Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 26 May 2025
If you're trying to lose weight but your stomach still feels bloated most days, don’t worry as it is a common problem. Bloating and weight loss often clash, and the effects can make it harder to see or feel progress. A bloated stomach might not reflect actual weight gain, but it can still affect how your clothes fit, how you feel, and how motivated you are to keep going. There are several reasons this can happen. Some link to digestion—like irregular bowel movements or too much intestinal gas. Others are tied to food choices, fluid retention, or even how fast you eat. Hormones, gut bacteria, and common triggers like carbonated drinks or fatty foods can all affect the digestive system in ways that cause bloating. For some people, bloating comes with other symptoms like stomach pain, chest pain, or even unexplained weight loss. These can suggest an underlying medical condition. If bloating shows up often or gets worse, it's important to seek medical care. The next section breaks down the most common causes of bloating that can slow weight loss. Keep reading to learn what might be affecting your body and what changes can help.

Why Bloating Can Disrupt Weight Loss Progress

Bloating and weight loss aren’t always linked to fat gain
It’s common to mistake a bloated stomach for belly fat. But in many cases, abdominal bloating is caused by water retention, gas, or irregular bowel movements rather than actual weight gain. This makes it harder to tell whether your weight changes are due to fat loss or temporary bloating.
During weight loss, bloating can affect motivation and progress tracking. The digestive system may respond to diet changes, shifts in hydration, or increased fiber by producing more intestinal gas or holding onto fluid. These effects may cause recent weight gain that isn’t related to fat, or mask unintentional weight loss when bloating covers visible changes.
Signs your bloating may be affecting your weight loss
• Your weight fluctuates by several kilos over a few days
• You feel tighter around the waist despite a calorie deficit
• Bloating is worse after eating certain foods or skipping meals
• You notice changes in bowel movements, including constipation or loose stools
What supports more accurate progress during weight loss
To track weight loss more clearly:
• Weigh yourself at the same time each day, ideally after waking and after going to the toilet
• Monitor symptoms like abdominal bloating, stomach pain, or digestive changes in a daily log
• Focus on how clothes fit and how your stomach feels, not just the number on the scale

Cause Of Bloating 1: Food Intolerances and Sensitivities

Impact of food intolerances on stomach bloating and weight loss
Food intolerances affect the digestive process by slowing down how the body handles certain ingredients. When this happens, food can ferment in the GI tract and produce intestinal gas. This often leads to bloated stomach, abdominal bloating, or irregular bowel movements. Over time, it can also affect weight loss progress or contribute to recent weight gain.
Common food triggers that cause abdominal bloating
Lactose intolerance, gluten intolerance, and foods high in FODMAPs are frequent triggers. These include ingredients found in dairy, wheat, and certain fruits and vegetables like apples, garlic, and onions. People with ibs symptoms or irritable bowel syndrome may be more sensitive to these and experience stomach pain or other symptoms after eating.
What can help reduce bloating caused by food sensitivities
A food diary can help you track symptoms and find specific triggers. Try removing one food at a time to see if it makes a difference. Switching to lactose-free dairy or gluten-free grains may reduce bloating. Some people also benefit from taking digestive enzymes that support the digestive process.
If you keep feeling bloated or notice symptoms like abdominal pain, unintentional weight loss, or changes in digestion, it’s best to seek medical care. A healthcare professional can help confirm food intolerances or rule out underlying medical conditions.
Read More
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Cause Of Bloating 2: Excessive Sodium Intake

