Author: Natalie Ng|Updated: 6 May 2025
Some parts of the body are just harder to slim down. You’ve probably noticed it’s not always the same for everyone—some people struggle with belly fat, others with thigh fat, and for many, it's the upper arms or love handles that don’t budge. These stubborn areas hold onto excess fat longer, even when the rest of your body starts to lose weight. This isn’t just about the workouts you do. Fat cells don’t shrink evenly. Where your body stores fat—and how it holds onto it—is affected by hormones, genetics, stress, and your daily habits. So while you can’t target fat loss from just one spot, you can reduce overall body fat with a consistent mix of healthy diet, calorie control, and exercise. Over time, this helps your body burn fat more effectively and improve body composition. If you've been stuck trying to lose belly fat, arm fat, or any other area that’s hardest to lose, you’re not alone. Fat retention in specific body parts is frustrating—but there are reasons behind it, and ways to deal with it. Keep reading—we’ll break down the most stubborn fat areas and show you how to target each one with realistic strategies that work.

Lower Belly Fat: The Infamous Pooch
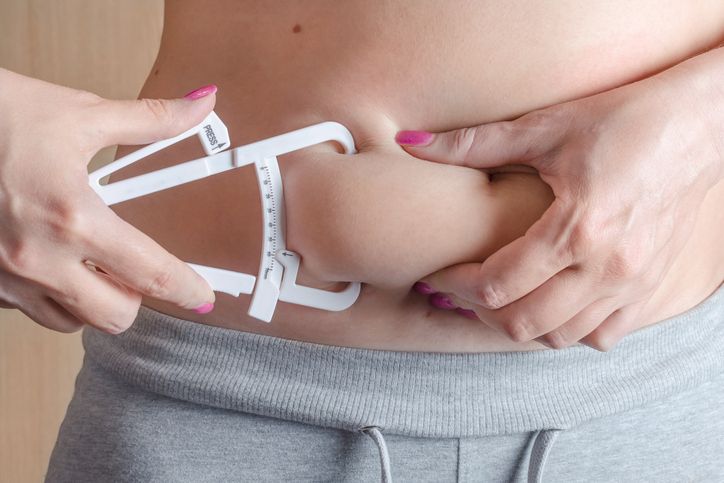
Why It’s So Hard to Lose
Lower belly fat is one of the hardest places to lose fat. The area below your navel is where the body often stores fat for long-term energy use. This fat—mostly subcutaneous and sometimes visceral fat—sticks around because of how the body stores fat and how stubborn fat cells respond to change. For many people, this area is slow to react to weight loss, especially after weight gain or hormonal shifts.
What Causes It
Lower abdominal fat builds up due to several reasons:
• Excess calories: A high intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and poor diet choices increase body fat, especially in the belly.
• Stress and hormones: High cortisol levels from stress promote fat storage in the midsection.
• Lack of sleep: Inconsistent sleep affects how the body stores and burns fat.
• Hormonal changes: Age, menopause, and other hormone-related factors can shift fat distribution to the lower belly.
• Muscle loss: Lower muscle mass means fewer calories burned, slowing down fat burning.
What You Can Do
You can’t target fat loss in one spot only, but you can lose belly fat by lowering overall body fat.
Focus on Fat Loss, Not Just Abs Workouts
Core exercises like planks or crunches build muscle under the fat but won’t remove the fat on top. To reduce lower belly fat, aim to:
• Burn more calories with regular cardio routines (like walking, cycling, or swimming).
• Build muscle through strength training, especially with large muscle groups.
• Follow a calorie controlled diet with lean proteins, healthy fats, and fewer processed foods.
• Stay consistent with habits that support fat burning and reduce fat retention.
Reducing abdominal fat takes time. The key is to focus on your whole body’s fat loss and give your body the chance to change where it stores and uses energy. Lower belly fat might be the last to go, but with the right mix of diet and exercise, it does go.

