Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 15 May 2025
Omega-3 fatty acids are natural helpers when it comes to managing appetite, burning fat, and easing bloating. You’ll find them in fatty fish like salmon, in fish oil supplements, and in plant-based sources like chia seeds and flaxseed oil. These healthy fats do more than support heart health and lower blood pressure—they also help your body balance hunger signals and use fat for fuel. While most people know omega 3s for their role in heart health or reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, there’s more going on behind the scenes. From improving gut health to supporting brain function, omega 3s offer a wide range of benefits that go beyond just one system in the body. Even small shifts, like adding more fish to your meals or taking an omega 3 food supplement, can help reduce bloating and support healthy digestion. In this article, we’ll go through the different ways omega 3s work in your body to support appetite control, fat burn, and better digestion. Keep reading to see how these essential fatty acids fit into a healthy routine, and why they’re worth adding to your day.

Importance of Omega-3 Food Supplement in Controlling Appetite Hormones

Leptin and ghrelin control hunger and fullness
Omega-3 fatty acids help manage hunger by supporting the balance between leptin and ghrelin. Leptin signals when you’re full, while ghrelin triggers hunger. When these two hormones work smoothly, it’s easier to eat in line with your body’s needs. Fatty acids from fish oil, oily fish like salmon, or plant-based foods such as chia seeds support this balance by helping the brain respond better to these signals.
Anti-inflammatory Effects Improve Brain-Hormone Connection
The anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a crucial role in enhancing the brain-hormone connection. Research has shown that omega-3s can significantly reduce inflammation in the brain, leading to improved communication between brain cells and hormones. This improvement can positively impact mental health, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3s support the health of the nervous system, potentially lowering the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. Incorporating fatty fish like salmon and sardines into your diet can provide these essential omega-3s, supporting overall brain-hormone health.
Anti inflammatory effects improve brain-hormone connection
Too much inflammation in the body can affect how well leptin works. Omega 3s reduce inflammation, especially around the brain’s appetite control center. This makes it easier to feel full at the right time. They also help keep ghrelin levels more stable, so hunger doesn’t spike out of nowhere. Clinical trials have shown this benefit in people using omega 3 food supplements regularly.
Daily intake from food or supplements supports results
You don’t need to overhaul your diet. Eating seafood like mackerel or sardines twice a week or taking fish oil pills daily is enough to support this hormone balance. Look for products that contain EPA and DHA, the two active types of omega 3s. These essential nutrients also support heart health, brain function, and may reduce risk factors linked to cardiovascular disease.

Omega-3s Support Fat Burning Through Gene Activation

Fatty acids trigger metabolic changes at the genetic level
Omega-3 fatty acids affect the body’s metabolism in a direct and measurable way. One of their key roles is activating a group of proteins called PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors). Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a crucial omega-3 fatty acid found in fatty fish and dietary supplements, supports these metabolic changes. These proteins act like switches for genes that control how fat is stored and burned. When omega 3s—especially from fish oil supplements or fatty fish—are part of your routine, they help flip these switches and increase the body’s fat-burning response.
This gene activation supports the body’s ability to use fat as a source of energy instead of storing it. By including omega 3 food supplements or increasing fish consumption, you’re giving your body the nutrients it needs to regulate metabolism at the cellular level.
Fatty acids increase brown fat activity
Another way omega 3 fatty acids support fat loss is by encouraging the formation of brown fat. Unlike white fat, which stores energy, brown fat burns calories to produce heat. This type of fat is metabolically active, and omega 3s help convert some white fat into brown fat, especially when supported by cold exposure or exercise.
You’ll find that food sources like salmon, sardines, or plant based sources such as flaxseed oil and chia seeds are effective in supporting this process. Including these in your meals gives your body a natural advantage in managing energy and promoting fat loss without relying on extreme changes or high doses of supplements.
Metabolic rate responds to omega-3 intake
Regular intake of EPA and DHA from fish oil, krill oil, or oily fish helps support a higher metabolic rate. This means the body burns more calories, even while resting. Omega 3s improve thyroid hormone sensitivity, increase mitochondrial activity in cells, and reduce the kind of inflammation that slows metabolism.
Fish oil pills, oil supplements, or eating seafood two to three times a week can all contribute to this effect. While some clinical trials show mixed results on whether omega 3s directly increase metabolism, their influence on fat oxidation, hormone sensitivity, and reduced inflammation points to meaningful support for long-term weight control.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Omega-3 Fatty Acids Improve Gut Health and Reduce Bloating

