
Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Author: Natalie Ng|1 April 2025
If your hair is thinning, there’s usually more than one reason behind it. Genetics, hormones, stress, and even your diet can all play a role. Some people have hereditary hair loss, while others lose hair due to medical conditions, medications, or harsh hair products. Hormonal changes from birth control pills, pregnancy, or thyroid disease can affect hair growth. Conditions like alopecia areata or androgenic alopecia may also lead to noticeable hair loss. Even everyday habits like heat styling or chemical treatments can weaken hair follicles. The sooner hair loss is diagnosed, the better your chances of slowing it down and regrowing hair. In this article, we’ll go over the hidden causes of hair thinning and what you can do about it.

1
Genetic Predisposition and Hereditary Factors

Genetics
Family History


2
Hormonal Imbalances and Endocrine Disorders

Thyroid Issues
Androgens and Hair Follicle Sensitivity
Hormonal Changes in Women
Stress Hormones

3
Nutritional Deficiencies and Diet
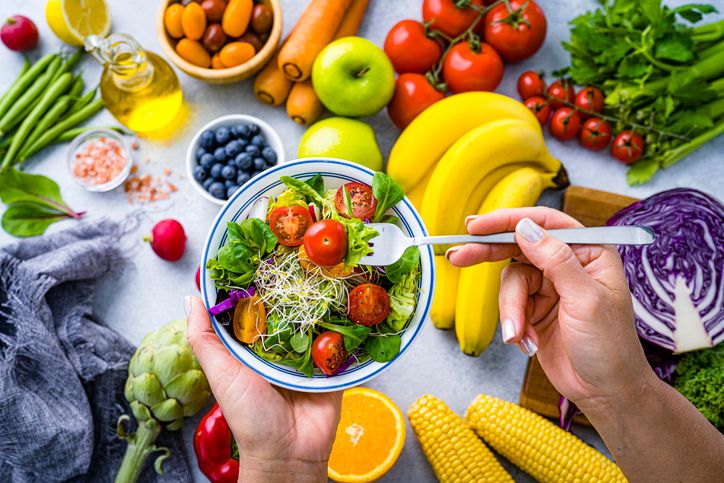

Key Nutrients for Healthy Hair
Lack Of Protein
Poor Absorption


4
Medications and Medical Treatments

Medications That Can Cause Hair Thinning

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

5
Stress-Related Hair Loss

Types of Stress-Related Hair Loss


6
Age-Related Changes in Hair Growth

How Aging Affects Hair Growth
Read More

7
Autoimmune Conditions
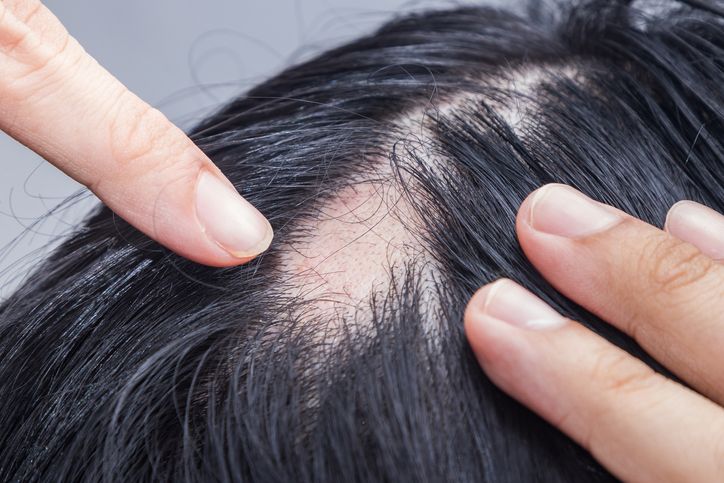
Common Autoimmune Conditions That Cause Hair Loss


8
Poor Hair Care Practices
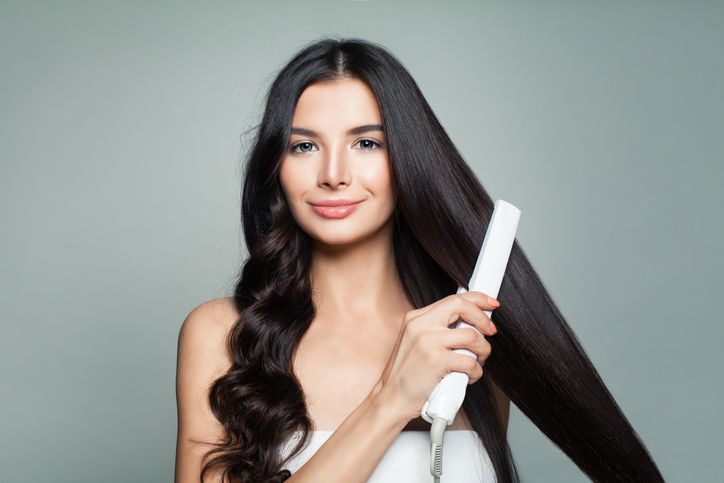

Heat Damage
Chemical Treatments

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date

9
Scalp Conditions and Infections
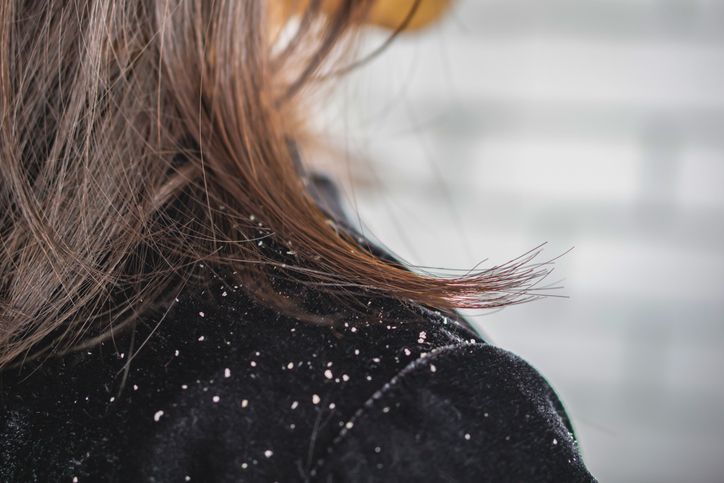

Common Scalp Infections That Cause Hair Loss


10
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment: A Solution for Thinning Hair
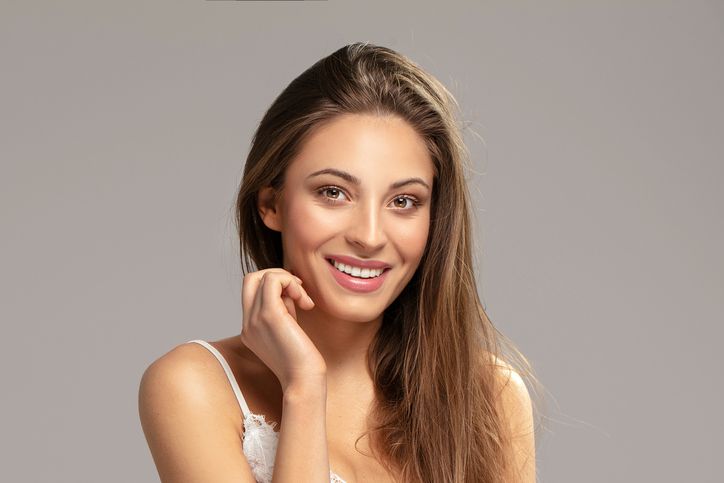

How Does the F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment Work?
Benefits of F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
Who Can Benefit from This Treatment?
FAQ
Can Wearing Hats or Helmets Regularly Cause Permanent Hair Thinning?
While regular hat or helmet use alone won't cause permanent hair loss, certain wearing habits can contribute to traction alopecia, a reversible condition caused by constant tension on hair follicles. You're at higher risk if you wear tight-fitting headgear for extended periods, especially when combined with damp conditions or poor hygiene. Early intervention and proper helmet fit can prevent long-term damage to your follicles.