Inner Thigh Fat: The Silent Struggler
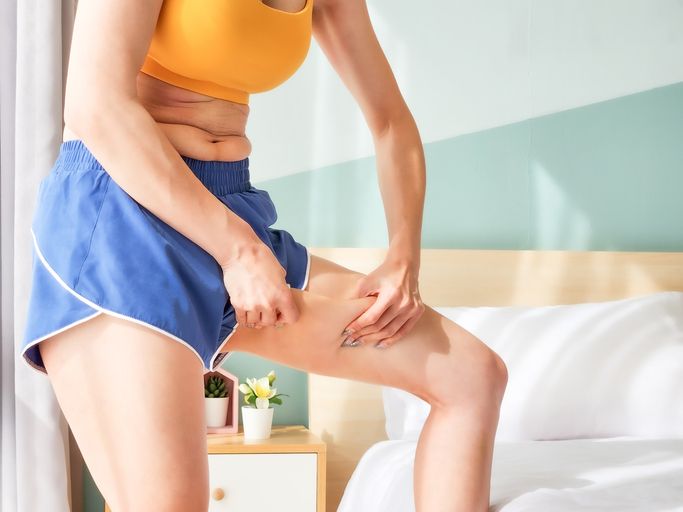

Why It’s One of the Hardest Places to Lose Fat
Inner thigh fat is stubborn because the fat cells here are often less responsive to fat-burning signals. This area stores subcutaneous fat, which is harder to break down compared to visceral fat. For people with a pear shaped body, the body stores fat around the hips and thighs more easily—and holds onto it longer during weight loss.
What Leads to Fat Buildup
A few key reasons inner thighs accumulate fat:
• Hormonal influences: Estrogen promotes fat storage in the lower body, especially in women.
• Lack of movement: Sitting for long hours without lower body activation limits fat burning in the area.
• Excess calories and poor diet increase overall body fat, including the thighs.
• Low muscle mass in the legs makes it harder for the body to burn fat in this zone.
Why Spot Reduction Doesn’t Work
Leg lifts or inner thigh squeezes may strengthen those muscles, but they won’t directly reduce thigh fat. Fat loss happens across the body, and the inner thigh just happens to be slower to respond. It’s not about how many thigh-targeted workouts you do—fat loss depends on your body’s overall energy balance.
What Helps Burn Inner Thigh Fat
Strengthen and Stimulate Large Muscle Groups
To target this area indirectly:
• Use compound leg exercises like squats, lunges, and step-ups to increase muscle mass and fat burning.
• Add cardio—especially low-impact options like incline walking, cycling, or swimming—that keeps the legs moving and encourages fat loss.
• Eat a balanced diet with lean meats, fewer processed foods, and enough protein to support muscle growth.
• Stay in a calorie deficit so the body uses stored fat as energy.
Inner thigh fat may be slow to go, but it does respond when your routine stays focused on whole-body fat loss, not just isolated leg movements.
Read More
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Love Handles: Tackling Side Fat
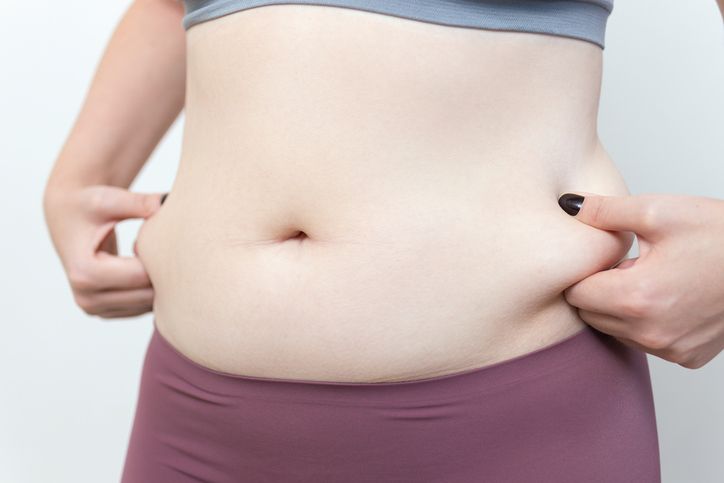

