Hair Regrowth Treatments
Patchy Hair Loss and Thinning Explained: 7 Causes, Symptoms, and Hair Regrowth Treatments
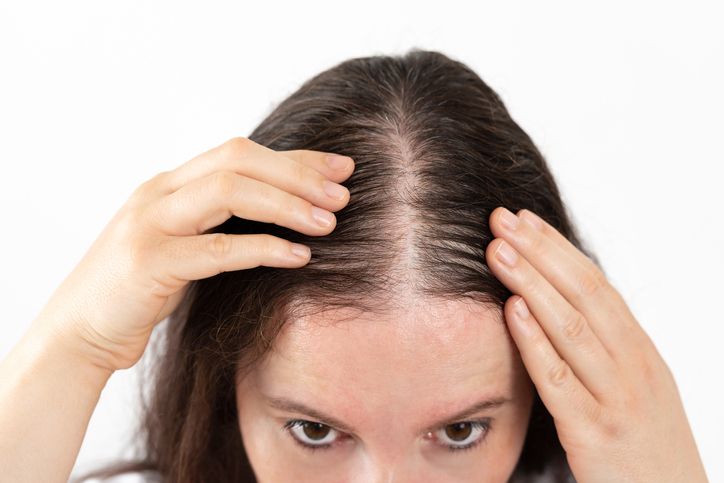
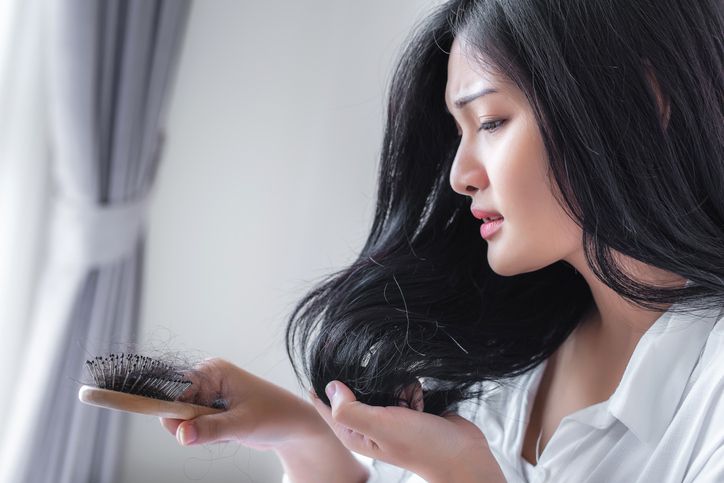
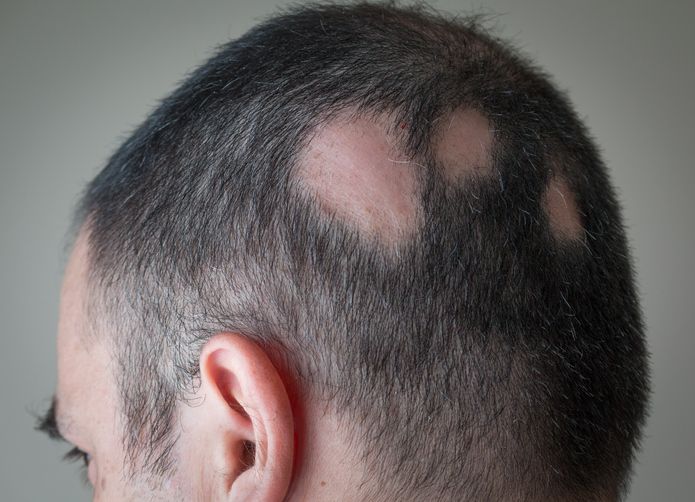
You might notice small bald patches, short broken hairs, or sections where your hair looks thinner. Patchy hair loss appears in different ways depending on the cause. Some people see clear bald spots on the scalp or body. Others experience overall hair thinning or sudden shedding. These changes often reflect a shift in how your hair follicles function or how your immune system is reacting. Alopecia areata is a common reason behind patchy areas. It happens when immune cells attack the follicles, leading to smooth bald spots. Hormonal changes linked to conditions like androgenetic alopecia, thyroid disease, or female pattern baldness also affect the normal hair cycle. Scalp diseases such as fungal infections, local inflammation, or other chronic conditions can cause hair to fall out. Some people lose hair due to emotional stress, certain medications, or nutrient deficiencies that affect iron or vitamin D levels. Hair typically falls when follicles are damaged or inactive. In some cases, hair regrows. In others, bald patches may spread or become more noticeable. Whether it’s related to severe alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, or slow regrowth, different causes lead to different outcomes. The sections below break down the most common causes of patchy hair and explain the treatments that can help restore balance.
