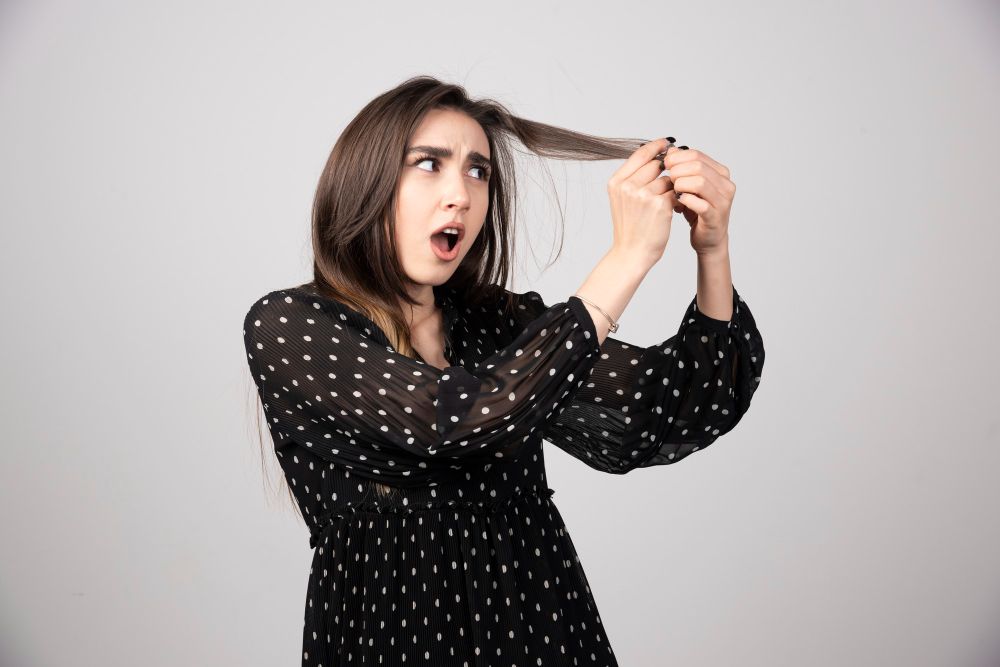

Early signs of hair thinning
When hair starts to feel different—finer, flatter, or weaker—it may signal that hair follicles are shrinking and producing thinner strands. A ponytail that used to feel full but now feels smaller in your hand is often one of the first things people notice. Hair may lose its bounce, feel soft and fragile, or stop holding its usual shape.
How texture changes develop
As hair follicles become smaller, they produce thinner hair shafts. This can cause your hair to feel more like soft fuzz than healthy strands. You might notice your hair becoming more brittle or breaking more easily, or even changing shape—curly hair might start looking straighter, and straight hair may seem limp.
These texture changes often happen across the scalp, but they may be more noticeable at the crown, temples, or along the hairline where hair density is naturally lower. They can also appear alongside other types of hair loss, such as central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, traction alopecia, or alopecia areata.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Hair Loss Sign 5: Slower Hair Growth and Recovery
Signs of slowed hair growth
Hair usually grows about half an inch each month, but when the growth rate slows, it can be an early sign of pattern hair loss or an underlying scalp issue. You may notice that your hair seems stuck at the same length for weeks, or that it takes much longer than usual for your hair to recover after a trim.
Some people also notice that areas like the hairline or crown take far longer to fill in after shedding, making the hair look sparse in those spots for longer stretches of time.
Why hair growth slows
Hair growth can slow down when more follicles shift into the resting phase of the growth cycle. This can happen due to hereditary hair loss, hormonal changes, thyroid diseases, or conditions like telogen effluvium, where stress or illness triggers a sudden change in hair cycle patterns.
When fewer hairs enter the growth phase, the overall length of the hair remains the same for months, and you may find your hairline isn’t filling in the way it used to. This slowdown can also be linked to scalp disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications that affect hair follicles.

Hair Loss Sign 6: Itchy Scalp and Increased Sensitivity

What scalp sensitivity reveals
An itchy or sensitive scalp is often an early sign of hair and scalp disorders that can lead to hair loss. You may feel a tingling or burning sensation, especially around the crown or temples, where male and female pattern baldness often begins. This discomfort can make brushing or styling your hair feel more irritating than usual, and you might find yourself scratching more often without even realizing it.
Causes of itchiness and tenderness
Scalp sensitivity usually happens when hair follicles become inflamed or irritated. This can result from hormonal changes, autoimmune disease, or conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and fungal infection. A tender scalp may also suggest early scarring from types of hair loss like frontal fibrosing alopecia or central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, which can cause permanent hair loss if left unaddressed.
It’s important to notice these sensations and where they occur on your scalp. If the itchiness is mostly in areas where you’re also seeing hair thinning—like the crown, temples, or hairline—it could be a sign that hair loss is progressing.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Hair Loss Sign 7: Widening Hair Part and Overall Thinning