Why Love Handles Are Hard to Lose
Love handles sit right above your hips and are one of the most stubborn fat areas to reduce. They don’t just appear from eating too much—they’re the result of how the body stores fat. Fat cells in this zone are slower to release energy, which makes this one of the hardest places to lose fat. On top of that, hormones, stress, and body fat distribution patterns often direct excess fat cells to the waistline.
Common Causes of Side Fat
These bulges can build up due to a combination of factors:
• Genetics: Some people naturally accumulate fat around the waist more than others.
• Hormonal changes: Imbalances, especially in insulin and cortisol, can promote fat storage here.
• Processed foods and sugary drinks: These increase overall calorie intake and spike blood sugar, which promotes fat retention.
• Lack of muscle mass: If you’re not working large muscle groups, you burn fewer calories throughout the day.
• Chronic stress or poor sleep: These influence fat storage patterns, especially around the abdomen.
What Actually Works to Reduce Love Handles
Train Smarter, Not Just Harder
You can’t spot-reduce fat from your sides, but a combined strategy helps shrink the area over time:
• Incorporate HIIT: High-Intensity Interval Training increases energy use and encourages fat burning across the whole body.
• Strengthen the obliques: Exercises like Russian twists, side planks, and woodchoppers tone the muscles underneath.
• Full-body strength training: This builds muscle, boosts metabolism, and improves how your body stores and uses energy.
• Improve your diet: Avoid excess calories from processed foods. Choose whole foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
Eat With a Purpose
• Create a calorie deficit by eating fewer calories than you burn—around 500 per day for steady fat loss.
• Prioritize protein to preserve muscle mass and feel full longer.
• Control portions and sugar intake to prevent fat storage spikes.
• Limit alcohol, which contributes to excess fat and slows fat burning.
Love handles are stubborn, but they’re not permanent. A clear, consistent approach helps the body reduce stored fat over time—including the fat that sits along your waistline.

Upper Arm Fat: Conquering the Wing Zone
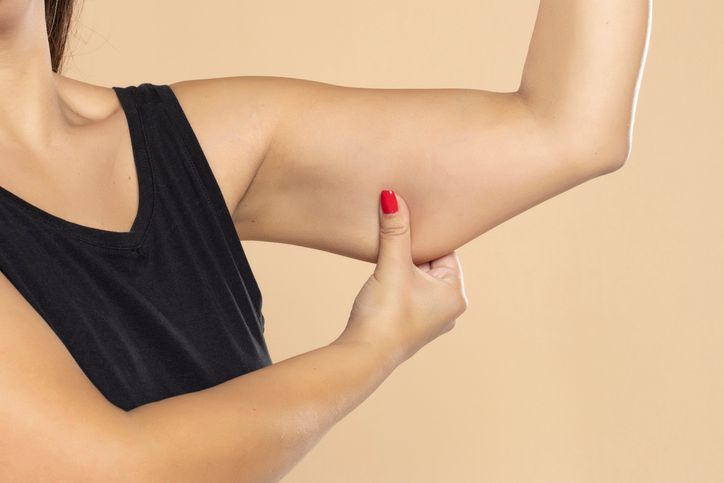
Why Upper Arm Fat Sticks Around
Upper arms—especially the area around the triceps—are a common place for fat to settle and one of the hardest places to lose fat. This is where the body stores excess fat cells that are slow to shrink, even during weight loss. Age, hormonal changes, and low muscle activity in this area all contribute to stubborn arm fat, especially if muscle mass has declined over time.
What Causes Fat to Build Up Here
Several factors lead to excess fat in the upper arms:
• Hormonal shifts, especially in estrogen or testosterone, can influence fat storage in the arms.
• Low muscle activity—the upper arms don’t get much stimulation in daily movement, which slows fat burning.
• Aging reduces muscle tone and increases the body’s tendency to store subcutaneous fat in the upper body.
• High-calorie diets and lack of strength training can lead to sagging skin and fat retention in this area.
How to Reduce Stubborn Arm Fat
Train the Full Body While Focusing on Strength
• Use compound exercises like push-ups, bench presses, and overhead presses. These build muscle in the upper body and increase calorie burn.
• Add triceps-specific moves like dips, kickbacks, triceps extensions, and diamond push-ups to target tone.
• Include HIIT workouts a few times per week to encourage overall body fat loss and keep metabolism high.
• Don’t skip large muscle group exercises—building total muscle helps your body burn more calories at rest.
Make Diet Work for Fat Loss
• Create a calorie deficit through a balanced, calorie controlled diet with fewer processed foods.
• Increase protein intake to preserve muscle while losing fat.
• Limit sugary drinks and snacks, which contribute to fat storage, especially in areas like the upper arms.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Double Chin: Targeting Facial Fat
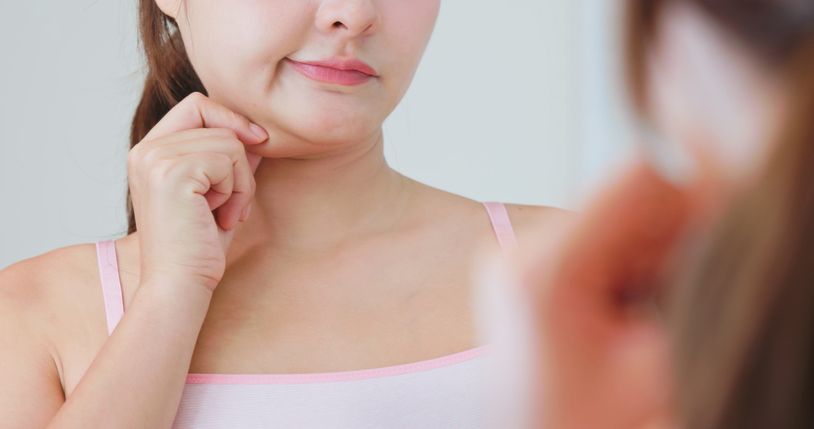