Sodium and its effect on water retention and bloating
Consuming too much sodium causes your body to hold onto water. This can lead to noticeable bloating in your stomach, hands, and feet. The digestive process slows as the body tries to balance fluid levels, making you feel puffy and swollen. This may affect how your stomach muscles feel and can make weight loss progress harder to measure.
Hidden sources of sodium that trigger bloating
Many people track their salt intake but overlook hidden sodium in everyday foods. Even items that don’t taste salty can contain high levels of sodium, which can cause fluid retention and stomach bloating.
Examples of common high-sodium foods:
• Sweetened breakfast cereals may contain up to 300mg of sodium per serving
• Pre-packaged deli meats often have over 500mg of sodium per slice
• Restaurant soups or broths can exceed 1,000mg of sodium per bowl
These foods contribute to rapid weight gain and bloating, especially when eaten often. They also make it harder to maintain a low-sodium diet that supports long-term weight loss.
What to do to reduce sodium-related bloating
To prevent bloating from excess sodium, check nutrition labels closely and aim to stay under 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day. Cook more meals at home using whole grains, fresh vegetables, and natural seasonings instead of salt. Avoid processed foods and carbonated beverages when possible, as both can worsen water retention.
To balance electrolytes and support digestion:
• Drink enough water throughout the day
• Eat potassium-rich foods like bananas and sweet potatoes
• Avoid large meals that strain your digestive system

Cause Of Bloating 3: Poor Gut Health and Digestive Issues
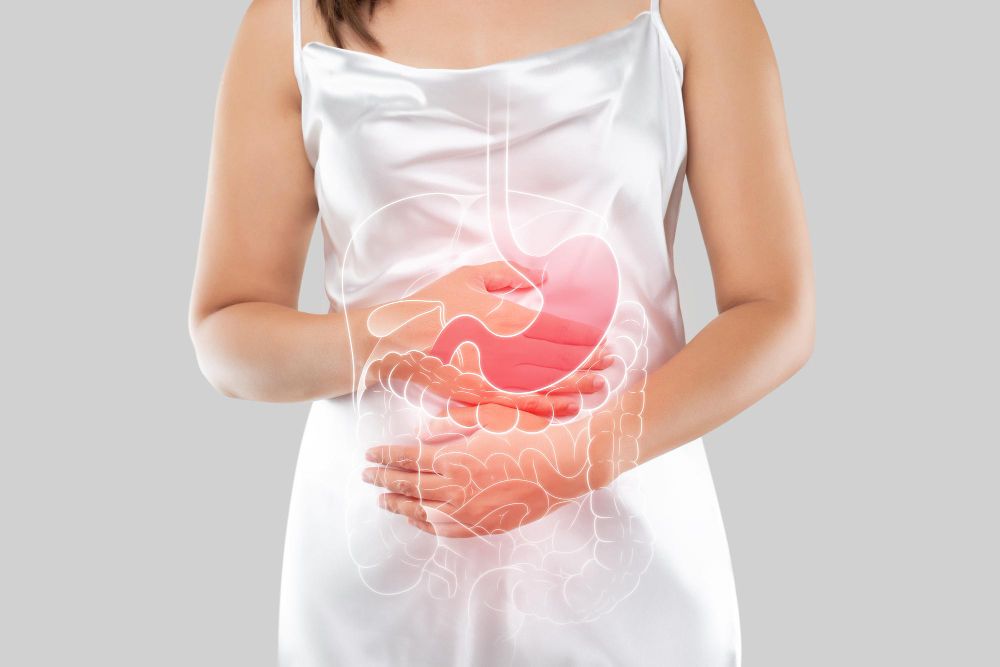
Digestive problems linked to bloated stomach and gas buildup
An unhealthy digestive system can lead to regular bloating, gas, and stomach pain. When gut bacteria are imbalanced or the GI tract isn’t functioning properly, bloating becomes more frequent. You may also experience changes in bowel movements, abdominal bloating, or feelings of pressure in the lower abdomen.
Conditions that affect the digestive system and trigger bloating
Medical conditions like irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease often cause bloated stomach symptoms. These issues can interrupt digestion and lead to excess intestinal gas or abdominal pain. In some cases, food starts fermenting in the intestines, which increases bloating and discomfort.
Gut bacteria imbalances may also lead to food reactions that didn’t exist before. Over time, this can make it harder to manage your diet or track which foods are causing symptoms.
Daily habits that support gut health and reduce digestive symptoms
Improving gut health starts with regular eating patterns, hydration, and avoiding processed foods that disrupt the digestive process. Add more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables that are high in fiber. Probiotics may also help balance gut bacteria.
Track symptoms in a food diary to identify patterns with meals, snacks, or FODMAP-rich foods. If bloating becomes chronic or you notice other symptoms like unintentional weight loss or stomach pain, seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can help check for underlying medical conditions and recommend treatment.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Cause Of Bloating 4: Hormonal Imbalances