Healthy fats support the digestive system
Omega-3 fatty acids help maintain a healthy gut by supporting the balance of bacteria in your digestive tract. The human body requires these essential fats for various functions, including gut health. When your gut microbiome is balanced, digestion runs more smoothly, and bloating becomes less frequent. Omega 3s, especially from fish oil supplements or fatty fish like mackerel and salmon, feed beneficial bacteria and help reduce gut-related inflammation.
This support goes beyond digestion. A healthy gut also plays a role in appetite control and nutrient absorption—two things that influence how your body stores and uses energy. Clinical trials continue to explore how omega 3s reduce risk factors related to chronic diseases that start in the gut.
Anti-inflammatory Effects Reduce Digestive Stress
Omega-3 fatty acids are also beneficial in reducing digestive stress, which can lead to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). EPA and DHA, the active forms of omega-3s, have been shown to decrease inflammation in the digestive tract, promoting a healthier gut and alleviating symptoms of digestive stress. This is particularly advantageous for individuals with digestive disorders, as it helps to reduce inflammation and enhance overall digestive health. Incorporating food sources rich in omega-3s, such as chia seeds and flaxseed oil, into your diet can support a healthier digestive system.
Anti inflammatory effects reduce digestive stress
One reason omega-3s are helpful for bloating is their ability to reduce inflammation in the intestines. When the gut lining is inflamed, it can lead to discomfort, irregular digestion, and swelling. Omega 3s calm this response by supporting the body’s immune system and helping cells in the digestive tract function more efficiently.
EPA and DHA from fish oil pills or dietary supplements also help protect the gut barrier, which acts as a filter for harmful substances. Keeping this barrier strong is important for preventing bloating and irritation.
Combining omega-3s with gut-friendly foods
For better results, combine omega-3s with prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, or asparagus. This combination encourages the growth of helpful gut bacteria. Eating seafood two to three times a week or using high-quality oil supplements—such as flaxseed oil or krill oil—gives your body a consistent supply of the fatty acids it needs.
Start with a daily intake of 1,000–2,000mg of omega-3s. This amount supports digestive health, especially when combined with a diet rich in fiber, water, and other nutrients that promote a balanced microbiome.

Omega-3s Reduce Inflammation That Triggers Water Retention
Lower inflammation for less swelling and puffiness
Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce water retention by calming inflammation in the body. When inflammation is high, your tissues can start holding onto fluid. This is often caused by overactive cytokines—proteins that signal the immune system. Too many cytokines can lead to puffiness in your hands, feet, and face. Omega 3s help regulate these signals and bring the body back into balance. Additionally, omega-3s contribute to lowering blood pressure, enhancing cardiovascular health.
By including more omega 3 food supplements or eating fish like salmon or sardines regularly, you support lower cytokine levels, which leads to less fluid buildup. This benefit is especially important for people managing conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or cardiovascular risk, where inflammation is more common.
Omega-3s help your cells hold the right amount of water
Water retention isn’t just about what you drink—it also depends on how your cells manage fluids. Omega-3s help balance electrolytes, including sodium and potassium. These minerals control how much water your cells keep or release. With enough omega 3 intake, your cells can stay hydrated without becoming swollen.
Try eating seafood two to three times a week, or use fish oil capsules daily. Start with 1,000–2,000mg of EPA and DHA combined. This helps maintain healthy fluid balance and reduces the bloating that comes from inflammation or poor electrolyte control.
Stronger cell membranes improve fluid control
Your cell membranes act like gates, controlling what enters and exits. Omega-3s make these membranes stronger and more flexible, which helps them resist inflammatory stress. When cells are healthier, they can respond better to hormonal signals and move fluid properly.
Omega-3s support this by:
• Reducing signals that cause cells to swell
• Helping cells repair faster
• Improving how cells respond to energy demands
By building stronger membranes, omega-3s make it easier for your body to manage bloating and feel lighter overall.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Omega-3s Support Stable Blood Sugar and Fewer Cravings