Why Fat Accumulates Under the Chin
A double chin forms when the body stores excess fat below the jawline. This area can hold both subcutaneous fat and, in some cases, deeper fat around the neck. It's one of the most visible places where fat collects, and it tends to be hard to lose because the muscles in this area are small and not often engaged.
What Triggers a Double Chin
Several factors contribute to fat accumulation under the chin:
• Genetic predisposition plays a major role in how the body stores facial fat.
• A calorie surplus and poor diet choices increase overall body fat, including in the face and neck.
• Aging and decreased skin elasticity can make fat under the chin more noticeable.
• Poor posture weakens the muscles in the neck, leading to sagging skin and deeper fat folds.
• Fluid retention from high sodium intake can increase puffiness and make fat more prominent.
What Actually Helps
Facial Muscle Exercises
These won’t burn fat directly, but they can help improve tone and definition under the chin:
• Tongue press: push your tongue against the roof of your mouth while looking up for 10 seconds.
• Kiss reach: pucker your lips and extend them upwards as if you’re kissing the ceiling.
• Neck rolls: slowly rotate your head in circular motions to stretch and engage neck muscles.
• Fish face: suck in your cheeks and hold while tilting your head back.
Diet and Hydration Tips
• Cut back on sodium to reduce puffiness and bloating in the face.
• Drink more water to flush out excess fluids and support healthy fat metabolism.
• Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables to manage calorie intake.
• Avoid processed foods and sugary snacks that promote fat storage.
Posture Habits That Help
Keeping your head level and shoulders back helps reduce pressure on the neck and jaw. Poor posture contributes to sagging skin and muscle weakness, which can exaggerate the appearance of a double chin over time.