Does Frequent Swimming in Chlorinated Pools Affect Hair Thickness?
While chlorine exposure won't directly cause hair loss, studies show that 85% of regular swimmers experience increased hair brittleness and breakage. You'll notice your hair becoming more fragile and prone to snapping, especially if it's chemically treated or fine. The chlorine strips your hair's natural oils and damages the protective cuticle layer, leading to increased porosity and breakage that can mimic thinning, though it's not actual follicle-level hair loss.
How Long After Pregnancy Does Postpartum Hair Loss Typically Last?
Your postpartum hair loss typically begins around 2.9 months after giving birth, reaches its peak at 5.1 months, and usually resolves by 8.1 months. While most women experience improvement within a year, coinciding with their baby's first birthday, some cases can extend up to 15 months. If you're experiencing shedding beyond 15 months, it's important to consult a healthcare provider, as this may indicate underlying issues like thyroid imbalances or nutrient deficiencies.
Can Using Dry Shampoo Too Often Lead to Hair Thinning?
Yes, excessive dry shampoo use can contribute to hair thinning through several mechanisms. When you use dry shampoo too frequently, it creates buildup that clogs hair follicles, potentially inhibiting new growth and trapping bacteria that cause inflammation. Additionally, many dry shampoos contain alcohol, which can dry out your scalp and lead to brittleness and breakage. To protect your hair, you shouldn't use dry shampoo more than 1-2 times per week.
Does Sleeping With Wet Hair Contribute to Hair Loss?
While sleeping with wet hair doesn't directly cause permanent hair loss, it can contribute to increased breakage and temporary thinning. Your wet hair is more fragile and prone to mechanical damage from friction against pillows, while prolonged scalp moisture may foster fungal growth that affects follicle health. Additionally, repeated swelling and contracting of wet hair strands can weaken their structure through hygral fatigue, leading to increased breakage.

Book Now to Experience
F8 Hair Regrowth Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Recommended Articles
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2026. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.