Fatty acids help reduce blood sugar spikes
Omega-3 fatty acids can help keep your blood sugar levels steady throughout the day. They also help lower triglyceride levels, which is beneficial for heart health. When blood sugar rises and falls too quickly, it often triggers cravings—especially for sweets or processed carbs. Including omega 3s from fish oil, flaxseed oil, or oily fish helps smooth out these spikes by improving how your body responds to insulin.
Research shows that omega 3s may lower post-meal blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, especially in muscle cells. This means your body can use glucose more efficiently, helping you avoid the crashes that lead to snacking.
Less inflammation means better energy use
Chronic inflammation can interfere with how your body processes blood sugar. Omega-3s reduce this inflammation, making it easier for your cells to take in and use glucose as fuel. This creates more stable energy between meals and lowers the urge to snack out of fatigue.
You can start supporting this process by adding omega 3 food supplements to your breakfast or eating fish like mackerel or sardines a few times per week. Including fiber-rich foods like vegetables or oats alongside omega 3s can also improve this effect.
Improved hormone function helps control appetite
Omega-3s also support the hormones that control hunger and satiety, which affects blood sugar indirectly. When your hunger hormones stay balanced, you're less likely to experience strong cravings caused by unstable glucose levels.
Aim for 1,000–2,000mg of EPA and DHA daily from fish oil supplements or natural food sources. Combined with regular meals and a stable eating routine, omega 3s help create a more predictable appetite pattern and reduce sudden food cravings.

Omega-3s Help Maintain Lean Muscle Mass

Fatty acids support muscle growth and recovery
Omega-3 fatty acids do more than support fat loss—they also help your body preserve and build lean muscle. This is especially useful if you're trying to lose weight without losing strength. EPA and DHA, found in fish oil and oily fish like salmon or sardines, support muscle by reducing inflammation after workouts and improving protein use in the body.
Unlike protein alone, omega 3s influence how your muscles respond to training and recovery. This makes it easier to build strength and maintain muscle over time, especially if you’re in a calorie deficit.
Omega-3s reduce muscle breakdown
When you don’t get enough nutrients or go too long without eating, your body can break down muscle for energy. Omega-3s help reduce this breakdown by supporting healthy hormone levels and improving the way cells use fat as fuel. This means your body is more likely to burn fat instead of muscle. Additionally, omega-3s are associated with a decreased risk of chronic diseases.
Including omega 3 food supplements or eating seafood a few times a week helps prevent this muscle loss. It also supports people dealing with chronic diseases like diabetes mellitus, where maintaining muscle is important for long-term health.
Daily intake supports better performance and recovery
You can support muscle function by aiming for 2–3 grams of combined EPA and DHA daily. Spread your intake across meals for better absorption. Whether through fish oil pills, krill oil, or plant based sources like ground flaxseed, these essential nutrients help reduce post-workout soreness and improve energy production.
Keeping your omega 3 intake steady supports stronger, more resilient muscles—without needing extreme changes to your routine.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Omega-3 Intake Supports Long-Term Metabolic Health

Fatty acids help maintain efficient energy use
While omega-3s might not directly speed up your metabolism, they play a steady role in keeping it running smoothly. These fatty acids support processes in the body that influence energy use, such as improving insulin sensitivity and reducing low-grade inflammation that can slow down how efficiently your body burns calories.
By supporting healthy cell function, omega 3s help your metabolism work without unnecessary stress. You’ll also find that they help regulate thyroid hormone activity, which controls how quickly the body uses energy throughout the day.
Omega-3s work through indirect but steady mechanisms
Research doesn’t show dramatic fat-burning effects from omega 3s alone. But consistent intake helps protect against metabolic slowdowns caused by inflammation, poor blood sugar control, or hormonal imbalance. Think of omega-3s as steady support for the systems that manage your energy—not as a quick fix.
To get this benefit, include fish consumption regularly—2 to 3 servings of fatty fish per week is a good target. You can also use oil supplements like fish oil or flaxseed oil if fish isn’t a regular part of your diet. Aim for 1,000–2,000mg of EPA and DHA each day through food or dietary supplements.
These healthy fats support the kind of energy balance your body needs to feel steady, strong, and less likely to store excess fat over time.