Hair Falling Out After Pregnancy? 10 Nutrients That Help Hair Grow Back Stronger
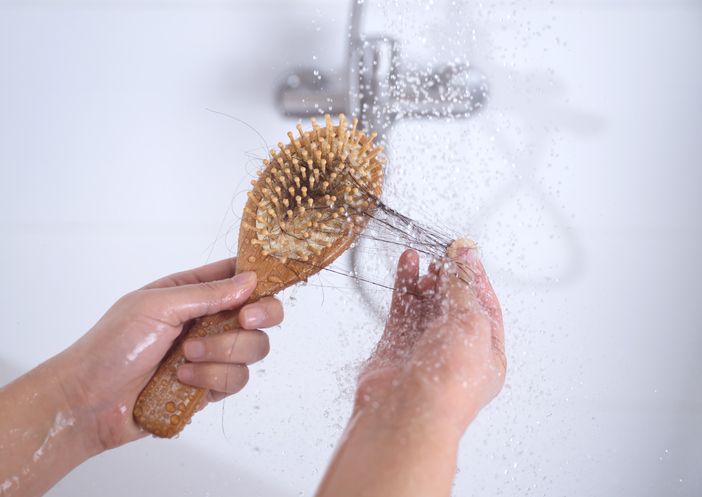
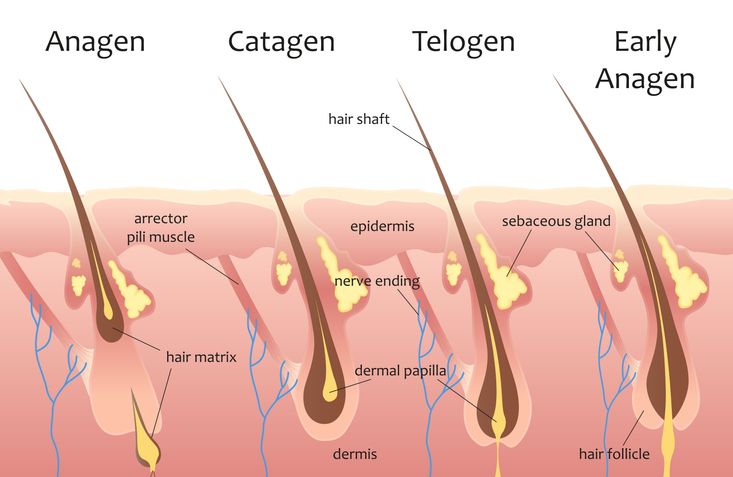
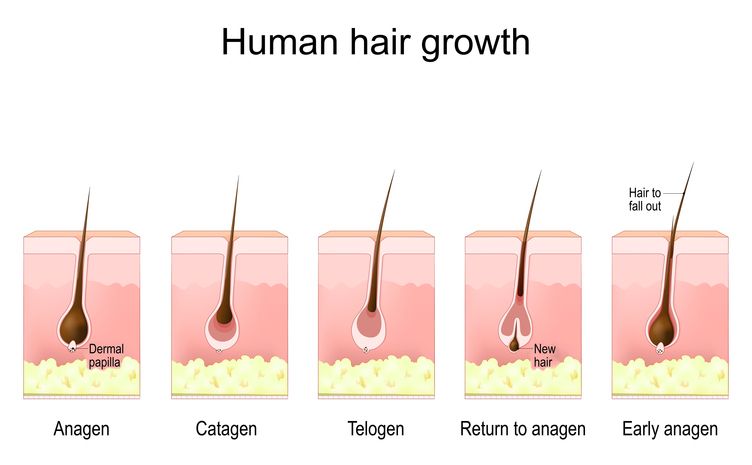
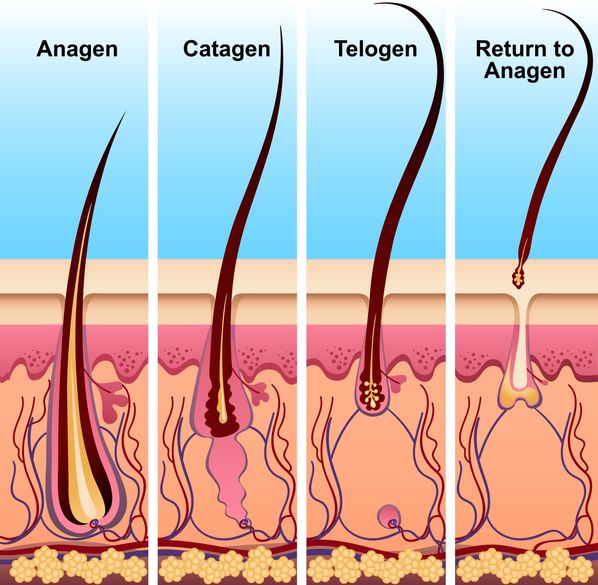
Hair falling out after pregnancy is something most women notice in the first few months after giving birth. It’s usually part of a normal hair growth cycle, but that doesn’t make it feel any less alarming—especially when you're seeing more hair in the shower drain or on your brush than usual. This type of increased hair loss, known as postpartum hair loss or telogen effluvium, happens as pregnancy hormones drop and hair shifts from the growing phase (anagen) to the resting phase (telogen). During pregnancy, high hormone levels often keep many hairs in the growing phase longer than usual, which makes your hair appear fuller. But once those hormones level out after delivery, many hairs enter the shedding phase at the same time. That’s when hair shedding picks up and total volume can feel noticeably reduced. This shift is a normal part of the postpartum period, but a healthy diet can help slow postpartum hair loss and support hair regrowth. Nutrients like iron, biotin, and omega-3s support hair health and may help prevent postpartum hair loss from lingering longer than it should. Eating well during this transitional phase helps your hair grow stronger as it returns to its pre-pregnancy state. Keep reading to see which nutrients support normal hair growth and may help reduce excessive shedding. Each one plays a different role in helping your hair grow back thicker and healthier.
Hair Falling Out After Pregnancy? 10 Nutrients That Help Hair Grow Back Stronger
Hair falling out after pregnancy is something most women notice in the first few months after giving birth. It’s usually part of a normal hair growth cycle, but that doesn’t make it feel any less alarming—especially when you're seeing more hair in the shower drain or on your brush than usual. This type of increased hair loss, known as postpartum hair loss or telogen effluvium, happens as pregnancy hormones drop and hair shifts from the growing phase (anagen) to the resting phase (telogen). During pregnancy, high hormone levels often keep many hairs in the growing phase longer than usual, which makes your hair appear fuller. But once those hormones level out after delivery, many hairs enter the shedding phase at the same time. That’s when hair shedding picks up and total volume can feel noticeably reduced. This shift is a normal part of the postpartum period, but a healthy diet can help slow postpartum hair loss and support hair regrowth. Nutrients like iron, biotin, and omega-3s support hair health and may help prevent postpartum hair loss from lingering longer than it should. Eating well during this transitional phase helps your hair grow stronger as it returns to its pre-pregnancy state. Keep reading to see which nutrients support normal hair growth and may help reduce excessive shedding. Each one plays a different role in helping your hair grow back thicker and healthier.