Back Fat: Eliminating the Bra Bulge
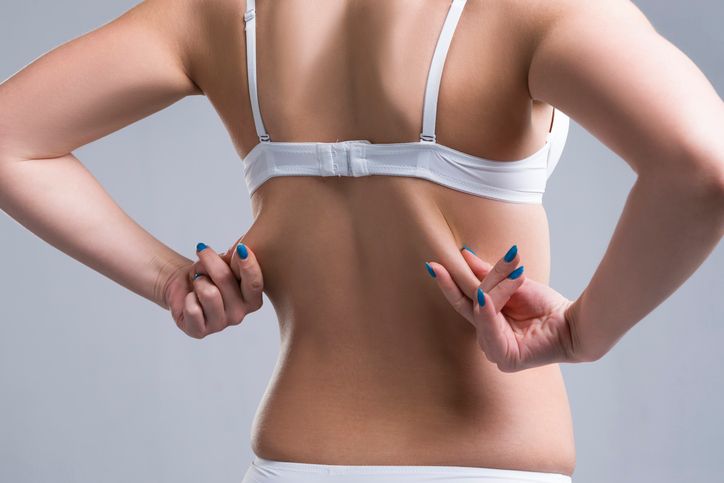

Why Back Fat Is Hard to Lose
Back fat—especially the area around the bra line—is one of the hardest places to lose fat. This region tends to hold subcutaneous fat that doesn’t respond quickly to weight loss. Since back muscles aren’t usually activated during everyday movements, fat in this area stays longer unless you target it through both exercise and dietary changes.
Common Causes of Upper Back Fat
• Fat retention in the upper torso often increases with age, particularly due to hormonal changes.
• A sedentary lifestyle limits back muscle use and contributes to fat storage.
• Poor posture weakens back muscles and exaggerates the appearance of bulging in this area.
• Wearing tight or poorly fitted undergarments can press into soft areas and make fat rolls more visible.
• Diets high in processed foods and excess calories lead to overall weight gain, including in the back.
How to Reduce Back Fat
Strengthen the Upper and Middle Back
• Use compound exercises like rows, lat pulldowns, and reverse flyes to build muscle in the back.
• Add resistance band pulls and back extensions to activate deeper stabilizing muscles.
• Aim to work these muscles at least two to three times a week as part of your routine.
• Improving back muscle strength helps create a more toned appearance and supports better posture.
Support With Consistent Cardio
• Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate cardio weekly to burn overall body fat.
• Include upper-body-friendly cardio like rowing or swimming to keep the back muscles active.
• Walking on an incline or hiking also engages the back more than flat-surface cardio.
Adjust Your Posture
• Maintain a straight spine and relaxed shoulders when sitting or standing.
• Poor posture contributes to muscle weakening and increased fat folds in the back.
• Practicing posture-conscious activities like yoga or Pilates can help reduce the appearance of bra bulge over time.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Hip Fat: Addressing Saddlebags
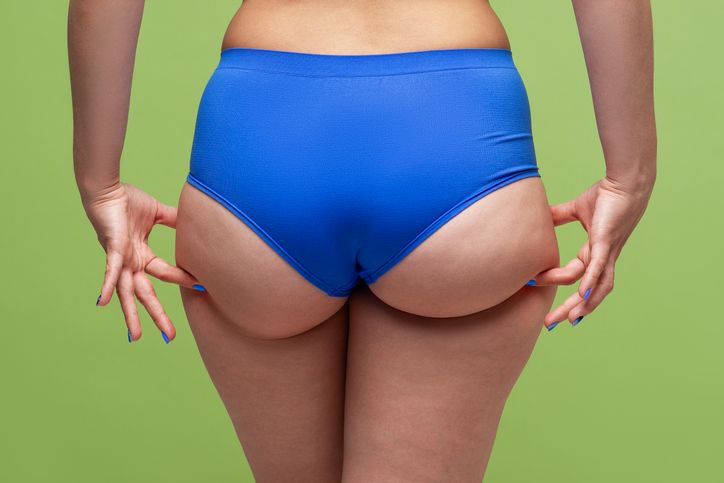

Why Hip Fat Is So Persistent
Fat around the outer hips, often called saddlebags, builds up just below the hip bones and is especially common in people with a pear shaped body. This is one of the hardest places to lose fat because the body tends to store fat here for long-term use. These fat cells are often more resistant to shrinking, even during overall fat loss.
What Causes Fat to Collect in the Hips
• Hormonal patterns, especially in women, encourage fat storage in the lower body.
• Genetics influence how your body distributes and stores fat, especially around the hips.
• Lack of lower body strength training reduces muscle mass, making it harder to burn fat in this area.
• Diets high in excess calories and processed foods increase total body fat, which shows up in areas like the hips.
• A sedentary lifestyle slows down fat burning, especially in areas that don't get much movement.
How to Tackle Saddlebags
Build Lower Body Strength
• Use compound movements like squats, lunges, and step-ups to activate the hip and thigh muscles.
• Add lateral exercises like side lunges and hip abductions to directly engage the outer hip area.
• Perform strength training at least three times a week to build muscle and improve fat burning.
Boost Calorie Burn With Cardio
• Incorporate cardio activities like running, stair climbing, or jump rope to burn more calories.
• Mix in HIIT sessions to elevate your heart rate and support fat loss more efficiently.
• Stay active throughout the day—walking, taking stairs, and even standing can help shift how the body stores fat.
Support Fat Loss With Diet
• Maintain a consistent calorie deficit by eating fewer calories than your body burns.
• Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support energy and reduce excess fat cells.
• Avoid processed snacks and sugary drinks that promote fat storage and make fat loss harder.