Early signs of a widening hair part
A widening part line is often one of the first signs of hair thinning, especially in female pattern hair loss. What starts as a pencil-thin line may slowly spread, making more of your scalp visible when your hair is parted. You may notice the difference most when styling your hair, as the part feels larger and harder to cover.
This change can happen over several months, often so gradually that it’s easy to miss at first. The hair along the part may feel finer, and the overall density in that area may look lighter, especially under bright light.
Thinning across the scalp
Alongside a widening part, many people experience general thinning across the entire scalp. This type of thinning is often diffuse, meaning it doesn’t leave obvious bald patches but makes the hair appear less full overall. You might find that your usual hairstyles don’t hold as well, and your hair looks flatter and lacks its usual volume.
The combination of a widening part and diffuse thinning can indicate female pattern baldness, androgenetic alopecia, or other hair and scalp disorders that cause hair to fall out more than normal.
Noticing these signs of hair loss is the first step, but understanding why they happen is just as important. Let’s take a closer look at the most common causes behind hair fall, thinning hair, and bald patches.

Common Causes of Hair Loss

Hereditary hair loss
Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of thinning hair in both men and women. Male pattern baldness often leads to a receding hairline and crown thinning, while female pattern baldness usually presents as diffuse thinning and a widening part. Family history can play a big role in whether or not you develop this type of hair loss.
Hormonal changes and imbalances
Hormonal shifts can also cause hair loss. Conditions like thyroid diseases, pregnancy, menopause, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may all trigger sudden hair loss or gradual thinning. Hormonal imbalances can also affect the hair cycle, leading to prolonged resting phases and shorter growth periods.
Scalp infections and disorders
Scalp infections like fungal infection or conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis can cause inflammation, which weakens hair follicles and leads to hair loss. Autoimmune diseases, including alopecia areata and alopecia totalis, can also cause patchy hair loss or even complete baldness across the entire body.
Lifestyle factors and external damage
Hair thinning and hair fall baldness can also be linked to external factors. Traction alopecia may occur when hairstyles pull too tightly on the scalp. Frequent use of heat tools, chemical treatments, and harsh products can weaken the hair shaft, leading to broken hairs and thinning.
Other triggers include severe stress, dietary deficiencies, certain medications, and medical treatments like chemotherapy for cancer cells, which can cause sudden hair loss known as telogen effluvium.
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Types of Hair Loss
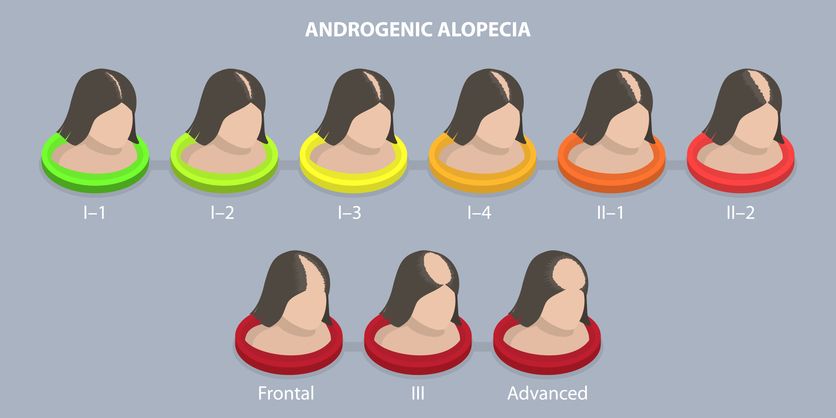
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness, is the most common type of hair loss. It usually develops slowly over time, with men experiencing a receding hairline and thinning crown, while women often notice diffuse thinning across the scalp and a widening part. Family history plays a major role in this condition, and it often becomes more noticeable with age.
Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium happens when large numbers of hair follicles enter the resting phase, leading to sudden hair loss. This can occur after stress, illness, hormonal changes, or certain medications. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium often causes diffuse shedding rather than patchy hair loss or a receding hairline.
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss. It can lead to bald patches across the scalp or body and, in some cases, progress to alopecia totalis, which results in complete baldness.
Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia is caused by repeated tension on the hair, often from tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or hair extensions. Over time, this tension can damage the hair follicles and lead to permanent hair loss if not addressed.
Scarring alopecia
Scarring types of hair loss, such as frontal fibrosing alopecia or central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, happen when inflammation damages hair follicles and replaces them with scar tissue. This can lead to permanent hair loss and is often associated with scalp tenderness, burning, or itching.