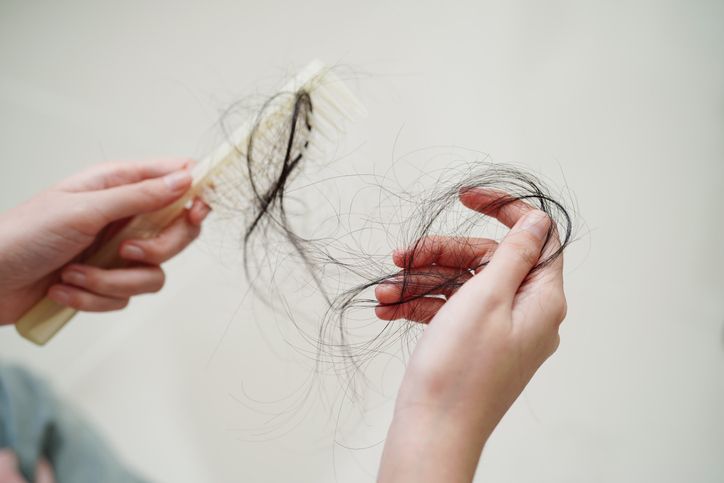
Is It Hair Shedding or Hair Loss? 6 Ways to Know What’s Happening to Your Hair
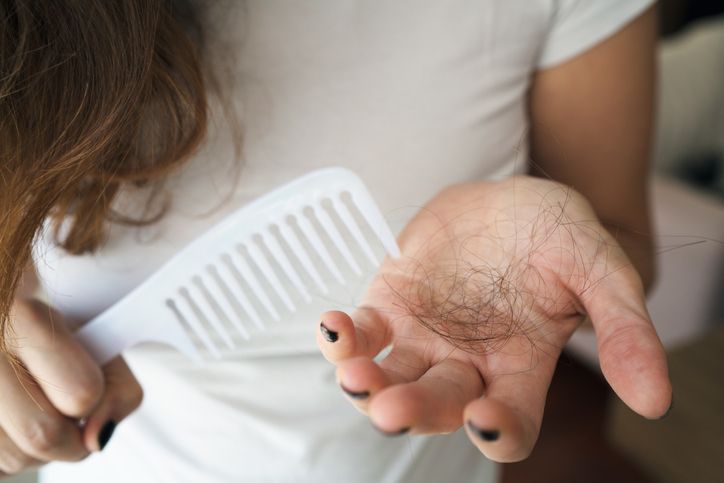
Not sure if you’re just shedding or actually losing hair? You’re definitely not the only one asking that. Hair falls out every day as it’s part of the normal hair growth cycle. Yet, when it starts feeling like way too much, it’s easy to wonder what’s really going on. There’s a difference between regular hair shedding and real hair loss, and spotting it early can make a big difference. Maybe you’ve noticed more hair in your brush, a receding hairline, or areas that look a bit thinner than usual. Maybe your strands just feel finer, or your scalp’s getting easier to see. These changes can mean a few different things, depending on what’s causing them. Hair shedding vs hair loss isn’t always black and white, but there are some clear signs that can help you figure it out. If you’ve been dealing with more hair falling than usual and want to get to the bottom of it, keep going. These six clues can help you tell what’s normal and what might need a closer look.
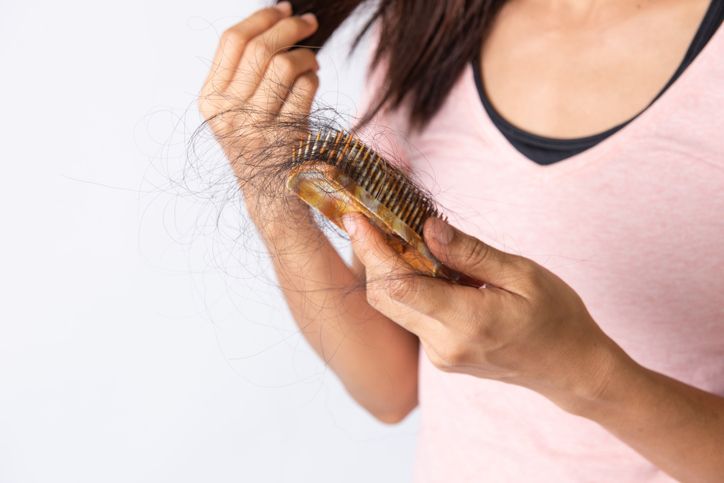
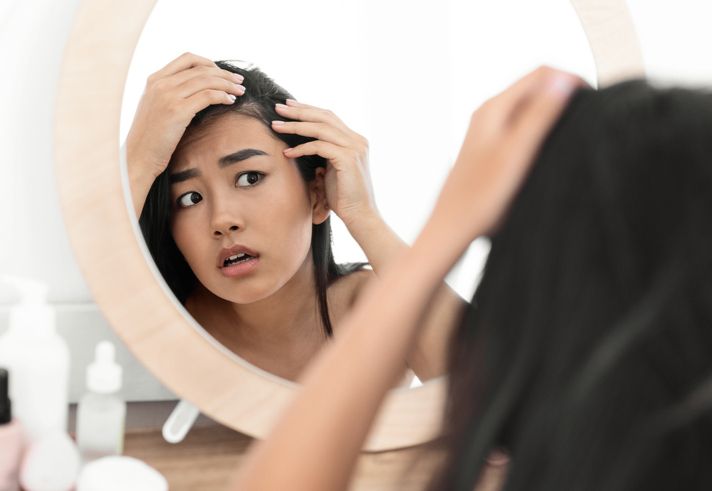
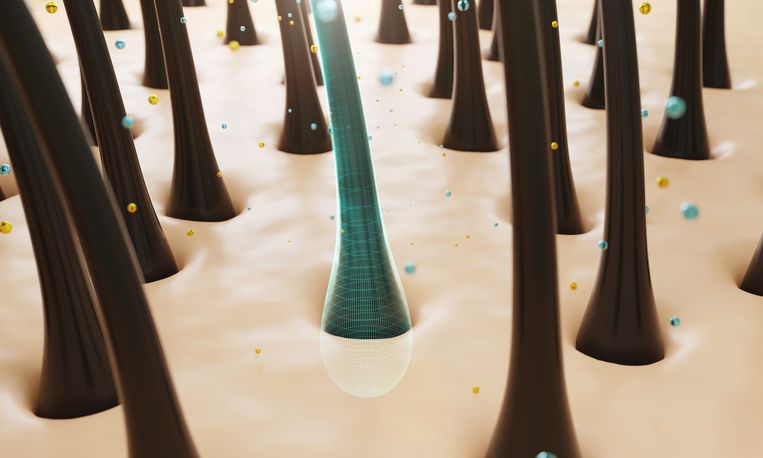
9 Causes of Thinning Hair You Need to Know—How Hair Follicles, Scalp Health, and Nutritional Deficiencies Affect Hair Growth