Hormonal changes linked to bloating and fluid retention
Hormones control several functions that affect digestion and water balance. When hormone levels shift, especially before your period or under chronic stress, bloating may increase. These changes can cause fluid retention, slow digestion, and disrupt bowel movements.
Hormone-related effects on digestion and stomach bloating
• Estrogen increases before menstruation and can lead to water retention and a bloated stomach
• Thyroid hormone imbalances may slow digestion and cause abdominal discomfort
• High cortisol levels from ongoing stress can upset gut bacteria and lead to intestinal gas
These hormone shifts can contribute to bloating that’s not always connected to food intake. Some people also notice abdominal pain, recent weight gain, or sluggish digestion during these periods.
Signs to monitor and when to seek medical attention
If bloating happens frequently without clear dietary links, track your symptoms over several weeks. This may help identify patterns related to your menstrual cycle or stress levels.
Light activity, balanced meals, and better sleep may support hormone balance. If symptoms like stomach bloating, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss continue, seek medical care. A healthcare provider can check for hormone-related conditions that affect digestion and weight loss.

Cause Of Bloating 5: Dehydration and Water Retention

Link between fluid retention and reduced water intake
Not drinking enough water can lead to bloating. When your body senses dehydration, it holds onto extra fluid as a defense. This can make your stomach feel tight or swollen and may cause sudden shifts in weight. You might also notice puffiness in your face, hands, or lower abdomen.
This reaction affects the balance of electrolytes and slows digestion. Over time, it can interfere with your efforts to lose belly fat and manage other symptoms like constipation or stomach pain.
Physical signs of dehydration that may cause bloating
• Dark urine
• Dry mouth or lips
• Headaches
• Low energy or fatigue
• Irregular bowel movements
These symptoms often show up before noticeable stomach bloating. Delaying water intake may increase the chance of fluid retention and make abdominal bloating feel worse.
Steps that support hydration and reduce bloated stomach symptoms
Drinking 8 to 10 glasses of water a day helps prevent water retention. Eating water-rich fruits and vegetables also supports hydration and aids the digestive system. Limit drinks that can dehydrate you, like caffeine or alcohol.
To monitor hydration:
• Use a simple app or journal to track water intake
• Eat foods with high water content like cucumbers, oranges, and leafy greens
• Spread fluid intake evenly through the day instead of drinking large amounts at once
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Cause Of Bloating 6: High-FODMAP Diet Consumption

Digestive reactions caused by FODMAP-rich foods
Some foods contain fermentable carbohydrates known as FODMAPs. These ingredients can trigger bloated stomach symptoms, especially in people with a sensitive digestive system or ibs symptoms. When FODMAPs aren’t fully absorbed in the small intestine, they draw water into the bowel and ferment in the colon. This leads to gas buildup, intestinal pressure, and abdominal bloating.
These reactions often appear within a few hours after eating and may also include stomach pain, bowel movement changes, or visible swelling in the lower abdomen.
Foods high in FODMAPs that trigger abdominal bloating
Several everyday items contain high amounts of FODMAPs:
• Fruits such as apples, cherries, pears, and watermelon
• Dairy products like milk, yogurt, soft cheese, and ice cream
• Vegetables including garlic, onions, cauliflower, and mushrooms
• Wheat-based foods like pasta, bread, and baked goods
Even small servings of these foods can cause bloating in sensitive individuals. Repeated bloating after eating them may affect weight loss by masking real changes in body shape or water retention.
Eating habits that help reduce bloating from FODMAPs
Track your meals to identify patterns between what you eat and when symptoms appear. Temporarily remove high-FODMAP foods for 2 to 6 weeks and slowly reintroduce them in small portions, one group at a time.
Switch to low-FODMAP substitutes:
• Use chives instead of onions
• Choose sourdough bread over standard wheat bread
• Try lactose-free milk or almond milk instead of regular dairy