Knee Fat: Dealing With Cankles
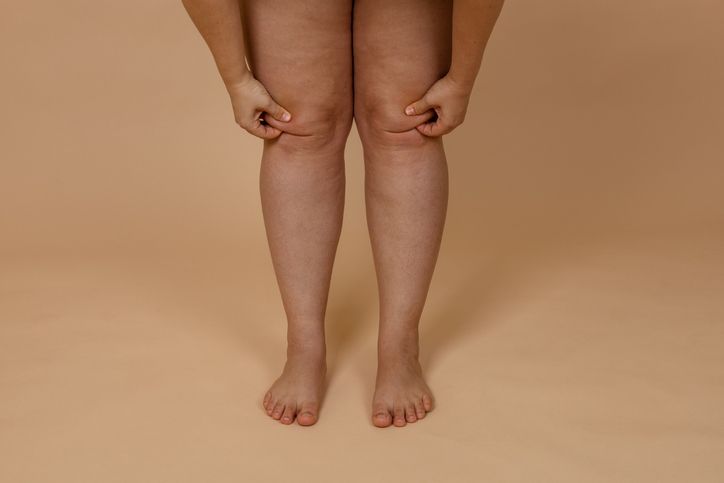
Why Knee and Lower Leg Fat Is Stubborn
Knee fat and the appearance of cankles—where the calf and ankle seem to blend without definition—are often overlooked but hard to change. This area holds onto subcutaneous fat and can also show signs of fluid retention, making the legs look bulkier than they are. Because the muscles around the knees and ankles are smaller, they don’t naturally burn much fat unless intentionally activated.
What Leads to Fat Around the Knees
• Excess calorie intake leads to fat storage in multiple areas, including the lower body.
• Poor circulation or long periods of sitting can cause fluid to accumulate in the legs.
• A high sodium diet increases water retention, making the lower legs look swollen.
• Hormonal imbalances can promote fat storage in the lower body.
• Lack of lower leg muscle engagement reduces the body’s ability to burn fat in this region.
Strategies to Reduce Knee and Ankle Fat
Strengthen the Muscles Around the Knee
• Use exercises like squats, lunges, and step-ups to target the muscles above and around the knee.
• Include calf raises and ankle rotations to shape the lower leg and improve definition.
• Step aerobics or incline walking also help strengthen this region while supporting fat loss.
• Stretch and mobilize regularly to prevent tightness and promote better movement patterns.
Support Fat Reduction With Full-Body Workouts
• Knee fat won't go away with isolated leg exercises alone. Focus on total body fat loss through regular cardio and strength training.
• Choose low-impact activities like cycling, swimming, or walking that reduce joint strain while supporting fat burning.
• Maintain a consistent workout schedule, aiming for at least 150 minutes of activity per week.
Reduce Fluid Retention
• Lower your sodium intake to prevent bloating in the legs.
• Drink more water to support healthy circulation and prevent fluid buildup.
• Keep your legs moving throughout the day—stand up, stretch, or walk every hour.
• Elevate your feet when possible to help with blood flow and fluid distribution.
Book Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

Upper Back Fat: Fighting the Buffalo Hump
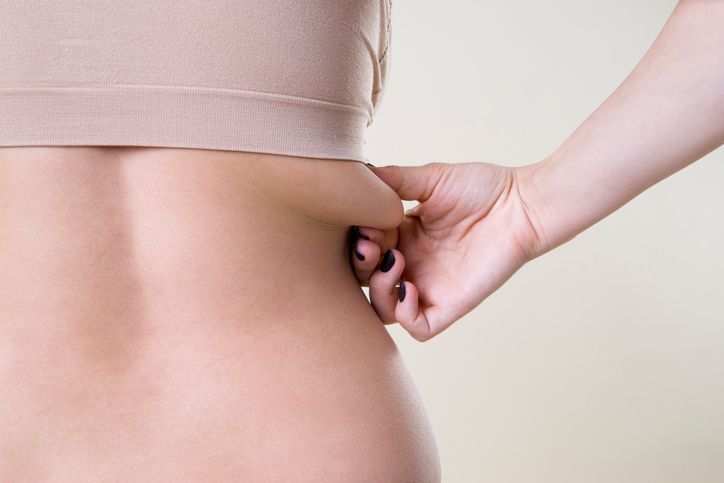