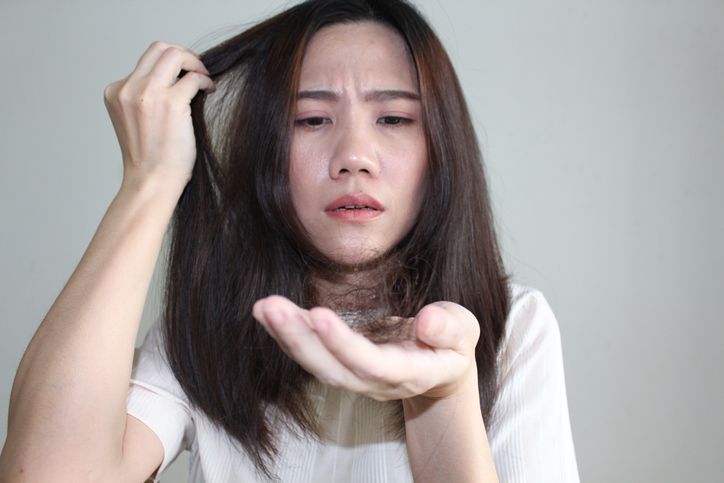
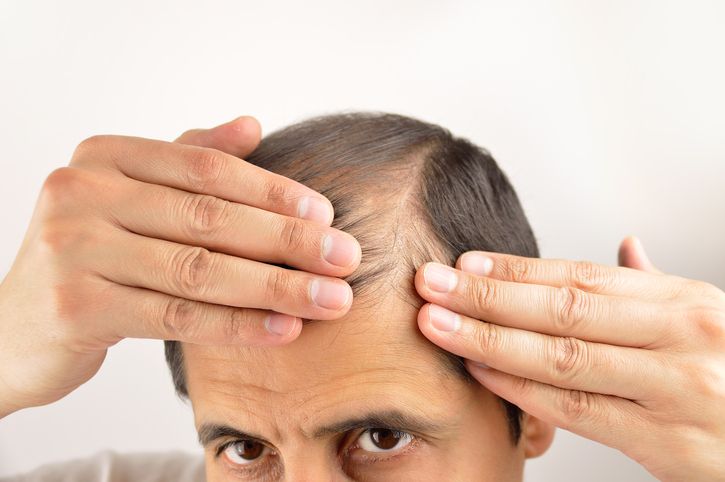
If your hair is thinning, there’s usually more than one reason behind it. Genetics, hormones, stress, and even your diet can all play a role. Some people have hereditary hair loss, while others lose hair due to medical conditions, medications, or harsh hair products. Hormonal changes from birth control pills, pregnancy, or thyroid disease can affect hair growth. Conditions like alopecia areata or androgenic alopecia may also lead to noticeable hair loss. Even everyday habits like heat styling or chemical treatments can weaken hair follicles. The sooner hair loss is diagnosed, the better your chances of slowing it down and regrowing hair. In this article, we’ll go over the hidden causes of hair thinning and what you can do about it.
9 Causes of Thinning Hair You Need to Know—How Hair Follicles, Scalp Health, and Nutritional Deficiencies Affect Hair Growth
If your hair is thinning, there’s usually more than one reason behind it. Genetics, hormones, stress, and even your diet can all play a role. Some people have hereditary hair loss, while others lose hair due to medical conditions, medications, or harsh hair products. Hormonal changes from birth control pills, pregnancy, or thyroid disease can affect