Cause Of Bloating 7: Stress and Anxiety

Digestive symptoms linked to emotional stress
Mental stress affects your digestive system more than many people realize. When you're anxious or overwhelmed, your body enters a state of heightened alert. This reduces blood flow to your digestive organs, slows down digestion, and can cause bloated stomach symptoms.
Stress also affects gut bacteria, disrupts bowel movements, and increases the chance of abdominal bloating or gas. These effects may appear even if your diet hasn’t changed, making stress a hidden contributor to stomach discomfort.
Reactions that connect stress to bloating and weight changes
• Stress hormones slow the digestive process and may cause food to stay longer in the GI tract
• Shallow breathing during anxious moments can lead to excess air swallowing, which increases intestinal gas
• Imbalance in gut bacteria under stress can make bloating feel more intense or last longer
In some cases, chronic stress may even lead to changes in appetite, unintentional weight loss, or fluid retention, all of which interfere with weight loss efforts.
Practical steps to reduce bloating caused by stress
Managing stress supports the digestive system and may reduce symptoms like gas, bloating, or abdominal pain. Regular exercise helps regulate hormones and supports stomach muscle function. Eating slowly and avoiding large meals can also reduce pressure on your digestive system.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Lifestyle Habits That Can Prevent Bloating During Weight Loss

Daily patterns that affect digestive health and stomach bloating
Your daily routine can either support or disrupt your digestive system. Beyond food choices, certain habits may increase the chances of experiencing abdominal bloating or intestinal gas. Making small adjustments to how you eat, move, and rest each day can help reduce bloating and support steady weight loss.
Habits that reduce bloating and support the digestive process
• Eat smaller, more frequent meals: Large meals put pressure on your abdominal muscles and slow digestion
• Chew food thoroughly: Rushed eating increases the chance of swallowing air and can trigger bloating
• Avoid chewing gum and drinking carbonated beverages: These habits add extra air into your GI tract and may cause gas buildup
• Exercise regularly: Physical activity stimulates bowel movements and helps move gas through the intestines
• Don’t lie down right after eating: Give your body time to digest properly before resting
These simple shifts can prevent bloating caused by physical habits, even when your food intake stays the same. They also help your digestive system function more smoothly, which supports belly fat reduction over time.

Foods That Reduce Bloating While Supporting Weight Loss

Choosing foods that ease digestion and lower water retention
Some foods help reduce abdominal bloating and support weight loss by improving digestion, lowering intestinal gas, and balancing fluid levels. These options are easy to digest, low in sodium, and high in water or fiber—supporting both the digestive system and fat loss without causing pressure in the stomach.
Bloating-friendly foods that support a flatter stomach
• Cucumbers: High in water and low in calories, cucumbers help reduce water retention
• Leafy greens: Spinach and kale are rich in fiber, promote bowel movements, and help flatten the stomach naturally
• Bananas: A good source of potassium, bananas help manage fluid balance and counteract the effects of salty meals
• Ginger: May help calm the digestive system and ease intestinal gas buildup
• Zucchini and pumpkin: Low-FODMAP vegetables that are easy on the stomach and supportive of steady digestion
• Chia seeds: Provide fiber and omega-3s while supporting gut bacteria and reducing bloating
Simple ways to include these foods in your diet
• Add leafy greens and cucumbers to salads or smoothies
• Snack on banana slices with cinnamon
• Use fresh ginger in soups or tea
• Add chia seeds to yogurt or oatmeal
• Steam zucchini or pumpkin as a low-bloat side dish
Avoid fatty foods and processed meals, which often trigger bloating and delay weight loss. Focusing on whole, water-rich foods can help reduce bloated stomach symptoms, support bowel movement regularity, and promote fat loss around the midsection.