Why Upper Back Fat Builds Up
Fat at the top of the back, sometimes called a buffalo hump, tends to develop between the shoulders and the base of the neck. This is one of the most stubborn fat areas due to how the body stores fat and how rarely this region is actively trained. It often becomes more noticeable with age or after weight gain, and it may also be linked to posture or hormone-related issues.
What Causes Fat to Accumulate in the Upper Back
• Poor posture weakens the muscles in the upper back, making fat deposits more visible.
• Sedentary routines and long hours sitting or hunched over reduce back muscle use.
• Hormonal changes, such as those caused by cortisol or medications like steroids, can promote fat storage in this area.
• High levels of body fat in general will lead to more noticeable fat around the shoulders and neck.
• Genetic factors also play a role in how the body stores fat in the upper back region.
How to Reduce Upper Back Fat
Build Upper Back Strength
• Exercises like rows, pull-ups, and lat pulldowns help tone and strengthen the muscles in this zone.
• Face pulls and reverse flyes also target smaller upper-back muscles for better definition.
• Aim to train your upper back at least twice a week, focusing on proper form and full range of motion.
• Strengthening this area improves posture and helps reduce the appearance of bulges.
Include Upper-Body Cardio Movements
• Choose activities that involve the arms and shoulders—like swimming or rowing—to engage the upper back.
• Add full-body cardio workouts, such as jump rope or shadow boxing, to promote overall fat burning.
• Mix in moderate-intensity sessions with bursts of high-intensity intervals to raise your metabolism.
Check Your Posture Daily
• Sit and stand with your spine straight, shoulders down and back, and chin level.
• Avoid slouching or leaning forward, especially during long hours at a desk.
• Practice posture exercises or stretching routines to improve muscle alignment.
Consult a Specialist if Needed
• If upper back fat is sudden or severe, consider checking with a healthcare provider to rule out any hormonal or medication-related causes.
Fat in the upper back doesn’t respond to quick fixes. With consistent training, better posture, and full-body fat loss efforts, this area will gradually become leaner and more defined.

Chest Fat: Mastering Moobs and Bra Fat
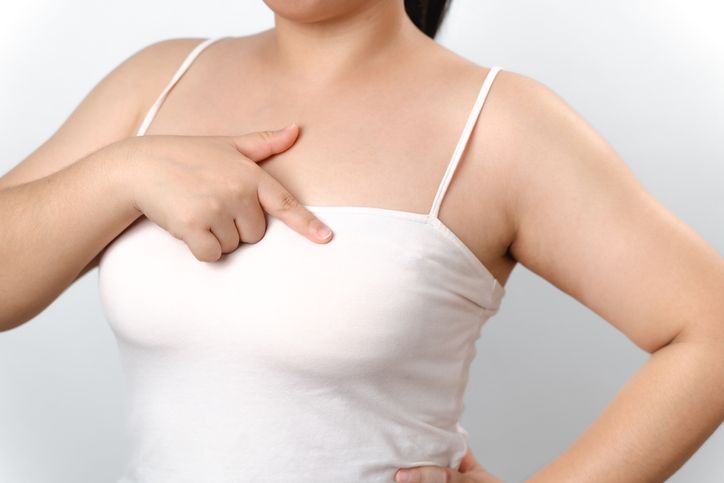

Why Chest Fat Is Hard to Lose
Chest fat can be one of the hardest places to lose fat for both men and women. In men, excess fat in this area is often referred to as "moobs," while women may notice bulging around the bra line. This fat can be a mix of subcutaneous fat and, in some cases, excess glandular tissue. It's stubborn because of hormonal influences and how the body stores fat based on genetics and overall body composition.
What Causes Chest Fat
• Hormonal changes, such as high estrogen or low testosterone, can lead to fat buildup in the chest.
• Genetics determine how your body distributes fat, including whether chest fat is likely to form.
• A high-calorie diet combined with lack of physical activity increases overall fat, including in the chest.
• Weak chest muscles make fat in the area more noticeable.
• Aging slows metabolism and may lead to fat gain in areas like the chest.
How to Reduce Chest Fat
Train the Chest Muscles
• Perform push-ups, chest presses, and dumbbell flyes to build muscle beneath the fat.
• Use both flat and incline movements to target the upper and lower parts of the chest.
• Incorporate compound lifts like bench presses and cable crossovers to increase strength and shape.
• Work your chest two to three times a week, focusing on proper form and moderate weight with higher reps.
Include Cardiovascular Exercise
• Add consistent cardio to help reduce overall body fat.
• Aim for 30–45 minutes of activity like swimming, brisk walking, or cycling, four to five times per week.
• Mix steady-state cardio with high-intensity intervals to promote fat burning.
Improve Your Diet to Support Fat Loss
• Maintain a calorie deficit of around 500 calories below maintenance to promote fat loss.
• Focus on lean proteins, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
• Cut down on processed foods and refined sugars that promote fat storage.
• Track your daily intake to stay within your calorie goal while meeting your protein needs.
Balance Hormones Naturally
• Get regular sleep, manage stress, and avoid excessive alcohol, which can disrupt hormone levels.
• If needed, consult a doctor for hormone testing to rule out any imbalances that could affect fat storage.