Treatment Options for Hair Loss
Diagnosing hair loss
Diagnosing hair loss starts with a detailed assessment by a dermatologist. They will examine your scalp, hair density, and patterns of hair loss. A scalp biopsy or blood tests may be recommended to check for underlying medical conditions like thyroid diseases, autoimmune disease, or hormonal imbalances that can lead to hair loss.
Medical treatments for hair loss
For many people, over the counter medications like minoxidil can help stimulate new hair growth and reduce further hair loss. Oral medications such as finasteride or spironolactone are often prescribed for male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss.
These treatments work by supporting hair follicles, reducing the resting phase in the hair cycle, and helping prevent permanent hair loss.
Advanced treatments and procedures
In cases of scarring conditions like central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, frontal fibrosing alopecia, or patchy hair loss from alopecia areata, medical treatments such as corticosteroids or immunotherapy may be used. For more advanced cases, hair transplant surgery or hair transplantation can help restore hair in areas of permanent baldness.
Everyday habits to support hair health
Making small changes can also help protect against further hair loss. Using gentle shampoos without harsh chemicals, avoiding heat styling and chemical treatments, and massaging the scalp can promote better blood flow to the hair follicles.
A healthy diet rich in protein, iron, and vitamins helps keep hair strong, while reducing tight hairstyles and heavy hair extensions lowers the risk of traction alopecia.
Each person’s hair loss is different, and working with a specialist can help create a treatment plan that suits your specific type of hair loss—whether it’s male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, androgenetic alopecia, or diffuse thinning.
While there are many ways to manage hair loss, some treatments stand out for their ability to support hair follicles and encourage natural hair regrowth. One such option is the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment, which combines low-energy laser technology with scalp care to help strengthen hair and reduce further hair loss.

F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment for Hair Fall Baldness
Hair fall baldness, whether from male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, or other hair and scalp disorders like androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata, often leaves people wondering how to restore healthy hair growth. The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment offers a non-invasive option that helps strengthen hair follicles, stimulate the scalp, and support new hair growth naturally.
How F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment works
The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment uses low-energy laser technology to deliver targeted beams of light to the scalp. These gentle laser pulses stimulate the hair follicles and the surrounding capillaries, helping improve blood flow to the scalp. This enhanced circulation supports the hair follicles during the growth phase, helping them stay healthy and active.
Alongside the laser treatment, a hair growth serum is applied to hydrate the scalp, balance oil production, and create a healthier environment for hair growth. This combination works to reduce scalp sebum, support hair follicles, and help manage symptoms like thinning hair and hair breakage.
Advantages of F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
The F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment is suitable for most people dealing with hair loss concerns, including postpartum hair loss, hereditary hair loss, male pattern hair loss, and female pattern hair loss. The treatment is safe, non-invasive, and does not require any injections, medication, or surgery.
Many people appreciate that F8 can help improve hair density, strengthen existing hair strands, and reduce hair shedding, all without the risks or downtime often seen with hair transplant surgery or chemical treatments. With regular sessions, it promotes long-term hair regrowth and supports the hair’s natural cycle for better overall scalp health.
If you’re noticing signs of hair fall baldness like a receding hairline, thinning crown, or a widening part, the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment may help you take control before the problem worsens.
Book F8 today and start your journey to stronger, healthier hair.
New Beauty's F8 Hair Regrowth TreatmentBook Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
1. Can hair fall baldness happen in women as well as men?
Yes, hair fall baldness can affect both men and women. Male pattern baldness typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning crown, while female pattern hair loss often presents as diffuse thinning across the scalp and a widening part. Women may also experience thinning hair after pregnancy, during menopause, or as a result of hormonal changes.
2. Does hair thinning always lead to complete baldness?
Not necessarily. Thinning hair can occur as part of the natural hair growth cycle, but when hair loss becomes progressive—such as in androgenetic alopecia or male and female pattern baldness—it can lead to more significant hair thinning and potentially permanent hair loss. Early treatment, a healthy diet, and proper scalp care may help slow the process and promote hair regrowth.
3. Can hair loss be reversed naturally without medical treatment?
While some types of hair loss, like telogen effluvium or hair loss from stress, may improve over time with lifestyle changes and a healthy diet, other conditions like male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, and hereditary hair loss often require targeted treatments. Using gentle hair care products, massaging the scalp to stimulate hair follicles, and protecting the hair from heat and chemicals may help maintain healthy hair, but they usually won’t fully reverse advanced hair loss without additional support.
4. What is the link between scalp health and hair regrowth?
A healthy scalp provides the foundation for strong hair growth. Scalp infections, scalp diseases, and buildup of sebum or dead skin can clog hair follicles, weaken the hair shaft, and contribute to hair loss. Keeping the scalp clean, balancing oil production, and supporting blood flow through scalp massage or treatments like the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment can help maintain scalp health and encourage new hair growth.
5. Are hair extensions safe for thinning hair?
Hair extensions can add temporary volume to thinning hair, but they can also cause damage if used too frequently or applied too tightly. Over time, hair extensions can lead to traction alopecia, a type of hair loss caused by constant pulling on the scalp. If you have thinning hair or hair loss concerns, it’s best to use extensions sparingly and avoid styles that put pressure on the hair follicles.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.