Support Weight Loss Goals with S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
Reduce stubborn fat and bloating in areas that don’t respond to diet alone
Weight loss isn’t always straightforward. Even with regular exercise, clean eating, and proper hydration, some areas—like the belly, thighs, and lower back—can remain unchanged. This is often due to slow fat breakdown, reduced circulation, or fluid retention, which also contributes to abdominal bloating.
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment offers a non-invasive solution for targeting these resistant areas. It helps reduce visible fat and bloated appearance in specific body parts, making it a supportive option for those looking to enhance their weight loss progress.
What the treatment does
S6 Body Sculpting uses a low-energy bio-laser to break down subcutaneous fat cells beneath the skin. These fat cells release fatty acids, which are gradually cleared out through the lymphatic system. Vacuum suction is applied at the same time to stimulate circulation, encourage lymph flow, and improve metabolic activity in the treated area.
The treatment also promotes collagen production, helping to firm the skin and reduce the sagging that can follow fat loss. Sessions are designed to target seven key areas: belly, arms, waist, back, thighs, calves, and lower buttocks—spots where fat and fluid tend to build up.
Key advantages of S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
• Non-surgical and does not involve injections or medication
• Targets specific body parts that are slow to respond to traditional weight loss efforts
• Enhances lymphatic drainage to reduce fluid retention and bloating
• Stimulates skin tightening for a firmer, smoother appearance
• Suitable for people with different body types, no recovery time needed
A supportive tool for better results
S6 works well alongside lifestyle changes by speeding up fat metabolism and improving visible body contouring. If bloating and weight loss are both concerns—especially in areas where results are slow—this treatment offers added support without disrupting your routine.
Book S6 today and take a focused step toward reducing stubborn fat and improving body shape—without surgery or downtime.
New Beauty's S6 Body Sculpting TreatmentBook Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
1: Can bloating cause temporary weight gain?
Yes, bloating can lead to temporary weight gain due to water retention, gas buildup, and delayed bowel movements. This type of weight gain is not fat but extra fluid or intestinal gas that increases your abdominal size. It may cause a bloated stomach or the appearance of belly fat, especially after large meals or certain foods. While it can affect how your clothes fit or the number on the scale, it typically resolves within a few hours to a day once digestion and hydration balance improve.
2: What foods help reduce bloating and support weight loss?
Foods that prevent bloating and promote healthy digestion include cucumbers, ginger, chia seeds, leafy greens, and bananas. These help reduce fluid retention, regulate bowel movements, and ease the digestive process. Whole grains like oats or quinoa are also helpful for stabilizing appetite and supporting weight loss. Avoiding processed foods, carbonated beverages, and foods high in sodium can also reduce abdominal bloating and support fat reduction efforts.
3: Is it normal to experience bloating during early stages of weight loss?
Yes, it's common to experience abdominal bloating when starting a new diet or exercise routine. Changes in dietary fiber intake, hydration levels, or food timing can affect digestion and gut bacteria. Some people also notice bloating as their body adjusts to increased protein intake or certain supplements. If symptoms include stomach pain, constipation, or other symptoms that persist, it may be helpful to track meals and seek medical advice to rule out underlying medical conditions.
4: Can bloating make it harder to see belly fat loss?
Bloating can make it difficult to see changes in body shape, especially in the waist and stomach areas. Fluid retention, poor digestion, or intestinal gas can mask actual fat loss by making the abdomen look and feel larger. This is why regular weight tracking, consistent bowel movements, and mindful eating habits are important for evaluating weight loss progress more accurately. Treatments like S6 Body Sculpting can support fat reduction by targeting stubborn areas where bloating and fat often overlap.
5: What are signs that bloating may be caused by an underlying medical condition?
If you experience bloating with other symptoms such as unintentional weight loss, chest pain, difficulty breathing, or frequent abdominal pain, it may be linked to an underlying medical condition. Conditions like liver disease, irritable bowel syndrome, gluten intolerance, or parasitic infection can cause chronic bloating. If over-the-counter remedies or dietary changes do not relieve the bloated stomach, it’s best to seek medical care for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.