Boost Results with New Beauty’s S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
Some fat just refuses to go, no matter how clean you eat or how consistent your workouts are. Areas like the belly, thighs, upper arms, and back hold onto stubborn fat cells that resist change—even when you’re losing weight elsewhere. That’s where treatments like the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment come in.
This non-invasive treatment is designed to support fat loss in the hardest places to lose fat, especially for people who’ve hit a plateau in their weight loss journey. It doesn’t replace a healthy lifestyle, but it can help enhance your results by directly targeting areas where the body tends to store fat the longest.
How the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment Works
S6 uses a low-energy bio-laser that penetrates subcutaneous fat layers—the fat that sits just under the skin. This laser energy encourages fat cells to release stored fatty acids, which your body then clears through the lymphatic system. At the same time, a built-in vacuum suction massage boosts circulation and metabolic rate in the treatment area.
What makes S6 unique is that it doesn't just reduce fat—it also stimulates collagen production, helping to tighten skin in areas that might otherwise experience loose skin after fat reduction. This dual approach makes it especially effective for people with stubborn belly fat, thigh fat, arm fat, or back fat.
Key Benefits of the S6 Treatment
• Targets stubborn fat areas like the belly, thighs, waist, arms, and calves—some of the hardest to lose.
• Non-surgical and non-invasive, with no downtime, injections, or medication.
• Enhances metabolism to help burn fat faster and support overall fat loss.
• Supports skin firmness, reducing the risk of sagging skin after fat loss.
• Customizable treatment plans based on body shape and fat distribution.
Whether you're struggling with stubborn arm fat, lower belly fat, or hip fat that won’t budge, the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment offers a supportive, no-recovery option to accelerate your fat reduction goals.
Book your S6 Body Sculpting session today and start targeting the fat your body won’t let go of.
New Beauty's S6 Body Sculpting TreatmentBook Now to Experience
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ
Can Hormone Imbalances Affect Where My Body Stores Stubborn Fat?
Hormones substantially influence where your body stores fat, with different hormonal imbalances causing distinct patterns of fat distribution. High cortisol levels can lead to increased belly fat, while estrogen dominance often results in fat accumulation in hips and thighs. Your thyroid hormones affect overall fat storage, and insulin resistance typically causes visceral fat storage around organs. Testosterone levels can also impact fat distribution patterns.
Does Genetics Play a Role in Which Body Parts Accumulate Fat?
Your genetic makeup substantially influences where your body stores fat, as inherited DNA patterns affect fat cell distribution and metabolic tendencies. You'll notice these genetic predispositions through your body's natural fat storage patterns, which often mirror those of your parents or close relatives. While you can't change your genes, you can work with your natural body type through targeted exercise and nutrition to manage fat distribution more effectively.
Will Drinking More Water Help Reduce Fat in Specific Areas?
While drinking water is important for overall health and weight management, it won't specifically target fat loss in particular areas of your body. You can't spot-reduce fat through water consumption, as your body follows its own genetically predetermined pattern when losing fat. However, staying properly hydrated helps optimize your metabolism, reduces water retention, supports proper digestion, and can help you feel fuller, contributing to overall fat loss.
At What Age Does Losing Fat Become Significantly More Difficult?
Your body's fat-burning efficiency typically begins to decline in your 30s. You'll notice significant changes between ages 40-50 when your metabolism naturally slows by 2-4% per decade, largely due to decreasing muscle mass and hormonal shifts. After 50, you'll need to work harder to maintain your body composition, as your body becomes more resistant to fat loss.
Can Certain Medications Cause Fat Accumulation in Specific Body Areas?
Yes, certain medications can cause localized fat accumulation in specific areas of your body. Corticosteroids, for example, often lead to fat deposits in your face, neck, and abdomen, while some antidepressants and antipsychotics can trigger overall weight gain with particular emphasis on abdominal fat. Hormone-based medications, including birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, may cause fat to accumulate in your hips, thighs, and breasts.
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.