Omega-3s Provide Essential Nutrients Often Missing From Modern Diets

Filling nutrient gaps for better health outcomes
Many people don’t meet the recommended dietary allowance for omega-3 fatty acids. That’s a problem, because these fats are considered essential—your body can’t make them, so they must come from food sources or dietary supplements. Low intake can affect more than just appetite or fat metabolism. It can also influence brain function, cardiovascular health, and even skin quality.
Modern diets tend to lack omega 3s due to low fish consumption and overreliance on processed foods. Including oily fish, plant based foods like ground flaxseed and chia seeds, or taking omega 3 food supplements can help correct this imbalance.
Omega-3s support different life stages
Certain groups may benefit even more from omega 3s. For example, pregnant women and breastfeeding women need more omega-3 fatty acids, especially docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), for fetal and infant brain development. Low intake during this time may also increase risk factors for postpartum mood changes or developmental issues.
Older adults may need more omega 3s to support cognitive function and manage inflammation linked to chronic diseases. People following plant based diets can include alpha linolenic acid from canola oil, walnuts, or flaxseed oil, though some may still choose oil supplements to meet their needs.
Omega-3s pair well with other nutrients
Omega-3s don’t work alone. They interact with other nutrients—like vitamin D, magnesium, and antioxidants—to support overall human health. Some studies suggest combining vitamin D with omega 3s may help with mood regulation, immune support, and bone health.
To follow dietary guidelines and support long-term wellness, aim for a variety of omega 3 food sources throughout the week. Eating seafood, using plant oils, and supplementing as needed gives your body a steady supply of nutrients that support more than just metabolism—they help maintain balance across multiple systems.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Dietary Sources and Guidelines
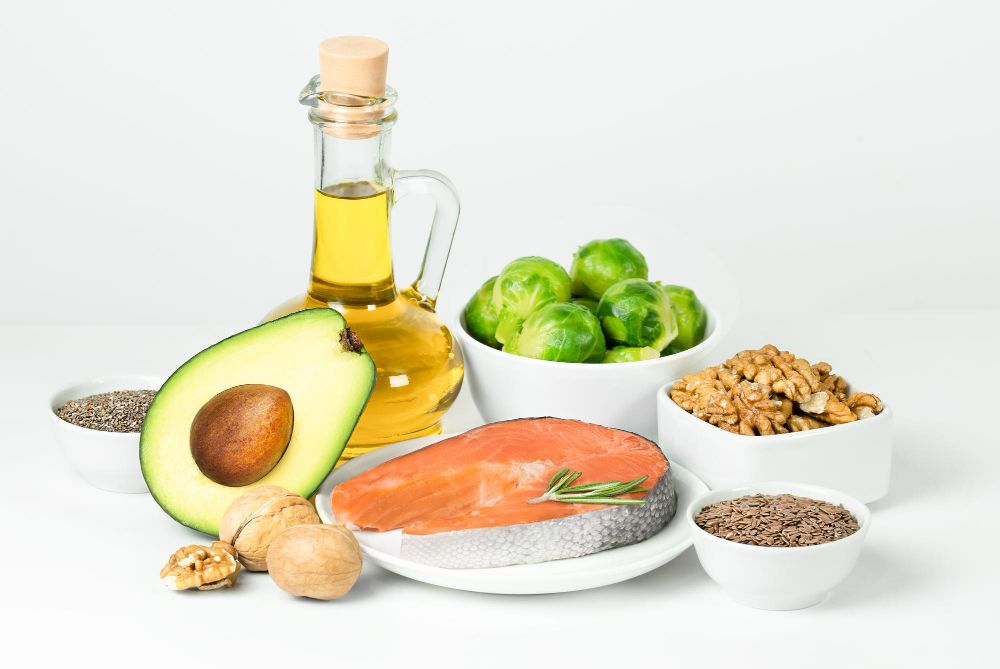

Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that must be obtained through dietary sources or supplements. Ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3s is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Food Sources of Omega-3s
Fatty fish, such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel, are excellent sources of omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA. Other food sources include flaxseed oil, chia seeds, and canola oil. Plant-based sources of omega-3s, such as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), can be found in ground flaxseed, walnuts, and soybeans. To support heart health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases, it is recommended to eat fish at least twice a week, with a serving size of about 8 ounces.
Guidelines for Omega-3 Intake
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is 1.6 grams per day for men and 1.1 grams per day for women. While there is no official RDA for EPA and DHA, most health organizations agree that 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day is sufficient for healthy adults. However, higher amounts may be recommended for certain health conditions, such as heart disease or high triglycerides. The American Heart Association recommends that people with coronary heart disease or heart failure take omega-3 supplements containing EPA and DHA daily. Pregnant women and breastfeeding women may also require higher amounts of omega-3s to support fetal brain development and overall health. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of omega-3 supplementation for individual needs. Additionally, it is crucial to choose high-quality fish oil supplements that are certified by a third-party organization to ensure purity and potency.