hair growth. Conditions like alopecia areata or androgenic alopecia may also lead to noticeable hair loss. Even everyday habits like heat styling or chemical treatments can weaken hair follicles. The sooner hair loss is diagnosed, the better your chances of slowing it down and regrowing hair. In this article, we’ll go over the hidden causes of hair thinning and what you can do about it.
How Can You Make Your Hair Grow Faster by Doing These 10 Things & Eating These 10 Foods
Everyone wants their hair to be long, beautiful, and healthy. But not everyone is lucky enough to have hair that grows on its own. If you have trouble with your hair falling out or growing slowly, this article is for you!
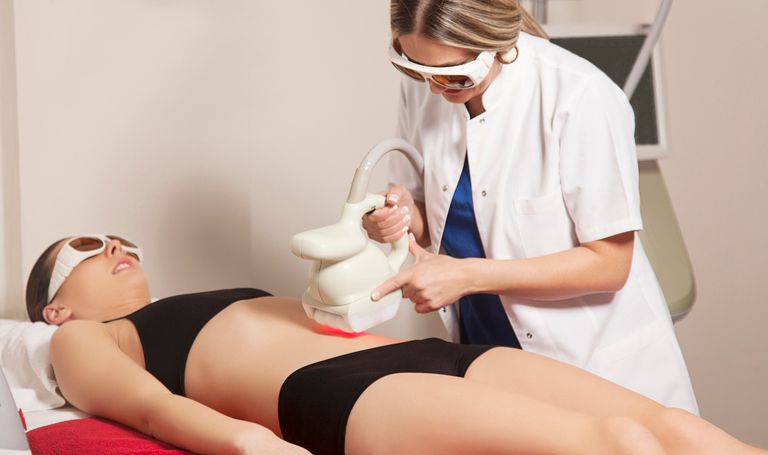
Hair loss is a common problem that affects both men and women. Fortunately, there are many effective hair loss treatments available, including medication, hair transplant, and laser therapy. Learn more about the different options and which one may be right for you.
Get to know what causes hair loss and how you can treat them
Have you suddenly notice that your hair is not as thick as before? Worry not, find out what is the cause and how you can treat them
Recommended Articles
Latest Article
COPYRIGHT© NEW BEAUTY MANAGEMENT LIMITED 2025. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.