Support Fat Loss Further with S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
Combine nutrition and non-invasive technology for better results
While omega 3 food supplements help regulate appetite, support fat metabolism, and reduce bloating internally, combining them with targeted external treatments can take your progress further. One treatment that works well alongside dietary support is the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment, a non-surgical therapy that helps reduce stubborn fat and shape specific body areas.
How the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment works
This treatment uses low-energy bio-laser technology that penetrates deep into the subcutaneous fat layer. It targets stored fat in hard-to-tone areas like the belly, thighs, arms, and lower back. As the laser stimulates fat cells, they begin to break down and release fatty acids, which are then cleared through the lymphatic system.
To support this fat breakdown, the treatment includes vacuum suction massage that speeds up lymphatic drainage and improves your metabolic rate. The laser also promotes collagen production, helping to tighten and firm the skin after fat reduction. Each session focuses on one or more of the seven most common fat-prone areas, including the waist, back, thighs, calves, and buttocks.
Why pair it with omega-3s?
While omega-3 fatty acids—such as those found in fish oil supplements or plant based foods like chia seeds and flaxseed oil—support fat oxidation, hormone balance, and metabolic health, the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment offers a more targeted, external boost. Together, they work to support both systemic and localized fat reduction. Omega-3s improve your internal fat-burning environment, while the treatment speeds up visible changes in specific areas.
This combination is especially helpful for people with sedentary lifestyles, busy schedules, or difficulty seeing results through diet and exercise alone. It supports healthy weight management from both inside and out.
Non-invasive, safe, and comfortable
The S6 treatment is completely non-invasive. There’s no surgery, injections, or medication required. Most people find the sessions relaxing, and there's little to no recovery time needed afterward. You can return to your regular routine right away. The full course typically includes 10 to 12 sessions spaced about a month apart.
If you’re already using omega 3 food supplements, adding this treatment can help you shape the body areas you feel need more attention, while continuing to enjoy the overall health benefits of fatty acids—like reduced bloating, better circulation, and increased fat metabolism.
Book your first consultation today to see how S6 Body Sculpting can enhance your results and support your body goals in a safe, effective way.
New Beauty's S6 Body Sculpting TreatmentBook Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
What is the best time to take omega 3 food supplements for fat metabolism?
The best time to take omega 3 food supplements is with meals, preferably those containing healthy fats, to improve absorption. Taking omega-3s with breakfast or lunch may support steady energy and help regulate appetite during the day. For people using them alongside body contouring treatments or exercise, post-meal consumption helps reduce inflammation and supports recovery.
Are plant based sources of omega 3 as effective as fish oil supplements?
Plant based sources like chia seeds, flaxseed oil, and walnuts contain alpha linolenic acid (ALA), which the body must convert into EPA and DHA—the active forms found in fish oil supplements. The conversion rate is low, so while plant-based foods are still beneficial, people who do not eat fish may need to take algae oil or other EPA/DHA-rich oil supplements to meet the recommended dietary allowance.
Can omega-3 fatty acids help reduce cancer risk?
Some clinical trials and meta analyses suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may support reduced risk of certain cancers, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and endometrial cancer, particularly due to their anti inflammatory effects and immune support. Additionally, omega-3s may have potential protective effects against colorectal cancers. While omega 3s are not a treatment, regular intake as part of a balanced diet may contribute to long-term protection against some health conditions.
Is it safe to combine fish oil supplements with other dietary supplements?
Yes, omega-3s are generally safe to combine with most dietary supplements like vitamin D, magnesium, or probiotics. However, people taking medications for heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes mellitus should check with a healthcare provider before combining fish oil with other nutrients, especially in high doses. Always follow current dietary guidelines when using multiple supplements.
Do omega 3s have an effect on mental health or brain function?
Yes, EPA and DHA are critical for brain function and are linked to reduced symptoms of depression, improved focus, and even reduced risk of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's disease. These polyunsaturated fatty acids support the nervous system and cell communication in the brain, making them valuable for mental health support across all age groups.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.




